![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
248 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Oil canning |
Wavy distortions of glass or metal panels, often seen in curtain wall construction |
|
|
Electric elevator |
An elevator operated by traction, in which steel cables with counterweight raise or lower the elevator car |
|
|
Lamella |
A roof structure comprised of a series of parallel skewed arches skewed to the axes of the building, which are intersected by another series of skewed arches so that they interact with each other |
|
|
Dead end corridor |
A corridor that is closed at one end, usually limited to 20 feet |
|
|
Terrazo |
Flooring material made from small chips of marble set in cement and polished |
|
|
Toughness |
A metals ability to withstand shock or impact |
|
|
Brass |
An alloy of copper and zinc that is corrosion resistant and very workable |
|
|
Clay |
A fine-grained, cohesive, inorganic soil |
|
|
Buck |
A door frame of wood or metal to which the finished frame is attached |
|
|
Architectural bronze |
An alloy of copper, zine, lead, and tin used for moldings and forgings |
|
|
Steel |
An alloy of iron and carbon, with a carbon content between 0.1% and 1.7% (more than that of wrought iron and less than that of cast iron) |
|
|
Expansive soil |
A fine-grained cohesive soil that undergoes large volume changes with changes in moisture content |
|
|
Insulation |
A material used to prevent or reduce sound transmission or heat flow |
|
|
Mullion |
A vertical member between windows or doors |
|
|
Sand |
Granular material, ranging from about 3/8 inch to 1/200 inch |
|
|
Bronze |
An alloy of copper and tin |
|
|
Softwood |
The wood of coniferous evergreen trees, such as cedars, pines, and firs |
|
|
K value |
The thermal conductivity of a material |
|
|
Hardness |
A metals resistance to abrasion and penetration |
|
|
Construction joint |
The joint between two successive concrete pours usually located where shear is minimum, such as at a midspan of beams |
|
|
Malleability |
The ease with which a metal can be shaped by hammering or by machine |
|
|
Built up roofing |
Roofing made up of piles of saturated roofing felts alternated with layers of pitch or hot asphalt cement and surfaced with gravel or a cap sheet |
|
|
Friable |
Soil that is easily crumbled or reduced to powder |
|
|
Insulating glass |
Two sheets of glass with an air space between to insulate against the passage of heat or sound |
|
|
Wrought iron |
Almost like iron with a very low carbon content, ductile, easily worked, and relatively resistant to corrosion |
|
|
Ductility |
The ability of a material to undergo large deformations without fracture |
|
|
Reflective glass |
Glass with a reflective film laminated between two sheets of clear glass, which behaves like a mirror by reflecting heat and glare |
|
|
IIC impact isolation class |
A rating of the degree of isolation of a floor against the transmission of impact noises |
|
|
Allowable stress |
The maximum units of stress permissible in a structural member. Also called working stress |
|
|
Thermal resistance (r) |
A measure of the resistance of a specific thickness of a given material to the passage of heat; the reciprocal of conductance |
|
|
Foot-candle |
The basic unit of illumination arriving at a work plane |
|
|
Aletropic or anisotropic would best describe which of the following materials? A Glass B Granite C Steel D Wood |
Wood |
|
|
Name the four soil groups from most to least stable. |
Gravels Sand Silt Clays |
|
|
Examples of: Igneous rock Sedimentary Metamorphic |
Granite Sandstone and limestone Marble or slate |
|
|
Name the primary wood preservatives. |
Water borne: no odor and is paintable. For installations off the ground Oil borne: water repellent, in contact with or just above the ground Creosote: solution of distilled coal tar. Unpleasant odor, dark in color, unpaintable |
|
|
Type III cement |
High early strength: quickest, high heat of hydration. Good for cold weather |
|
|
Vitricification |
Measure of ceramic tile density Impervious, vitreous, semi-vitreous, and non-vitreous |
|
|
Type III construction |
Heavy timber, combustible |
|
|
Name 3 types of flat roof membranes |
Built up: multiple pile of asphalt impregnated felt. Aggregate is embedded in the top Single ply: elastomeric membrane applied in single layer. Less prone to cracking. Weather resistant Fluid applied: rubbery membrane applied several coats with roller or spray gun. Also used for waterproofing below grade |
|
|
Lightweight concrete |
Superior thermal insulation and fire resistive qualities. Lacking in compressive strength, it is easier to handle, easier to nail to, does not require complex support structure |
|
|
Vehicle |
Liquid portion of paint mixture that consists of binders, dryers, and solvents |
|
|
Aluminum |
Most abundant element on earth. Alloy to improve strength and hardness. Corrosion resistant but prone to oxidation and scratching |
|
|
Copper |
Resistant to corrosion. Excellent electrical conductor. Prone to oxidation. Bronze is an alloy of copper and tin. Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc |
|
|
Split ring connector |
Used for wood to wood lap joints to develop shear and slippage resistance in the connection |
|
|
Shear plate connector |
Wood to steel connections and wood to wood connections. Flat plates with a flange extending from the face of the plate to a hole in the middle for bolting. |
|
|
Centering |
Temporary masonry formwork used to construct an arch, dome, or vault |
