![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
95 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

|
Etruscan Temple Virtruvius Etruscan |
|

|
Apollo of Veii Etruscan |
|

|
Dancers and Diners Etruscan |
|

|
Sarcophagus of a Reclining Couple Estruscan |
|

|
Tomb of the Reliefs Etruscan |
|

|
Tomb of the Triclinium Etruscan |
|

|
Capitoline Wolf Etruscan |
|

|
Patrician Carrying Busts of Ancestors AKA Togate Male Republican |
|

|
Aulus Metellus (The Orator) Republican |
|

|
Pont du Gard Republican |
|

|
Temple to Portunus Republican |
|

|
Augustus of Primaporta Augustan |
|

|
Augustus of Pontifex Maximus Augustan |
|

|
Ara Pacis Augustan |
|

|
Tellus Mater, Ara Pacis Augustan |
|

|
Imperial Processon, Ara Pacis Augustan |
|

|
Gemma Augustea Augustan |
|

|
Atrium, House of the Vettii Pompeii |
|

|
Samnite House (1st style) Pompeii |
|

|
Villa of the Mysteries (2nd style) Dionysiac Mystery Frieze Pompeii |
|

|
Villa of Agrippa Postumus (3rd Style) Pompeii |
|

|
Ixion Room (4th style) Pompeii |
|

|
Arch of Titus Imperial |
|

|
Spoils from the Temple of Jerusalem Imperial |
|

|
Titus as Triumphator Imperial |
|

|
Flavian Amphitheater (Colosseum) Imperial |
|
|
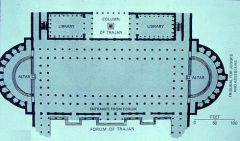
Basilica Ulpia Imperial |
|

|
Trajan's Market Imperial |
|

|
Trajan's Column Imperial |
|

|
Pantheon Imperial
|
|

|
Equestrian Statue of Marcus Aurelius Imperial |
|

|
Column of Marcus Aurelius Imperial |
|

|
Column of Antonius Pius Imperial |
|

|
Baths of Diocletian (Santa Maria degli Angeli) Imperial Groin Vault |
|

|
Circus Maximus Imperial |
|

|
Tetrarchs Tetrarchy |
|

|
Palace of Diocletian Tetrarchy |
|

|
Arch of Constantine Tetrarchy |
|

|

Basilica of Maxentius and Constantine Tetrarchy
|
|

|
Constantine the Great Tetarchy |
|

|
Aula Palatina Tetrarchy |
|
|
Cella |
A room |
|
|
Podium |
Elevated platform with one set of stairs in the center |
|
|
Tufa |
volcanic rock |
|
|
Terracotta |
Clay |
|

