![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
88 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

|
Early Byzantine Art Justinian as World Conqueror, Baberini Ivory, 6th century Justinian is on the horse. Jesus is above him giving the 2 finger blessing, know it's Christ because there's a nimbus and holding the cross. Christ is blessing Justinian on his mission. Significant because this is the first time that we've had Christian imagery being used for political propaganda** Artist is using hierarchy of scale- more important people are bigger. Foreign people that he's conquering are below him. Show them in caps (East), elephants and lions (foreign), divine aspect- figures in the right of Justinian on top and bottom (ideas of victory, Pagan imagery). Holding Justinian's foot to show that he's divine. |
|

|
Anthemius of Tralles and Isidorus of Miletus, Hagia Sophia, Constantinople, 532-537 7 years after they're married- in 532 there's a terrible fire in Constantinople. There's a riot that breaks out in the amphitheater. Fight breaks out (riot that takes over the city). Nike (Victory) Riot. City begins to burn, all of the buildings that Constantinople builds burn to the ground, Justinian gets out of the city, Theodora tells him that he's the only one that can make it right. He has to stay and fix it. He does stay and the first thing that he does is rebuild the most important church in the city- Church of Divine Wisdom- Hagia Sophia. Minorettes were later additions. Became a mosque after Turks invaded. To preserve it was kept as a separate building. 30,000 killed in Nike Riot. Hagia Sophia- Divine Wisdom. Hagia- holy, sophia- wisdom. When Justinian decides to build a new church, looks at the Pantheon, wants to build a church with a dome. Nobody had done this since the classical period, people had forgotten how to build and use the same materials, 400 years had passed. Does not look to chief architects to ask them but asks two mathematicians- Athemius of Tralles (specialists in geometry and optics) and Isodorus of Miletus (physics, how to build vaults). |
|

|
Archangel Michael, early 6th century Ivory. Next section is still about Justinian, and objects that were created during his reign. 6th century ivory of the archangel, Michael. He has a sword- fights with Satan. He kicked Adam and Eve out of the garden. He's the one that has to use force.* He has a lot of outfits but we see him in military garb frequently. Orb- Symbol of Christ dominion over the earth. |
|

|
Monastery of St. Catherine's, Mt. Sinai, Egypt, c. 548-65 Mount Sinai- there was a memo to destroy Christian images and this mountain didn't get the memo. Has the best images of Iconoclasm. Monastery of St. Catherine's in Egypt. Walled city in which people live and practice religion. Monastery for men. Covenant for women. Prayer, singing, possibly chanting. Most monasteries have an industry that they're known for. Would usually have a library where they would copy texts. Monks were icon makers. Artists that lived at St. Catherine's. They would have products that they would make. |
|

|
Icon of St. Catherine, Mt. Sinai, Egypt, c. 548-65 Her relics appeared here, where Moses received the 10 commandments and that's why it's named after her.Justinian built the monastery of St. Catherine. |
|

|
Transfiguration, apse mosaic, Mt. Sinai, Egypt, c. 548-65 Byzantine aesthetic- heavy reliance on gold~ it's a show of wealthy and power. Luxury good. No desire to show realism in Byzantine art. By removing a natural setting- makes it universal. Focus primarily on the figures. Blues and purples- used to surround the most important figure. Byzantine art- stylized, since of the artificial to it. Awkward. Almost always with the exception of St. Peter, it's a frontal art. Could care less if the folds in the fabric is molded to the human body. It's all done on purpose. Want you to focus on figures. There's a lack of depth, no sense of shading or modeling, flat. No sense of emotion. |
|

|
Virgin and Child with Saints and Angels, Icon, 6th century Virgin and Child between Saints Theodore and George. Theodore on the left and George on the right. Behind them there are two angels and a hand reaching down giving the blessing. Theotokos is the virgin. George and Theodore- saints- their roles-> represent the communion of saints. This is something that never happened. Represent a devotional image. It's made up. Want to inspire the viewer and what they represent. This is about prayer. George and Theodore are intercessors. Saints are now morphing. Before they were martyrs. Now they are our advocates. Representing us in heaven on our behalf. |
|

|
Sinai Icon, or Christ Icon, Monastery of St. Catherine's, 6th century Huge image. On the iconostasis- large picture depicting Christ. With arm raised, 2 fingered blessing, and book~ pantocrater- has a wandering eye. Left side (Christ's right side)- kind, merciful, Right side- bad ass Jesus, judge, Two sides are equal. In the early Byzantine images- Church wants to clearly define Christ in divinity and that they were both legitimate. |
|

