![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
149 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

|
Main Hall or Hall of the Bulls, Lascaux cave.
Prehistoric (Paleolithic or Old Stone Age). |
|

|
Stonehenge, England.
Prehistoric (Neolithic or New Stone Age). Post and lintel. |
|

|
Venus of Willendorf.
Prehistoric (Paleolithic or Old Stone Age). Female fertility figurine. |
|

|
Palette of King Narmer.
Egyptian. Palette, hieroglyphs. |
|

|
IMHOTEP.
Step Pyramid of King Zoser, Saqqara. Egyptian. |
|

|
Great Pyramids, Giza.
Egyptian. |
|

|
The Great Sphinx, Giza.
Egyptian. |
|

|
Temple of Ramsses II, Abu Simbel.
Egyptian. |
|

|
Ziggurat, Ur.
Sumerian. |
|

|
Stele of Hammurabi.
Babylonian. Cuneiform. |
|

|
Dying Lioness.
Assyrian. |
|

|
EXEKIAS.
The Suicide of Ajax. Archaic. Greek. Black-figure style. |
|

|
MAKRON.
Paris Abducting Helen. Archaic. Greek. Red-figure style. |
|

|
Kouros (New York Kouros).
Archaic. Greek. Closed-form sculpture, kouros. |
|

|
Anavysos Kouros.
Archaic. Greek. Archaic smile. |
|

|
Peplos Kore.
Archaic. Greek. Peplos, kore. |
|

|
ICTINUS and CALLICRATES.
The Parthenon, Acropolis, Athens. Classical. Greek. Doric order, pediment. |
|

|
The Kritios Boy.
Classical. Greek. Contrapposto. |
|

|
POLYCLITUS.
Doryphorus (The Spear-Bearer). Classical. Greek. Idealized. |
|

|
LYSIPPUS.
Apoxyomenos (The Scraper). Classical. Greek. Open-form sculpture. |
|

|
Dying Gaul.
Hellenistic. Greek. Naturalistic. |
|

|
Laocoon and His Two Sons.
Hellenistic. Greek. |
|

|
The Flavian Amphitheater, or Colosseum, Rome.
Roman. Concrete, true arches, engaged columns. |
|

|
The Pantheon, Rome.
Roman. Corinthian order. |
|

|
The Pantheon (interior), Rome.
Roman. Dome, drum, oculus. |
|

|
A Patrician Holding Portrait Heads of His Ancestors.
Roman. |
|

|
Arch of Titus.
Roman. Triumphal arch. |
|

|
Menorah Procession, detail from the Arch of Titus.
Roman. |
|

|
West wall with Torah niche, Dura Europos.
Judaism. |
|

|
Christ as the Good Shepherd.
Early Christian. Christianity. Catacomb. |
|

|
Good Shepherd.
Early Christian. Christianity. |
|
|
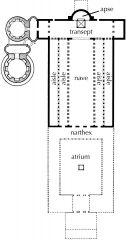
Floor plan of Old St. Peter's, Rome.
Early Christian. Christianity. Basilica-plan church, nave, aisles, apse, transept. |
|

|
ANTHEMIUS OF TRALLES and ISIDORE OF MILETUS.
Hagia Sophia (exterior), Istanbul (formerly Constantinople). Byzantine. Christianity. |
|

|
ANTHEMIUS OF TRALLES and ISIDORE OF MILETUS.
Hagia Sophia (interior), Istanbul (formerly Constantinople). Byzantine. Christianity. Pendentives. |
|
|
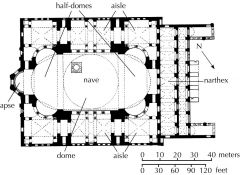
ANTHEMIUS OF TRALLES and ISIDORE OF MILETUS.
Hagia Sophia (plan), Istanbul (formerly Constantinople). Byzantine. Christianity. Central-plan church. |
|

|
St. Sernin (exterior), Toulouse, France.
Romanesque. Christianity. Buttresses. |
|

|
St. Sernin (interior), Toulouse, France.
Romanesque. Christianity. Barrel vault, rounded arches. |
|

|
Notre Dame (exterior), Paris, showing flying buttresses.
Gothic. Christianity. |
|

|
Chartres Cathedral (interior), nave.
Gothic. Christianity. Pointed arches. |
|

|
Great Mosque and Minaret, Samarra, Iraq.
Islam. Mosque, minaret, qibla. |
|
|
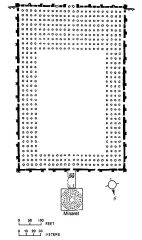
Great Mosque and Minaret (plan), Samarra, Iraq.
Islam. Mosque, minaret, qibla. |
|