Cinerary Urn |
Cinerary refers to the cremation process "Human-headed cinerary urn" Made of terra cotta |
|
|
Tumulus |
Tomb |
|
|
Necropolis |
City of the dead |
|
|
Tarquinius Superbus |
was the legendary seventh and final king of Rome, reigning from 535 BC until the popular uprising in 509 that led to the establishment of the Roman Republic |
|
|
Virtruvius |
Marcus Vitruvius Pollio, commonly known as Vitruvius, was a Roman author, architect, and civil engineer during the 1st century BC, known for his multi-volume work entitled De Architectura |
|
|
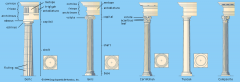
Tuscan Columns |
|
|
Lares |
Family Spirits |
|
|
Opus Caementicium |
opus=work caementicium=cement cheap fast buildings venir=layed on top of cement |
|
|
Romulus & Remus |
FOUNDERS OF ROME 753 bce: She-wolf saved the twins when their uncle, the king of Alba Longa, ordered them killed Descended from Aeneas (a prince of Troy Virgil, the Aeneid)
|
|
|
Aeneas (Aeneid=Virgil) |
A prince of Troy Virgil, the Aeneid |
|
|
Patricians |
Land owners |
|
|
Plebians |
Urban lower classes (people who work for a living) |
|
|
Pax Romana |
Peace of Rome |
|
|
Iconography |
Word Image |
|
|
Pontifex Maximus |
Maintains the peace of the gods |
|
|
Horologium |
the sun dial that looks like an obelisk |
|
|
Garlands |
Vines of bone, snakes, or ivy |
|
|
Personifications |
air, fresh water, earth, sea |
|
|
SPQR |
Senatus Populusque Romanus The Roman Senate and People |
|
|
Stucco |
applied wet and hardens to a very dense solid. It is used as decorative coating for walls and ceilings and as a sculptural and artistic material in architecture. |
|
|
Engaged Columns |
Fake Columns |
|
|
Insula |
Island |
|
|
Triumphal Arch |
Fake gate/portal |
|
|
Spandrel |
Space that connects the big rectangle and an arch |
|
|
Adventus |
the name of the ceremony of arrival |
|
|
Menorah |
7 pronged candelabra |
|
|
Apotheosis |
the highest point in the development of something; culmination or climax.
person becomes a God after death |
|
|
Arena |
Sand |
|
|
nave |
In traditional Western churches it is rectangular, separated from the chancel by a step or rail, and from adjacent aisles by pillars. |
|
|
Atrium |
entry way before the temple sacred space in front of the church |
|
|
Oculus |
a round or eyelike opening or design, in particular. a circular window. the central boss of a volute. |
|
|
Similitudo & Concordia |
Concordia=Concord(Agreement) Augusti Caesari |
|
|
In hoc signo vinces |
In this sign you will conquer.
|
|
|
Parentalia |
a nine-day festival held in honor of family ancestors, beginning February 13. Although the Parentalia was a holiday on the Roman religious calendar, its observances were mainly domestic and familial. |
|
|
Forum |
open public space within a Roman city |
|
|
Cardo Decumanus |
The main cardo was called cardo maximus. Most Roman cities also had a DecumanusMaximus, an east-west street that served as a secondary main street. |
|
|
Mystery Religion |
Mystery religions, sacred mysteries or simply mysteries, were religious schools of the Greco-Roman world for which participation was reserved to initiates |
|
|
Impluvium |
the sunken part of the atrium in a Greek or Roman house (domus). |
|
|
Domus |
Roman house |
|
|
Bucranium |
was a common form of carved decoration in Classical architecture used to fill the metopes between the triglyphsof the frieze of Doric temples |
|
|
Parthians |
Parthia is a historical region located in north-eastern Iran, best known for having been the political and cultural base of the Arsacid dynasty, rulers of the Parthian Empire. |
|
|
Augustus |
Augustus was the founder of the Roman Empire and its first Emperor, ruling from 27 BC until his death in 14 AD. He was born Gaius Octavius into an old and wealthy equestrian branch of the plebeian Octavii family. |
|
|
Damnatio memoriae |
is the Latin phrase literally meaning "damnation of memory" in the sense of a judgment that a person must not be remembered. |
|
|
spoila |
the re-use of earlier building material or decorative sculpture on new monuments. |
|
|
liminal |
occupying a position at, or on both sides of, a boundary or threshold. |
|
|
adlocutio |
was an address by a general (usually the emperor) to his massed army and a general salute from the army to their leader. |
|
|
Composite order |
The composite order is a mixed order, combining the volutes of the Ionic order capital with the acanthus leaves of the Corinthian order. |
|
|
Dacians |
The Dacians were an Indo-European people, part of or related to the Thracians. Dacians were the ancient inhabitants of Dacia, located in the area in and around the Carpathian Mountains and west of the Black Sea. |
|
|
Castellum |
small Roman detached fort or fortlet used as a watch tower or signal station. The Latin word castellum is a diminutive of castra, which in turn is the plural of castrum; it is the source of the English word "castle" |
|
|
Tetrarchy |
any form of government where power is divided among four individuals, but in modern usage usually refers to the system instituted by Roman Emperor Diocletian in 293, marking the end of the Crisis of the Third Century and the recovery of the Roman Empire. |