|
San Vitale, Ravenna, Italy, 546-548 Justinian builds in Mt. Sinai and in Ravenna- reminder of power. Build to make their mark. Builds the Church of San Vitale. 8 sided building in the shape of an octagon. This is a church. Have two other 8 sided buildings which are baptistries. Built starting in 526. |
|

|
San Vitale, Christ in Majesty In the apse of San Vitale. Christ in majesty. See Christ in the center. Sitting on symbolic representation of the world. In the left hand- book. Right hand- martyrs crown. Handing the martyrs crown to the man on the left- St. Vitale- "Titular Saint"- saint to whom a church is dedicated. He was an early Christian martyr in Ravenna. Sometimes they wear things over their hands= act of reverence. Hands are not worthy to touch such a sacred object. Guy on the right side is Ecclesius- Bishop who was alive when the building was founded. Holding a little model of the building itself. In the act of presenting it to Christ. Ecclesius does not have a halo. Has not been sanctified.How Christ is depicted- without a beard, youthful. Appears more human. Mosaic looks different from other Byzantine mosaics- ground, reference to naturalistic imagery. Four rivers coming out of the ground, trees, grass, lilies. Representing nature, clearly a sign that you're outside the normal confines of the Byzantine East, usually closer to the West. Usually see in Roman art.** Easier to tell where you are in the world. Halo- nimbus. |
|

|
San Vitale, Justinian and Attendants Maximianus- one of the identities on a figures has changed. Writes his name. Justinian is one of the first to start blurring lines between church and state and now he's putting political propaganda beside the alter. Maximianus also wants us to know he's bishop. Clothing- priests in white and brown. Guy on the right- censor- incense jar. Priest #2- holding the gospels. Maximianus- bishop. Read as a processional. See this by looking at feet to figure out that they're moving. Grumpy man- John the nephew- added later. Justinian- has a halo. Odd. Holding an offering plate, holds bread. Left of Justinian- Belisauius- general who is responsible for conquering Ravenna and regaining rule. Military general. Anastasius- illegitimate grandson of Theodora. Soldiers on the left. Shield. Justinian's army still has the chi-rho |
|

|
San Vitale, Theodora and Attendants Parade fashion. Notice that there's a curtain and attendant is opening and coming back through the curtain. Theodora still hasn't entered the sacred space. Theodora's presentation- also has a halo. She has the 3 maji inscribed on the hem of her robe. Holding the chalice.- wine for communion. Two women to her right- Antonina and Joanina. Wife of Belasarius and Belasarius' daughter. Joanina (right) is engaged to Anastasius.Know- message through mosaics. Emperor, empress, general, alliance between emperor and general. Want them to remember that church and state are connected. Justinian and Theodora never came to Ravenna. For people who lived in Ravenna- see panels and have never seen Justinian before. Political propaganda bleeding into religious world. |
|