|
Shiva Nataraja.
Hinduism. |
|

|
Great Stupa, Sanchi, India.
Buddhism. Stupa. |
|

|
Seated Buddha.
Buddhism. |
|

|
ELVIS.
King of Rock 'N Roll. |
|
|
Female Fertility Figurine
|
Prehistoric figures of females, small land portable
|
|
|
Neothicical Revolution
|
The domestication of plants & animals
-learned how to farm & ranch -very first cities/settlements found in New Stoneage |
|
|
Post and Lintel
|
Building technique consists of two upright posts and a horizontal lintel across the top. Used to build Stonehenge.
|
|
|
KA
|
Egyptian soul
|
|

|
Upper Egypt
Located in South Egypt; beginning of the Nile River |
|
|
Lower Egypt
Located North of the Nile River |
|
|
Palette
|
a surface in which makeup is mixed; Eygptian
|
|
|
Narmer
|
May have been the one to unite Upper and Lower Egypt (this event is shown on The Palette of Narmer), was from Lower Egypt
|
|
|
Egyptian Three Stylistic Rules
|
- most important figure is shown the largest
- figures stand on a ground line - figures shown in multiple view points (front & side) |
|
|
Hieroglyphs
|
The Egyptian picture writing system, one-to-one meaning
|
|
|
Horus
|
The Falcon God; every pharaoh is the current living form of Horus
|
|
|
Mastaba
|
Early Egyptian burial structures build of mud brick; burial chamber underground
|
|
|
Saqqara
|
Burial location for Egyptians
|
|
|
Sphinx
|
A guardian figure; human head with lion's body
|
|
|
Dream Steele
|
Located in between the legs of The Great Sphinx
|
|
|
Ramesses the Great
|
Greatest builder in Egypt's history
|
|
|
Howard Carter
|
British archeologist who discovered King Tut's tomb in 1922 in the Valley Of Kings; located in Upper Egypt
|
|
|
Sumerian
|
Earliest culture in Mesopotamia
|
|
|
Mesopotamia
|
Land between two rivers; Modern day Iraq
|
|
|
Ziggurat
|
Mountain of brick with a temple on top
- place of worship - solid structure |
|
|
Babylonian
|
Second civilization in Mesopotamia
|
|
|
Steele
|
An upright stone marker; set in public places, meant to be seen by people
|
|
|
Cuneiform
|
Mesopotamian writing system; wedge like
|
|
|
Assyrian
|
Third culture in Mesopotamia; very militaristic
Two subjects in art: - battle scenes - lion hunting scenes |
|
|
Development of Style
|
Greek art changes over the years; begins very abstract and moves to very realistic
|
|
|
Black-figure style
|
First vase painting style in the Archaic period;
- figures shown in black - background is the natural red of the clay - carve away to create detail |
|
|
Red-figure Style
|
Second vase painting style in Archaic Period.
- figures are the natural red of the clay - background painted black - detail is added by painting |
|
|
Kouros
|
Class of sculptures; means youth. ALWAYS male, nude, freestanding, marble. Found in cemeteries and temples
|
|
|
Closed-form Sculpture
|
One that is very compact, retains the blockiness from which he came from
|
|
|
Archaic Style
|
Refers to the grin on sculptures from the Archaic Period. May have been included to bring more life to the stiffness of the kouros body.
|
|
|
Kore
|
Class of female sculptures; ALWAYS female, clothed, freestanding, marble, pale flesh. Painted with colorful garments. Found in temples ONLY.
|
|
|
Peplos
|
the dress Kores wear
|
|
|
Order
|
An architectural style
|
|
|
Doric Order
|
1st order the Greeks invented. Is characterized by a PLAIN capital; male type of architecture.
|
|
|
Capital
|
The top of a column
|
|
|
Ionic Order
|
2nd architectural style created; DOUBLE-SCROLL or VOLUTE
|
|
|
Corinthian Order
|
3rd style created; CARVED LEAVES in the top of the capital
|
|
|
Acropolis, Athens
|
High point of the city
Acro=high Polis=city |
|
|
Cella
|
The main room in a temple
|
|
|
Nike
|
Greek term for victory - woman with wings
|
|
|
Pediment
|
Triangular architectural space
|
|
|
Contrapposto
|
Weight shift visible in a figure (sculptures); "weight leg"- holds most of the weight; other leg is the "engaged/free leg"
(THE KRITOS BOY) |
|
|
Polyclitus
|
Sculpture of original 440 BC Greek bronze sculpture Doryphorus
|
|
|
Idealized
|
A figure who is shown perfected and without flaws (Greek Art)
|
|
|
Naturalistic
|
One who is shown very normal and everyday (DYING GAUL)
|
|
|
Wet drapery
|
Drapery or clothing that looks wet; clings tightly to the body of women sculptures; emphasizes the body form. (THREE GODDESSES)
