![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
7 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
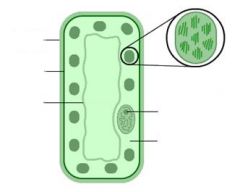
Label this leaf palisade cell. |
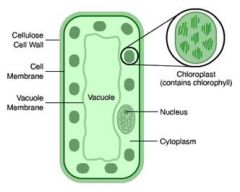
|
|
|
How is a palisade suited to its function as a site of photosynthesis? |
-Long, thin cells that form a layer to absorb sunlight.
-Chloroplasts that arrange themselves to collect maximum amount of light. -Large vacuole that pushes cytoplasm and chloroplasts to the edge of the cell. |
|
|
Describe the structure of a Chloroplast. |
- The chloroplast envelope: A double plasma membrane that surrounds the organelle. It’s highly selective in what enters/exits the cell.
- The grana: Stacks of up to 100 thylakoids. Within these is the pigment chlorophyll. Some thylakoids have tubular extensions that join up with others in adjacent grana. - The stroma: Fluid-filled matrix where the second stage of photosynthesis takes place. |
|
|
How are Chloroplasts adapted to their function as the site of photosynthesis? |
- The granal membranes provide a large surface area for attachment of chlorophyll, electron carriers and enzymes that carry out the first stage of photosynthesis.
- The fluid of the stroma possesses all enzymes needed to carry out the second stage of photosynthesis. - Chloroplasts contain DNA and ribosomes so they can quickly manufacture proteins needed for photosynthesis. |
|
|
Describe the cell wall. |
- They consist of the polysaccharide Cellulose.
- There is a thin layer called the middle lamella, which marks the boundary between adjacent cell walls and cements them together. |
|
|
What is the function of the cell wall? |
- To provide mechanical strength. - To allow water to pass along it. |
|
|
What are the differences between a plant cell and an animal cell? |
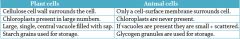
|