|
Transfiguration of Christ and Saint Apollinaris, Sant' Apollinare in Classe, Ravenna, 533-549 Instead of Peter, James, and John- 3 lambs. Christ is in the cross. Little portrait. Little hand of God coming down to bless. Images of God the father are almost nonexistent in this period.Couldn't have full images but could have a hand. Instead of a gold background- naturalistic. Indicative that it was done in the West. 12 sheeps- 12 apostles. |
|
|
Justinian |
First Byzantine Emperor- Justinian the Great- 527- 565 (reign)- great vision, lots of energy, believed to be incredibly pious and utterly ruthless, one of his greatest accomplishments is that he attempts to regain the borders of the Roman empire. Empire that he starts flourishes for 1000 years. Until 1453- Ottoman Turks come in and conquer Constantinople and then it becomes Istanbul, modern capital of Turkey. Justinian- revises the legal code (formal revision), architecture that he builds. |
|
|
Theodora |
Wife of Justinian |
|
|
Byzantium |
Early Byzantine art begins at 500 CE, beginning of 6th century. City of Rome was declining and the eastern part of the city, the city of Constantinople rises, becomes known as Byzantium (name for the culture). Eastern half of the Christian church will be centered here. There is a heavy Greek influence here and the language is Greek. Latin spoken in West, Greek in East. Divides church, moves in 2 different directions. Tree with different branches. West- church being led by Pope, East- Patriarch is the leader. Patriarch does not have the same legendary story- lacks early legend, mythology that the Pope seems to have. Roman emperor sees himself as the head of the church on Earth. In the East the emperor would rule. |
|
|
Constantinople |
Byzantium becomes Constantinople. Until 1453- Ottoman Turks come in and conquer Constantinople and then it becomes Istanbul, modern capital of Turkey. |
|
|
Hagia Sophia |
Hagia Sophia- Divine Wisdom. Hagia- holy, sophia- wisdom. When Justinian decides to build a new church, looks at the Pantheon, wants to build a church with a dome. Nobody had done this since the classical period, people had forgotten how to build and use the same materials, 400 years had passed. Does not look to chief architects to ask them but asks two mathematicians. |
|
|
Isodorus of Miletus |
Isodorus of Miletus (physics, how to build vaults). |
|
|
Athemius of Tralles |
Athemius of Tralles (specialists in geometry and optics) |
|
|
Pendentive |
Build a central dome and it's supported on either side by half domes and holding up the center dome is a new element- pendentive. |
|
|
Naos |
Center area of Hagia Sophia. |
|
|
St. Catherine |
popular for being super smart. Maxintius wanted her hand in marriage but she would work out deals. She told him to send 50 of his biggest brains to debate her and then she converted all of them. She was stretched on the wheel to be killed since they couldn't be married. The wheel breaks and then she's beheaded. |
|
|
Transfiguration |
Jesus goes out one night to pray with Peter, James, and John- three of his apostles. Important because John is the beloved, or witness. John is always shown as the youngest without a beard. Peter usually has white hair and a bad attitude. James- half brother/ cousin. While they're praying- Moses and Elijah come down and Jesus starts glowing and begins to levitate. Bathed in dazzling white. Jesus light show. Rays and put Christ in an almond shaped halo in a *mandorla. Afterwards- Peters says that there should be structures built and Jesus says no, "it's the first time that Christ reveals himself as a divine figure to the apostles." Prior to this he was only known because of human characteristics. |
|
|
Mandorla |
Almond shaped halo. |
|
|
Icon, from GK "Ikones" |
Icon- comes from "Ikones" meaning image. Byzantines create icons. Come from the idea- painting by El Greco, St. Veronica- name means true image. Christ was carrying his cross and Veronica wipes his face. His image was transferred onto the cloth. Relics- objects once owned by a holy figure. Byzantine's feel like the origin of the icon come from. |
|
|
"Vera icon", sudarium |
Sudarium is the cloth that the image is transferred onto. |
|
|
Theotokos |
Theotokos is the virgin in the virgin and child. |
|
|
Bishop Ecclesius, St. Vitalis |
Ecclesius- Bishop who was alive when the building (San Vitale) was founded. Holding a little model of the building itself. In the act of presenting it to Christ. Ecclesius does not have a halo. Has not been sanctified. |
|
|
Maximianus |
Bishop |
|
|
Belisarius, Antonina |
Military general who is responsible for conquering Ravenna and regaining rule. Antonina-Wife of Belasarius. |
|
|
Joanina, Anastasius |
Anastasius- illegitimate grandson of Theodora. Belasarius' daughter, Joanina is engaged to Anastasius. |
|
|
Eagle, Man, Lion, Ox |
John the Eagle, Matthew the Man, Mark the Lion, and Luke the Ox- 4 gospel writers. |
|

|
The Cross, apse mosaic, St. Irene, Constantinople, after 740. Allowed to have an image of a cross in a church. |
|

|
Triumph of Orthodoxy Icon, Constantinople, 1400 (display of Hoegetria by Empress Theodora and her son Michael III) Skip forward to 843- Another empress named Theodora- restores icon worship on March 11, 843- feast of orthodoxy- icon is the triumph of orthodoxy icon. Shows restoration of icons. Empress Theodora- patriarchs and high ranking priests on right. Virgin and child of Christ in the middle. Mary holding the Christ child- has hand pointing toward Christ- Virgin Hodegetria- virgin that shows the way. (way to salvation) |
|

|
Simon Magus and Patriarch Nikephorus, from the Khlodov Psalter, c. 850-75 shows that Simon is being trumpled on. One of the major people arguing against the use of icons. Patriarch is triumphant. |
|