|
|
Electric elevator |
Pulled up on steel cables using counterweights. Gearless type is high speed. Geared type is low speed |
|
|
In protecting against moisture how is a reglet used? |
They are used in the termination of flashing in masonry and co nc rete walls. |
|
|
Brazing |
Joining of two or more pieces of metal at a temperature above 800 using a nonferrous filler metal |
|
|
Stainless steel |
A steel alloy containing 12 to 27 percent chromium. Nickel is added to increase resistance to corrosion and improve cold workability |
|
|
Flitch |
A portion of a log sawn on two or more sides intended for re-sawing into lumber or veneer. |
|
|
What affects the ductility of steel? |
The addition of carbon. Carbon increases strength but decreases ductility. |
|
|
Terne plate |
Often used in roofing, an alloy of lead and tin. Usually applied over a sheet of steel. |
|
|
Dropped panel |
A thickened slab at the top of a column which resists high shear forces and is used in two way flat slab concrete construction |
|
|
Name the four types of mortar in order of strength |
M - strongest S - below grade or at foundation walls N - used on interior and exterior, above grade load bearing walls O - used on interior and exterior, non-load bearing walls |
|
|
Heat strengthened glass |
Twice the strength of annealed glass. Similar to tempering but less expensive and less resistant glass |
|
|
Annealed |
Process of slow controlled cooling of metal or glass |
|
|
What is the best method of terrazo installation? |
Sand cushion method which requires a membrane and 1/4" sand cushion below. Allows floor system to move independently which helps prevent cracking. |
|
|
Categories of plywood |
Interior or exterior Softwood or hardwood Grades - based on face veneer (A is best quality) Span rating - measure of strength and stiffness Construction or decorative |
|
|
Types of copper alloy |
Manel, muntz, nickel silver - strong and ductile. Used for roofing and kitchen equipment |
|
|
Bentonite |
Material used for waterproofing. Formed by decompression of volcanic ash. Flat panels sandwiched between kraft paper. Kraft paper deteriorates and the clay swells to several times its dry volume and when saturated with water thus creating a waterproof barrier. |
|
|
Stress/Strain graph |
A graphic representation of the ability of a material to resist forces |
|
|
Elastic limit |
The greatest unit stress that a material can resist without permanently changing its shape. Hookes' law applies to this area |
|
|
Yield point |
A point above the elastic limit where a material continues to deform with only a small increase in load and any change in shape is permanent |
|
|
Ultimate strength |
The maximum unit stress of a material just prior to failure |
|
|
Moment |
The tendency of a force to create rotation about a point. It is equal to the magnitude of the force multiplied but the shortest distance from the force to the point (the moment arm) |
|
|
Moment simple beam with distributed load formula |
M=WL/8 or M=w(l)squared/8 |
|
|
Simple beam with a single concentrated load formula |
M=PL/4 |
|
|
Maximum moment |
When the shear diagram crosses zero |
|
|
Under an axial load, tension or compression, the overall length of a member will change. How is this computed? |
^L=PL/AE ^L= change in length of the member P= load L= length of the member A= area of cross section E= modulus of elasticity |
|
|
What type of spread footing is used when the soil has a low bearing capacity? |
Mat footing - acts as a two way slab |
|
|
Gravity wall |
Resists overturning and sliding by sheer weight and volume of mass. Used for walls less than 10' high |
|
|
T type cantilever wall |
Walls up to 20' high |
|
|
Counterfort wall |
Triangular shaped cross walls to stiffen the vertical slab add weight to the base |
|
|
Deadman |
Timber, stone, or concrete mass buried in the ground as an anchor, used for walls over 3' high and placed 6' o.c. |
|
|
Type I construction |
Major building elements of noncombustible materials such as concrete, masonry, or steel |
|
|
Type II construction |
Similar to type I, non combustible except for a reduction in the required fire resistance ratings of the major building elements. |
|
|
Type III |
Non combustible exterior walls and major interior elements of any material |
|
|
Type IV |
Heavy timber construction, noncombustible exterior walls and major interior elements of solid or laminated wood of specified sizes |
|
|
Type V |
Any materials Protected - load bearing to be 1 hr Unprotected - no requirements |
|
|
Flutter |
Refers to rapid oscillations of a flexible cable or membrane structure caused by aerodynamic effects of wind. i.e tall buildings are subject to flutter |
|
|
Radius of gyration |
The distance from an axis at which the mass of a body may be assumed to be concentrated |
|
|
Slenderness ratio |
Ratio of the columns effective length to its least radius of gyration |
|
|
Shear wall |
A wood, concrete, or masonry wall capable of resisting changes in shape and transferring lateral load to the ground foundation |
|
|
Framing to ensure lateral stability |
Rigid framing - least efficient, low to mid rise structures Shear wall Braced frame |
|
|
Soft story |
Has lateral stiffness or strength significantly less than that of the stories above |
|
|
Moment of inertia |
This is a measure of the bending stiffness of a structural members cross sectional shape |
|
|
Modulus of elasticity |
Measure of the stiffness of the material of a structural member |
|
|