|
|
|
Open-form Sculpture
|
Negative space or openings within or around the sculpture.
|
|
|
Triangular Composition
|
Figures can fit into a triangle
|
|
|
True Arch
|
Semi-circular shape to it
|
|
|
Voussoirs
|
Wedge shape blocks that make up an arch
|
|
|
Key Stone
|
Top block in an arch
|
|
|
Barrel Vault
|
Vault is a ceiling - curved ceiling; series of true arches stacked like dominos
|
|
|
Groin Vault
|
Intersection of two barrel vaults
|
|
|
Engaged columns
|
Columns that are attached to the wall, do not provide any structural support
|
|
|
Dome
|
Made of concrete; hemispherical top to a building thicker at the base than at the top (THE PANTHEON)
|
|
|
Oculus
|
Round opening (THE PANTHEON'S DOME)
Three Uses: - Light source - Allows smoke from sacrifices to leave temple - Lightens the weight of the dome |
|
|
Drum
|
Cylindrical area that supports the dome; dome sits on top of the drum
|
|
|
Basilica
|
Roman multipurpose building; entrances on the long side
|
|
|
Nave
|
Long central area in a Basilica
|
|
|
Aisles
|
Walk ways in a Basilica
|
|
|
Apses
|
Semi-circular ends of a Basilica; typically at shorter ends of the building
|
|
|
Triumphal Arch
|
An arch that commemorates a victory
|
|
|
Catacomb
|
Underground burial & worship area
|
|
|
Basilica-plan Church
|
Church with a long nave down the center
|
|
|
Early Christian Church:
|
Nave: where people sit
Aisles: from entrance to alter Apse: one apse behind alter Transept: short crossing arm of a church |
|
|
Transept
|
Short crossing arm of a church; creating a cross shape
|
|
|
Central-plan Church
|
Very compact church; no long nave. Dome
|
|
|
Pendentives
|
Triangular areas that support a dome; allows for more windows
|
|
|
Romanesque
|
Rome-like; year 1,000; southern France
|
|
|
Buttress
|
Vertical element that supports a wall and vault; attached to the wall.
|
|
|
Barrel Vault
|
Adopted instead of using wooden ceilings as before; Lasts longer and sounds better acoustically
|
|
|
Four Christian Periods:
|
- Early Christian
- Byzantine - Romanesque - Gothic |
|
|
Abbot Suger
|
Conceived the new Gothic style at St. Denis church; believed that light flooding through stained glass windows became DEVINE LIGHT
|
|
|
Elements of Gothic Churches:
|
- Large stain glass windows
- Height (very tall) - Delicate appearance - Pointed arches - Flying Buttresses |
|
|
Pointed Arches
|
Help emphasize vertical look; disperses weight better
|
|
|
Notre Dame
|
"Our Lady" - virgin Mary. Many churches dedicated to her
|
|
|
Flying Buttress
|
Detached from the wall and allows for more light; still supports wall
|
|
|
Allah
|
The God worshiped in the Islam faith
|
|
|
Mohammed
|
The profit in the Islam faith
|
|
|
Mecca
|
Very important holy sight; focal point of Islamic architecture
|
|
|
Mosque
|
Islamic place of worship; early mosques were places of prayer
|
|
|
Elements of Islamic Mosque:
|
- Quibla
- Minaret |
|
|
Qibla
|
Wall facing Mecca
|
|
|
Minaret
|
Tower from which people are called to prayer; located in the front of the Mosque
|
|
|
Hinduism
|
Primary religion of India; many God faith
|
|
|
Shiva
|
Powerful God that represents balance of the universe
|
|
|
Icon
|
Means "image" and shows Christian figures
|
|
|
Illuminated Manuscripts
|
Elaborately decorated pages from books
|
|
|
Mosaic
|
Image made of colored tesserae
|
|
|
Shiva Nataraja
|
Hindu God as "Lord of the Dance"
|
|
|
Arabesque
|
Vegetal or geometric designs typically found in Islamic art
|
|
|
Buddha
|
Indian prince Guatama; known for his enlightenment
|
|
|
Krishna
|
Playful Hindu God; often shown with blue skin
|
|
|
Ushnisha
|
Bump of Buddha's head that suggests his supreme wisdom
|
|
|
Stupa
|
Buddhist mound that marks a holy site; vary in size
|
|
|
Exekias
|
Painter of "The Suicide of Ajax"
|
|
|
Makron
|
Painter of "Paris Abducting Helen"
|
|
|
Ictinus & Callicrates
|
Architects of the Parthenon
|
|
|
Lysippus
|
Artist of "Apoxymenos (The Scraper)"
|
|

|
Mycernius and His Queen, Giza.
Egyptian. High relief statue. |
|

|
Ramesses II Holding Nubian, Libyan and Syrian Prisoners
Egyptian. |
|

|
Throne of King Tutankhamen, Valley of the Kings.
Egyptian. |
|

|
Funerary Mask of King Tut, Valley of the Kings.
Egyptian. |
|

|
Three Goddesses, East pediment of Parthenon.
Classical. Greek. Wet drapery. |

