![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Define Polymer |
A large molecule made up of repeating units |
|
|
|
Define a Monomer |
Small molecules, the basic sub unit of a polymer |
|
|
|
Condensation Reaction |
Joining of two monomers by removing a water molecule |
|
|
|
Give the three elements found in Carbohydrates |
Carbon, Hydrogen and Oxygen |
|
|
|
What is the gerneral formula of a Monosaccharide? |
(CH2O)n |
|
|
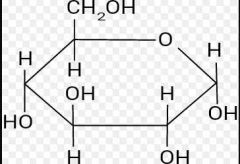
Alpha or Beta Glucose |
Alpha Glucose |
|
|
|
What is the test for Reducing sugars ? |
Add Benedict's reagemt and heat. Brick red is positive. |
|
|
|
Monosaccharides. Go!!! |
Glucose, Galactose, Fructose - all hexose sugars. |
|
|
|
Disaccharides. Name them all and their monosaccharides. |
Maltose- Glucose +Glucose Lactose-Glucose+Galactose Sucrose-Glucose+Fructose |
|
|
|
Test for NON-reducing sugars |
Benedict's test If remains blue: -add HCL and boil -Add sodium hydrogen carbonate to neutralise -Repeat Benedict's Brick red is positive as the HCL hydrolises the nonreducing sugars into reducing sugars (monosaccharides ) |
|
|
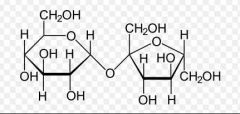
Name the bond. |
Glycosidic bond -oxygen left over from the removal of H2O |
|
|
|
What is the test for Starch? |
Add Iodine-blue/black is positive |
|
|
|
Cellulose Name its monomer and features |
Beta Glucose Forms Long, Unbranched chains with Hydrogen cross links that help strength. Found in cell walls. |
|
|
|
Glycogen. |
Alpha glucose Animal starch Large insoluble molecule Short branched chains Compact |
|
|
|
Starch |
Alpha Glucose Found in plants Storage molecule for glucose Insoluble Coils like DNA |
|
|
|
Give features of Lipds |
Contain Carbon, Hydrogen and Oxygen Insoluble in water Soluble in organic solvents such as alcohols and acetene. |
|
|
|
Triglycerides and Phospholipids Features and Functions |
Triglycerides : 3 fatty acid chains and glycerol Ester bonds Phospholipids : Two fatty acids, glycerol and phosphate Hydrophobic head and hydrophilic tail Found in cell surface membrane |
|
|
|
Test For Lipids |
Add ethanol Shake Add equal parts water Shake Cloudy is positive |
|
|
|
Monomer of a protein |
Amino acid |
|
|
|
Which part of a protein's structure differs |
The R Group |
|
|
|
What bond is found in polypeptides? |
Peptide Bond- bond between OH on the carboxyl grouo and a H in the NH2 group |
|
|
|
Give the 4 structures of a protein |
Primary Structure -sequence of amino acids Secondary structure -chain folds to form an alpha helix or beta pleat -Held eith Hydrogen bonds Tertiary Structure -3D shape -Determined by amino acid sequence -Hydrigem, Ionic and Disulfide bonds -single polypeptide chain Quaternary Structure -More than one polypeptide chain -Sometimes a prosthetic group is added |
|
|
|
Which three factors affect the rate of reaction in an enzyme controlled reaction? Why? |
Temperature -increasing temperature increases ROR as kinetic energy increases -optimum temperature is the fastest rate -After optimum temp higher temps cause enzymes to denature as H bonds are broken PH -Enzymes only work in optimum PH and start to denature in other PHs -PH alters the charge of the amino acids in tertiary structure. Substrate Conc. -ROR increases in direct proportionality to substrate conc. -Enzyme conc. becomes the limiting factor because at a certain point all active sites are filled. -Reaction CONTINUES at a constant rate as substrate is continued to be increased Enzyme Conc. -Like substrate Conc only reaction STOPS at a certain point as enzyme conc. Continues to increase as there's no substrate left. |
|
|
|
What is the function of the mitochondria? |
To produce ATP which can be broken down to release energy for use in the cell. They do not produce energy |
|
|
|
What is the Function of the ribosomes? |
Assembly of amino acids into chains. |
|
|
|
What is the resolution of a transmission electron microscope? |
0.2nm |
|
|
|
What is the resolution of a scanning electron microscope? |
3.0 nm |
|
|
|
What is the resolution of a light microscope? |
0.27um |
|
|
|
How do you calculate Magnification? |
Magnification= Image / Actual |
|
|
|
How do you convert mm to Um ? |
Divide mm by 1000 |
|
|
|
How do you convert Um to nm? |
Multiply by 1000 |
|
|
|
What are the differences between Eukaryotic cells and Prokaryotic cells? |
Prokaryotic - has a capsule , circular DNA, plasmids, free dna Eukaryotic- membrane bound organelles, dna in chromosomes, cell walls made of cellulose |
|
|
|
Purpose of the cytoskeleton |
Structural support To form the spindle for division To provide pathways for the movement of organelles in the cell. |
|
|
|
Define Chromosone/ Chromatin |
A linear DNA molecule wrapped around histone proteins |
Histones |
|
|
Define DNA |
A polymer of nucleotide molecules that form the instructions for the synthesis of proteins found within organisms. |
Polymer |
|
|
Define Gene |
A length of DNA that carries the code for the synthesis of one specific polypeptide |
|
|
|
Name the molecule that is made up of amino acids held together by peptide bonds. |
Peptide |
|
|
|
Which nucleotides are Purines? |
Adenine Guanine |
|
|
|
Which nucleotides are pyrimidines? |
Thymine Cytosine |
|
|
|
Define Globular Proteins Give one example |
Compact, water soluble, somewhat spherical. Hydrophobic R groups on the Amino acids fold inside the protein so the hydrophilic R groups are on the outside meaning it's soluble. Insulin- hormone responsible for regulating blood glucose level |
|
|
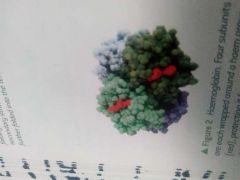
Define Conjugated proteins |
Globular proteins that contain a prosthetic group which is non protein. They form lipoproteins or glycoproteins. They also bokd with some metal ions. |
|
|
|
Fibrous proteins! |
Long insoluble molecules due to the presence of lots of hydrophobic R groups. They contain only a few amino acids so the structure is repetitive . Eg keratin Elastin Collagen |
|