Max allowable height between landings or floors of stairs Handrail height Risers height max Tread depth max |
12' 34"-38" 7" 11" |
|
|
How much fire protection-rated glazing (wire glass) permitted in a 90 min rated door in an exterior wall? |
None. A a 90 min door not in an exterior wall is permitted to have 100 square inches of wired glass. |
|
|
Non combustible |
It will not ignite and burn when subjected to fire |
|
|
Methods of damproofing |
Admixtures for concrete, bituminous coatings, membranes, and plastics |
|
|
Methods of waterproofing |
Elastomeric membranes, liquid applied membranes, and bentonite panels |
|
|
A deep excavation for a high-rise building in an urban area would require A. Battered walls B. Needle beams C. Steel sheeting D. Tiebacks |
A deep excavation would require the use of vertical soldier beams supporting horizontal timber breast boards or cribbing. Must be anchored with grouted tiebacks. |
|
|
A soils report indicates that bentonite is present below the site of a proposed two story manufacturing building. What type of foundation system would be used? A. Drilled piers with grade beams B. Raft foundation C. Caissons with pile caps D. Extended spread footings |
Bentonite is an expansive type clay that can push foundations upwards. To prevent this, drilled piers are used to support building weight. Voids are left below the grade beams to allow for soil expansion |
|
|
Raft foundation use |
To distribute a building load over a large area of low bearing capacity soil. |
|
|
Cassius with pile caps use |
To distribute a load from one column to two or more cassions or piers |
|
|
If a soil is analyzed as being primarily silty how should it be characterized? A. Very fine material of organic matter B. Rigid particles with moderately high bearing capacity C. Particles with some cohesion and plasticity in their behavior D. Smaller particles with occasional plastic behavior |
D Choice C describes clay Choice B describes gravels |
|
|
Which if the following accounts for the highest cost of a lighting system over time? A. Lamps B. Luminaries C. Installation D. Operation |
D. The continual operating costs for electricity is the single largest expense. |
|
|
Which of the following wood flooring types has the lowest material cost? A. Maple strip over sleepers B. Oak strip no. 1 common C. Oak plank D. White oak parquet |
B. Oak strip no. 1-oak strip flooring is one of the least expensive wood flooring types. White oak parquet and oak plank are the most expensive |
|
|
Which of the following door frame materials would provide the greatest durability at the lowest possible cost? A. Aluminum B. Hollow metal C. Stainless steel D. Wood |
Wood frame would be the least expensive but not as durable as the hollow metal |
|
|
Which of the following has the highest material cost? A. Acrylic glazed coating B. Cork tile C. Commercial grade grass cloth D. Medium weight vinyl wall covering |
most expensive Grass cloth Grass cloth Cork tile - most expensive Grass clothVinyl wall coveringAcrylic glazed - least expensive Vinyl wall covering Acrylic glazed - least expensive |
|
|
Kelly ball test |
Tests the workability of fresh concrete. Determines the depth to which the apparatus will sink under its own weight |
|
|
K slump test |
Can test already poured concrete and comparative to slump test |
|
|
Laitance |
Surface deposit of low-strength material containing cement and fine aggregates brought to the surface of concrete. Basically, water bleeding to the top as a result of too much water in the mixture. |
|
|
Efflorescence |
White crystalline deposit of water soluble salts on the surface of masonry. Water seeps in - dissolves the salts which are brought to the surface. |
|
|
Expansion joints in concrete walks should get located at a max spacing of... |
5' Expansion joints with filler at a max of 20' |
|
|
What type of concrete would be used in slip form construction? |
Type III- high early strength |
|
|
Concrete mix ratio |
Cement:sand:coarse aggregate |
|
|
M, S, N, O mortar |
M - high strength for heavy loads N - exterior walls and interior walls under normal loads S - heavier loads for exterior walls at or below grade O - light loads, no freezing |
|
|
If cracking occurred along the joint of a brick wall in a generally diagonal direction from a window up to the top of a wall which of the following would most likely be the case? A. Lack of vertical control joints B. Horizontal reinforcement placed too far apart C. Poor grouting of the cavity D. Inadequate mortar |
A. Vertical cracking is an indication that the brick wall is not able to move laterally |
|
|
What is the most important fire resistant property of a CMU partition? A. Overall width B. Density C. Joint reinforcement D. Equivalent thickness |
D. Usually hollow so equivalent thickness is used to rate the fire resiatance |
|
|
In masonry walls, water is prevented from seeping back into the wall thru capillary action by using A. Base flashing B. Coping C. drips D. Weep holes |
Drips |
|
|
Horizontal masonry reinforcement is required every.......inches. |
16 |
|
|
Which mortar has the highest compressive strength? |
M - 2500 psi O - 350 psi |
|
|
Which of the following engineered products would be best to use in place of traditional wood joists for spans from 16'-20'? A. Wood I joists B. Glue lam members C. Medium density fiberboard D. Parallel chord wood trusses |
A Glu lam would be more expensive and heavier than necessary. Medium density fiberboard is a panel product and is not designed for structural use. Parallel chord would be more efficient for longer use. |
