![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
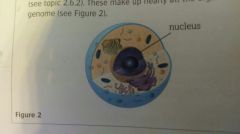
Nuclear Envelope |
Surrounds the nucleus, is a double membrane with pores, separates the nucleus from the rest of the cell, double membrane fuses to allow defusion. |
|
|
|
Nucleolus |
The centre of the nucleus, contains and creates RNA. |
|
|
|
Chromatin |
Genetic material, DNA wound around histones, coil up into chromosomes when the cell divides. |
|
|
|
Rough Endoplasmic Recticulum |
A system of fluid filled membranes that provide a S/A for ribosomes, is an intracellular transport system. |
|
|
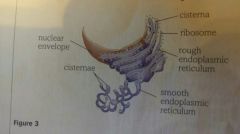
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum |
A system of fluid filled membranes, no ribosomes on this, catalyses reactions involving lipids, steroids, hormones as well as the transport and synthesis and absorbtion of lipids from the gut. |
|
|
|
Golgi Apparatus |
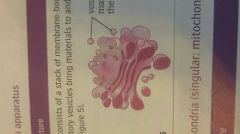
A stack of membrane bound flattened sacs, vesicles bring materials to and from, modifies proteins by giving them 3D shape ready to be exporyed |
|
|
|
Mitochondria |
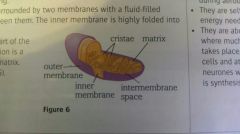
Spherical (2-5nm big), separated by 2 fluid filled membranes, site of ATP production (aerobic). |
|
|
|
Chloroplasts |

(4-10microm) Only in plant cells, double membrane envelopes, stacks of thykloids called granum - where energy is trapped and H ions split; surrounded by a fluid called stroma, contains DNA. Site of P/S, Carbohydrates are made in stroma in leaves. |
|
|
|
Vacuole |
Air pocket surrounded by a membrane: tonoplast. Only in plant cells, keeps them turgid which helps support the plant |
|
|
|
Lysosomes |
Small bags formed from the Golgi Apparatus, contains strong digestive enzymes and protects the rest of the cell from these. Contain white blood cells to digest pathogens and old organelles for reuse. |
|
|
|
Cilia and Undulipodia |
Hair like protrusions from surface membranes, made of microtubules from centrioles. For sensing, movement and moving things. |
|
|
|
Ribosomes |
Spherical organelles (20nm), made in the nucleolus, produces ribosonal DNA, attaches to RER or floats. Synthesis of proteins |
|
|
|
Centrioles |

Bundles of microtubules arranged to form a cylinder. Help support cell structurally and aid during cell division. |
|
|
|
Cytoskeleton |
Rod like filaments made if subunits of actin (a protein 7-9nm) straight cylindrical microtubules called tubulin (18-30nm), cytoskeleton motor proteins (myosins, kinesins, dyeins, these are also enzymes allowing hydrolysis of ATP for energy) Offers mechanical strength and shape, and movement of organelles , can connect cells. |
|
|

Cellulose Cell Walls |
Cellulose fibres, outside of plasma membrane on plants. Prevents cell from bursting, strength, support, maintain shape, are permeable |
|
|
|
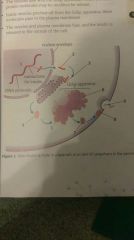
How organelles work together? |
1. mRNA is made in the nucleus (instructions for protein) 2. mRNA leaves through a nuclear pore and attaches to a ribosome attached to RER, the ribosome assembles the protein 3. The protein molecules are pinched off by vesicles and taken to Golgi Apparatus, which if fuses to. 4. The Golgi Apparatus process' the protein 5. Which is pinched off the Golgi Apparatus by a vesicle which takes it out of the cell by fusing to the cell membrane. |
|