|
The Crucifixion and Iconoclasts Whitewashing an Icon of Christ, from the Khludov Psalter, c. 850-75 Symbolic parallel. White washing the image of Christ. In the background- John the Grammarian is white washing the image of Christ meant to be symbolic. Crucifixion- crucifying all over again when an image is destroyed. Political commentary. |
|

|
Virgin and Child Enthroned, Hagia Sophia, Constantinople, 867 First mosaic to be put back in Hagia Sophia. Goes in 20 years after Triumph- 867- mosaic of the Virgin Hodegetria or Virgin Enthroned with Constantine 1 and Justinian. 16 feet tall. Points hand towards Christ. |
|

|
Emperor Leo VI in Proskynesis before enthroned Christ, Hagia Sophia, Constantinople, c. 900 In the foyer- Mosaic is built in around 900- one of the more interesting images in the narthex- Subject is Christ it is a pantacrater image. Feet- portrait of one of his emperors Leo the 6th- married 4 times, this was bad because they weren't supposed to get married more than twice so he's begging for forgiveness at the foot of chirst. Posture- proskynesis. In early Christian church- under the impression that during ritual- it's an example of humility. Intercessor |
|

|
Virgin Enthroned with Constantine I and Justinian, Hagia Sophia, Constantinople, 10th century Virgin enthroned with Constantine I and Justinian. Constantine on the right and Justinian on the left. Constantine- building to the Virgin and child- Constantinople. On the left- Justinian- Hagia Sophia. Two benefactors offering their gifts tot he virgin and child |
|

|
Deesis, south gallery, Hagia Sophia, Constantinople, c. 1260 Deesis image- has only 3 people. Christ, on the right, Virgin Mary, on the left- Shaggy John the Baptist. Form the Deesis. Why? Both usher Christ into the world. Through birth and prophecy. Two most powerful intercessors in Christian theology. Two people that he trusts most. Dates to 1260. Important in 1204- fourth crusade came through the city of Constantinople. 4th campaign from Europe to the holy land. On the way back crusaders stopped in Constantinople and robbed the city. Brought treasures back to Italy and places in the west. Low point in the cities history. First image erected after crusade to the people of constantinople. |
|
|
Emperor Leo (726) |
8th century- 726 year in which the emperor Leo decrees that all religious images were idols and they should be destroyed thus is the beginning of the iconoclasm. Iconoclasm means image breaking. |
|
|
Feast of Orthodoxy (March 11, 843) |
March 11, 843- feast of orthodoxy- icon is the triumph of orthodoxy icon. Shows restoration of icons. |
|
|
Chalke Gate |
Chalke Gate- gate outside of Constantinople- place where first gate is placed. |
|
|
Virgin Hodegetria |
Virgin Hodegetria- virgin that shows the way. (way to salvation) |
|
|
John of Damascus |
John of Damacus- Theologian- indebted to him because he wrote that religious imagery helps to teach the next generation about religion and argued that when someone is praying before an icon they were not venerating the wood that the icon was made out of but venerating the person that the wood is dedicated to. Teaching quality to icons |
|
|
John the Grammarian |
white washing the image of Christ meant to be symbolic |
|
|
Proskynesis |
Posture. In early Christian church- under the impression that during ritual- it's an example of humility. |
|
|
Deesis |
Only has 3 people |
|

|
Icon of the Holy Ladder, late 12th century, Late Byzantine Unique to the Eastern Church. The earliest holy ladder dates to 600. Inspired by John Climicus- monk with imagery about 30 steps of aesthetic life. Ladder is the evolution spiritually in 30 steps. All the good and temptations that come from aesthetic life. |
|

|
Icon of the Virgin and Child (the Vladimir Virgin), c. 1131 Late Byzantine East. Multiple copies of this type of image. 1131- patriarch (head of the Eastern Orthodox Church) in Constantinople gave copy of this icon to the grand duke of Keyove in Russia. Icon had mystical powers. So powerful that Mary evolved as the patron of mother Russia. Russian orthodoxy is the same as Greek Orthodoxy with other languages. Different from Hadagitria- virgin that shows the way. Objective of this particular image- much more about intimate relationship between mother and child. |
|

|
Anastasis (The Harrowing of Hell), Kariya Camii, Constantinople, 1316-21. Late Byzantine Fresco seen in the East. Center image is Christ, mandorla is surrounding him.Sarcoughagii are surrounding him- he's pulling people out of them. People who never had the ability to be baptized but lived good lives that should have the ability to go to heaven. Adam, Eve, Moses, King David- Holy Saturday. |
|