|
|
Kitchen work triangle max length |
26' |
|
|
Most appropriate for damproofing an above-grade concrete wall with a moderately rough surface... A. Cementitios B. Bituminous C. Synthetic rubber D. Silicone coating |
D. Best coverage for rough walls because it can be sprayed, painted or rolled. If walls were below grade, cementitios or bituminous |
|
|
What is used to keep water from penetrating an expansion joint at the intersection of a roof and a half? A. Base flashing B. Counterflashing C. Sealant D. Coping |
B. Counterflashing Base flashing - extends from roof over the can't strip and up the wall Counterflashing - extends from the wall over the base flashing and to cover any expansion joint |
|
|
Lower perm rating means better or worse vapor retarder? |
Lower means better |
|
|
2 examples of structural memebers that are statically indeterminate. |
*Fixed end beams *Rigid frames The bending moment can not be determined by only using the equation for equilibrium |
|
|
Statically determinate |
When the equation for equilibrium can be solved without any other information |
|
|
Space frames |
Series of rigid frames that intersect each other in a grid pattern. Similar to two way reinforced concrete slab. Used to span large, column free areas. Statically determinate. |
|
|
Flexural strength |
The ability of a beam to resist bending forces |
|
|
Coefficient of utilization |
Ratio of useful light arriving at the work plane to the amount emitted by the source |
|
|
Shading coefficient |
Ratio of solar heat gain thru a window with shading devices to solar heat gained by clear glass window |
|
|
Luminous intensity |
Light emitted by the source |
|
|
Illumination |
Intensity of light falling on a surface, expressed in foot-candles |
|
|
Hookes law |
Physical law that states that up to a certain stress, called the elastic limit, unit stress is directly proportional to unit strain |
|
|
Invert |
Lowest point of inside of drain pipe |
|
|
Rehabilitation |
Restoration or substantial improvement of a building |
|
|
Strain |
The change in size of a body caused by external forces. Also called deformation |
|
|
Stress |
An internal force in a body that resists an external forces |
|
|
Statically determinate |
Describing a structure whose reactions can be determined from the equations of equilibrium. Simple beams, cantilever beams, and overhanging beams on two supports |
|
|
Ceramic mosaic tile in a public shower room is best installed over A. Water resistant gyp B. A bed of Portland cement mortar C. Concrete block walls coated with a waterproofing membrane D. Rigid cement composition board made for this purpose |
B. Offers the best durability and water resistance for high-use, wet areas |
|
|
On floors subject to deflection, both terrazo and granite installations should include A. A membrane B. A latex additive in the mortar C. Thinset mortar D. A sand cushion |
A membrane is part of the total assembly that also includes reinforcing and a thick bed of mortar on which the granite is laid. The membrane allows the structural slab to move independently of the finish flooring so that any deflection does not crack the floor. |
|
|
Materials with a with NRC generally have A. A high STC B. A low STC C. A high reverberation time D. A low absorption coefficient |
B. NRC (noise reduction coefficient) is a measure of how absorbitive a material is to sound. STC measures how well materials block sound transmission |
|
|
MB EIFS system |
Mineral based, conventional 3 coat stucco system. Very impact resistant, does not offer insulation of PB or PM systems |
|
|
PB EIFS |
Polymer based, thin base coat, thin finish coat of polymer based stucco over EP (expanded polystyrene) lighter in weight than PM systems, do not resist impact well |
|
|
PM EIFS system |
Polymer modified, impact resistant and provide good insulation. Finish coat applied over XPS (extruded polystyrene) |
|
|
Modulus of elasticity |
Ratio of unit stress to unit strain is constant up to the elastic limit. |
|
|
Moment of inertia |
Measure if a members resistance to deflection |
|
|
Section modulus |
Resistance of a member to bending moment |
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
|
Safety glass |
Laminated glass, consisting of thin sheet of transparent plastic laminated between 2 layers of clear glass. Aka shatterproof glass |
|
|
Elastomeric flooring |
Synthetic resins applied in liquid form, producing a durable, seamless floor surface |
|
|
Perlite |
A lightweight volcanic rock used as an aggregate in lightweight concrete |
|
|
Actinic glass |
Tinted glass that absorbs a high percentage of solar radiation. Aka heat-absorbing glass |
|
|
Plasterboard |
Prefabricated, paper covered sheets having a gypsum core, used for covering interior walls and ceilings or as a base for interior plaster |
|
|
Calcium chloride |
Common accelerating admixture used for concrete |
|
|
Laitance |
Low strength layer of fine particles that floats to the surface of wet concrete |
|
|
Water repellant |
Incapable of transmitting water by capillary action but able to transmit water under pressure |
|
|
Bitumen |
A substance derived from petroleum or coal used to resist waster penetration, such as asphalt or coal tar pitch |
|
|
Anodizing |
Process of coating aluminum with a hard oxide film by electrolytic action to prevent corrosion and improve appearance |
|
|
Sherardizing |
Method of coating steel with thin layer of zinc |
|
|
SDC |

