![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Aegan: Cycladic |
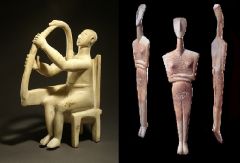
-(c.3000-1600 BCE) *1st: Harpist, from Amorgos, Cyclades. Latter part of the 3rd millennium BCE *2nd: Figure (Idol), from the Cyclades. ca. 2500 BCE, marble, height 15 3/4” (40cm)
|
|
|
Aeagan:Minoan |
(c.1900-1700 BCE) |
|
|
Minoan (Old Palace) |

(c. 1900-1700 BCE) *Beaked jug (Kamares ware), from Phaistos. ca. 1800 BCE |
|
|
Minoan (Second Palace) |
(c. 1700-1450 BCE) *1st: Octopus Vase, from Palaikastro, Crete. Second palace period, Marine style ceramic, 28 cm, ca. 1500 BCE *2nd: Knossoss "Palace" diagram |
|
|
Late Minoan |

(c. 1450-1375 BCE) *Bull Leaping, from the palace complex, Knossos, Crete. ca. 1550–1450 BCE (restored), 62.3 cm |
|
|
Aegan:Mycenaean |
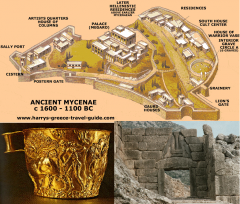
-(ca.1600–1100 BC) *1st top: Aerial view of Mycenae, Greece. ca. 1600–1200 BCE *2nd left: Minoan and Mycenaean cup from Vapheio, near Sparta, c. 16th C. BCE, gold, 3 ½ inches high *3rd right: The Lion Gate, Mycenae, Greece. ca. 1250 BCE
|
|
|
Mycenaean Architecture |

“Treasury of Atreus,” Mycenae, Greece. Limestone, height of vault approx. 13m ca. 1300–1250 BCE
|
|
|
Mycenaean Mask |

Mask of Agamemnon from Mycenae, c. 100 bc Beaten gold, approx. 12 inches
|
|
|
What geographic region does “Aegean” denote?
|
Crete, the Cyclades and the Greek mainland. |
|
|
Naturalistic vs. stylized vs. abstractized depictions |
*Naturalistic: derived from real life or nature *Stylized: depict or treat in a mannered and nonrealistic style. *Abstractized: does not attempt to represent external reality, but seeks to achieve its effect using shapes, forms, colors, and textures. |
|
|
Provenance |
the place of origin or earliest known history of something. |
|
|
Buon fresco |

Akrotiri, Thera, Cyclades, before 1630-1500 BCE *Italian for true fresco, is a fresco painting technique — in which alkaline resistant pigments, ground in water, are applied to wet plaster. |
|
|
Secco fresco |

is a fresco painting technique in which pigments ground in water are tempered using egg yolk or whole egg mixed with water which are applied to plaster that has been moistened (using this temper) to simulate fresh plaster. |
|
|
Kamares ware |

style of painted pottery associated with the palace culture that flourished on Crete during the Middle Minoan period (c. 2100–c. 1550 bc. in which combinations of abstract curvilinear designs and stylized plant and marine motifs are painted in white and tones of red, orange, and yellow on black grounds. |
|
|
Marine style |

In which the entire surface of a pot was covered with sea creatures, octopus, fish and dolphins, against a background of rocks, seaweed and sponges |
|
|
Megalithic Struture |

describes structures made of such large stones, utilizing an interlocking system without the use of mortar or concrete, as well as representing periods of prehistory characterised by such constructions. |
|
|
Corbel |

In architecture a corbel or console is a structural piece of stone, wood or metal jutting from a wall to carry a superincumbent weight, a type of bracket. |
|
|
Corbel Arch |
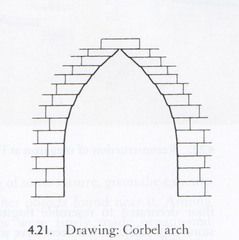
an arch-like construction method that uses the architectural technique of corbeling to span a space or void in a structure, such as an entranceway in a wall or as the span of a bridge |
|
|
Ashlar |
masonry made of large square-cut stones, typically used as a facing on walls of brick or stone. |
|
|
Repousse |
(of metalwork) hammered into relief from the reverse side. |