|
San Marco, Venice, 1063-1090, Byzantine Italy Most important church in Venice. Palace of Doge- highest ranking person in the city- Governor like position. Dedicated to the apostle St. Marc because in 829- Venetians recovered (stole) the relic of St. Marc from his burial place in Egypt. Present day church began in 1063 completed in 1071Byzantine Characteristics- basic layout is in a greek cross plan- all sides are equal. 5 domes based on Byzantine models. After the Hagia Sophia- every building had a dome. Interior was decorated by Byzantine artists- mosaicists. Domes almost universally have the following 2 things- sit on pendentives. Many of them have some type of band of light (window course) at the bottom. |
|

|
Genesis dome, San Marco, 1063-1090, Byzantine Italy Have a dome covered in mosaics and it's divided into 3 registers telling us stories from the Book of Genesis. Almost an identical replica of a book "Cotton Genesis" Images for the text were translated from this. Looking at manuscripts. Different types of manuscripts for different ideas. Adam and Eve, Noah and the Flood |
|

|
Pala d'Oro, c. 1105-1209, reassembled in the 14th century. Byzantine Italy liturgical object on the back of the alter. Alter object- sacred. Not necessarily a backdrop. Completely made of gold and little enamel figures. Golden table Objective- mimic a Byzantine Iconostasis or screen. Origin of the golden alter- comes from the upper layer. |
|

|
Christ Crowning King Roger II of Sicily, Martorana, Palermo, Sicily, c. 1148. Byzantine Italy |
|

|
Pantokrator, Cappella Patina, Palermo, Sicily, 1143. Byzantine Italy Makes capital the city of Palermo- capital of Muslim, showing dominance. Builds cathedral. Maquarnas ceiling- Muslim/ Islamic in character. Basically like a honeycomb type technique that would have been painted.Dome looks very Byzantine. Village of the Pentacrator- Christ as the judge, Christ as the benevolent person that blesses us. Byzantine in tradition. |
|

|
Nativity, Cappella Patina, Palermo, Sicily, c. 12th century. Byzantine Italy Roger had a special seating area in the church in which him and his court could attend church. This is the nativity, inscriptions are not in Greek which was common, but these are in Latin. Image of traditional nativity. Christ's first bath. |
|

|
Entry into Jerusalem, Cappella Patina, Palermo, Sicily, c. 12th century. Byzantine Italy Marks the beginning of what leads up to crucifixion. |
|

|
Pantokrator, Cathedral of the Virgin, Monreale, Sicily, 1180s. Byzantine Italy. Images of Christ in the apse of the church. Jesus of the big hair. Making image in curved space. Image of Christ is becoming much more western looking. Eastern Byzantine follow a particular pattern. Very rigid structure. Gorgeous mane in the West. Hierarchical structure is not there in the west. |
|

|
Page from Koran, 9th century. Early Islamic.
Page from the Koran. Islam adheres strictly to the second commandment- worshipping false idols or imagery. Find script or calligraphy, find geometric pattern, find some type of botanicals or vegetative scroll work. Illusions to the idea of paradise.Aniconic- anti icon imagery to refer to islamic design* |
|

|
Prophet Muhammed and His Companions Traveling to the Fair, c. 1594. Early Islamic Muhammad on his way to the fair- strong push to not give any type of figural representation to Muhammad. Figure on a camel- very purposely did not want him to become a saint. |
|

|
Detail of the facade, palace, Mshatta, Jordan, c. 740s. Early Islamic. Wall from a palace in Jordan. Example of the type of imagery that you would find. Birds, flowers, animals- images of paradise. |
|

|
Dome of the Rock, Jerusalem, c. 687-691. Early Islamic. Technically a shrine, not a mosque. Encompasses a holy place. Shrine encapsulates a giant rock3 meanings- 1) Muslims believe where Muhammad had his night journey 2) Spot that it's believed that Abraham almost sacrificed his son Ishmal. Test of faith on the part of Abraham. 3) In 70 A.D., site of the temple in Jerusalem that was sacked in 7080. Exterior- don't have a lot of muslim architecture. Looking for sources for a form of architecture- borrowing from Rome. Byzantines would give us a gold dome. Mosaic work on the exterior of the building. Instead of any type of figural decoration. It's all in arabic. Words replaced figures. |
|