|
|
|
A building in which core walls provide the only significant lateral force resisting elements may be inadequate to resist A. Bending B. Torsion C. Vertical acceleration D. Diaphragm stress |
B |
|
|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
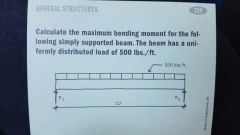
|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
|
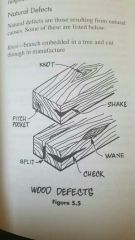
Wood defects |
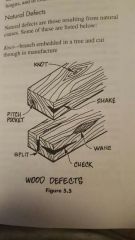
|
|
|
Manufacturing defects of wood |
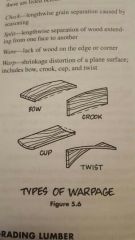
|
|
|
Wood defects |
|
|
|
Manufacturing wood defects |

|
|
|
Hardboard |

|
|
|
Fiberboard |

|
|
|
Flakeboard |

|
|
|
Particleboard |

|
|
|
Beadboard |

|
|
|
Plastic laminate |

|
|
|
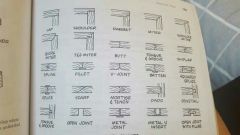
Wood joints |
|
|
|
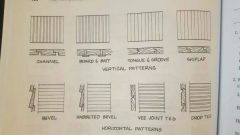
Wood siding patterns |
|
|
|
Galvanic action metals |

|
|
|
Damproofed wall |

|
|
|
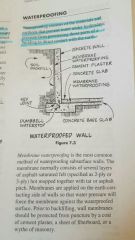
Waterproofed wall |
|
|
|
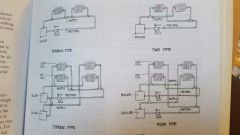
Hydronic systems |
|
|
|
Single pipe hydronic |

