![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the the two techniques of blood pressure monitoring? |
Indirect - cuff devices Direct - arterial cannulation and pressure transduction with wavefrom display |
|
|
How do you definie ibpm |
The insertion of a catheter into a suitable vessel and then display the measured pressure wave on a monitor |
|
|
Define arterial pressure monitoring |
A thin catheter inserted into an artery, to measure beat to beat arterial blood pressure |
|
|
Arterial pressure monitoring indications |
Continuous beat-to-beat blood pressure measurement - major surgery, hemodynamically unstable patients, all types of shock Frequent arterial blood gas analysis - severe acid based disturbance |
|
|
What are the complications of apm |
Haemorrhage Haematoma Infection Thrombosis Nerve damage |
|
|
Apm contraindications |
Absent pulse Full thickness burn Raynauds phenomenon Inadequet circulation to the extremity |
|
|
What is raynuads phenomenon |
Condition in which the body reacts to steong emotions or exposure to the cold by restricting blood flow to the extremities, resulting im colour change in the skin and pain. Last from a few minutes to many hours |
|
|
What is the modified allens test? |
Meaures arterial competence and should be performed before any arterial cannulation or catheterization |
|
|
Allens test procedure |
1.Hand is elevated and the patient is asked to make a fist for 30 seconds 2. Pressure is applied over rhe ulnar and the radial arterias so as to occlude both of them 3still elevated the hand is then oppend and should appear blanched 4. Ulnar pressure is released and rhe colour should return into 5 to 15 seconds |
|
|
How to determine the results |
Colour of the hand returns between 5-15 seconds. It is positive and the ulnar artery supply to the hand is sufficient |
|
|
Insertion sites of apm |
Radial Ulna Brachial |
|
|
Insertion sites apm |
Femoral Foralis pedis Axillary |
|
|
What does an arterial line set up include |
Sterlie gauze Sterile gloves Sterile towels Skin preparation solution 1% lignocaine 5ml syringe Cannual device Scapel Sterile dressing 3 way tapa Pressure transducer tubing Flush device pressure transducer cabels Pressure bag 500ml saline Heparin Arm board /towel roll |
|
|
Arterial monitoring mechanism of action |
- the column of saline in the arerual set transmits the pressure chsnges to the diaphragm in the transducer - the transducer reads the changing pressure and changes it into an electrical singnal |
|
|
Levelling/ phelbostic axis |
The preseure transducer must be set at the appropriate level in relstion to the patient to meassure blood pressure correctly this is taken to be level with the patients heart at the 4th intercostal space |
|
|
How do you get the transducer to read accurately? |
Atmospheric pressure must be discounted from the pressure measurement it is achieved by exposing the transducer to atmospheric pressure and off to the patient |
|
|
Arterial trace |
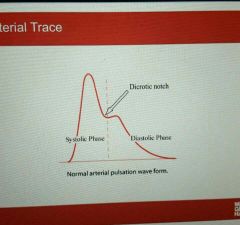
|
|
|
Damping |

|
|
|
What does over damped look like |
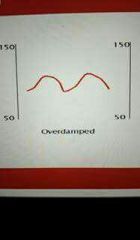
|
|
|
Overdamped features |
Wave characteristics - wide, slurred, flattened traces Possible causes - air bubbles, kinked tubing, blood clots Result - underestimates blood pressure |
|
|
Underdamped features |
Wave characteristics - resonate spiked traces Possible causes - reverberations, increased vascular resistance Results- overestimates blood pressure |
|
|
Static wave characteristics and possible causes |
Characteristics -Flat line Cause - occlusion thrombosis Positional line - tip on wall, kinking |
|
|
Damping |

|
|
|
Characteristics of arterial wave form |
Systolic uptake- Peak systolic pressure Systolic decline Dicrotic notch Diastolic runoff End of Diastolic pressure |