|
Prayer Hall, Great Mosque, Cordoba, Spain, 785-86. Islamic Spain. When it was completed it could hold 5500 people. Largest mosque in the West. Architecturally- arches are most important. One distinguishing characteristic are the striped arches- alternating voussoirs. Voussoirs- wedge shaped blocks that make up the arch. Held in place by the middle block which is called the keystone. Painted on, not true voussoirs. Becomes distinguishing characteristic. Always tell when we go on in Christian architecture because there's a borrowing of alternating voussoirs. |
|

|
Court of the Lions, Palace of the Lions, Alhambra, Granada, Spain, 1370-80. Islamic Spain In El Hombre, Complex that was to create piece on earth. Lush garden with free flowing water. |
|
|
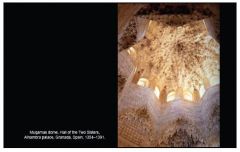
Muqarnas Dome, Hall of the Abencerrajes, Palace of the Lions, Granada, Spain. Islamic Spain. The Hall of the Two Sisters was used for poetry readings and concerts. All made out of stucco. Multilayered effect- acoustically amplified the space. Sat above the layer of windows- meant to reflect to light down below. |
|

|
Banner of Las Novas de Tolosa, southern Spain, 1212-50. Islamic Spain Ideas are transmitted through trade. In this period- more difficult to trade. Find Islamic rugs/ textiles. Down below- arabic text/ script. In the middle ages- people didn't know that that was arabic script. 1492- Ferdinand and Isabella sent Columbus on his trip. Also finally expel the Muslims out of Spain. Ferdinand loves this carpet and gives it to his favorite monastery where he wishes to be buried for them to have and use. |
|
|
Fourth Crusade |
1204 Venetians took over the city of Constantinople and ruled from 1204- 1264 (?). Saw mosaics that marked the end of the 4th crusade. |
|
|
Doge |
Highest ranking person in the city- Governor like position. |
|
|
Iconostasis |
Screen. Pala d'Oro. Alter object mimics this. |
|
|
Cloisonne |
Way of decorating with enamel and jewels. |
|
|
Normans |
Byzantine Sicily- Sicily- bottom of the boot in Mediterranean Ocean- dominated by all 3 major constituents of the Byzantine period. Byzantine's gave way to Muslim invaders. Begins as a Byzantine strong-hold in middle ages. Muslims invade and takeover in 1060- Roger of Normandy comes in and takes over Sicily. Normandy is in France. Roger is one of the relatives of William the Conquerer. Normans up in northern France conquer England. Western Latin Christians. Hybrid of the 3 cultures. Live there in some harmony. |
|
|
Roger of Normandy |
Comes in and takes over Sicily. |
|
|
Muhammed
|
Muhammad preaches about a faith in one god, monotheistic, one true God, Allah. 5 pillars of faith- Must profess faith in Allah, pray 5 times a day in the direction of Mecca, give alms to the poor, fast during the month of Ramadan, if you are able you must make a pilgrimage to the Kaaba. (Haj). |
|
|
Alternating Voussoirs |
Striped wedges. Voussoirs- wedge shaped blocks that make up the arch. Held in place by the middle block which is called the keystone. Painted on, not true voussoirs. |
|
|
Minbar |
It's literally a podium, typically elevated. Like a pulpit in Christian context. Place to preach from that stands high above the audience. Leader of muslim believers- Imam. |
|
|
Minaret |
Towers on mosque. Used to call to prayer. |
|
|
Muezzin |
Young criers. |
|
|
Koran |
Islamic bible. |
|
|
Haj |
Pilgrimage to Kaaba. meteorite in the middle that's seen as being sacred. |
|
|
Kaaba
|
Place where Muslims make pilgrimage to. |
|
|
Aniconic Imagery |
anti icon imagery to refer to islamic design |
|
|
Kibla Wall |
When communities come together, people kneel and pray in front of the Kibla Wall. Function of Kibla Wall- always faces Mecca |
|
|
Mihrab |
Inside the wall is a niche- recessed wall is a mihrab- 2 symbolic functions- represents the place where Muhammad would preach. Also seen as a portal- entryway to paradise. |
|
|
Mosque |
Inside the wall is a niche- recessed wall is a mihrab- 2 symbolic functions- represents the place where Muhammad would preach. Also seen as a portal- entryway to paradise. |
|
|
Muqarnas |
Used for poetry readings and concerts |
|
|
Tesserae |
Tiles used to create mosaics |