|
|
|
Two pipe hydronic |

|
|
|
Three pipe hydronic |

|
|
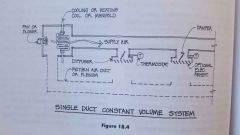
Single duct constant volume |

|
|
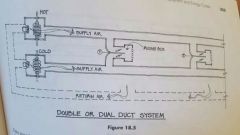
Double duct |

|
|
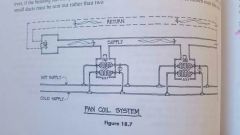
Fan coil system |

|
|
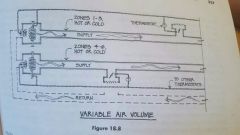
VAV |

|
|
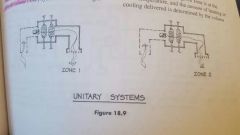
Unitary system |

|
|
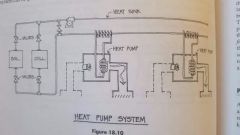
Heat pump sysem |

|
|
|
Parallel resistance |
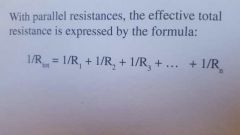
|
|
|
Single phase circuit power formula |

|
|
|
Three phases circuit power formula |

|
|
|
Inverse square law |

|
|
|
Point grid method |
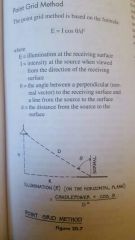
|
|
|
Zonal cavity method |
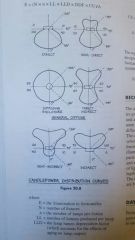
|
|
|
Control mech equip noise |
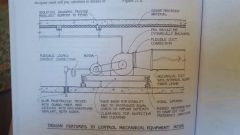
|
|
|
Critical stairs dimensions |
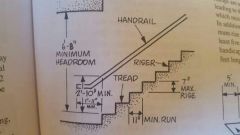
|
|
|
Ramp dimensions |

|
|
|
Door ratings |

|
|

Drag strut |
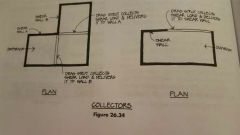
|
|

Accidental torsion |

|
|
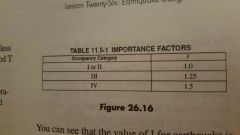
Importance factor |

|
|
|
Seismic Design Categories |

|
|
|
Special moment resisting frame SMFR |

Concrete frames assigned to SDC D and above must be SMRF |
|
|
Intermediate moment resisting frame IMRF |

|
|
|
Ordinary moment resisting frame OMRF |

|
|
|
Building orientation |

|
|
|
Externally load dominated |
Aka skin loaded - energy use is determined mainly by heat loss or gain through the exterior envelope |
|
|
Internal load dominated |
High heat gain from occupants, lighting, and equipment i.e. Office buildings, schools, labs, hospitals |
|
|
Building shape based on climate |

|
|
|
Building shading |
South facing - moderate overhangs or louvers East west facing - vertical louvers |
|
|
Extensive green roof |
Less than 6" soil |
|
|
Intensive green roof |
Thicker than the extensive 6" soil and supports complex landscape, including shrubs and small trees |
|
|
Green roof construction |
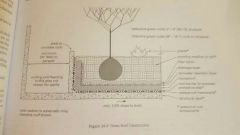
|
|
|
Superinsulation |
Providing higher levels of insulation, tightly sealing all joints and cracks, and preventing any thermal bridges. I.e. outlets on exterior walls are avoided |
|
|
Transparent insulation |
Thick layer of polycarbonate honeycomb material, acrylic foam, or fiberglass sandwiched between layers of glazing. Permits light |
|
|
Permeance |
Property of a material that prevents water from diffusing through it |
|
|
Lighting and cooling energy load on commercial bldg? |
30-40% |
|
|
Daylight factor |
Ratio, expressed in %, of indoor Illuminance at a point on a horizontal surface to the unobstructed exterior horizontal illuminance |
|
|
*Standard daylighting with no overhang *Daylighting with overhang |
1.5x the window height 2-2.5x the window height |
|
|
Direct gain system |
Collect heat through south facing glass and store the heat in high mass materials such as concrete |
|
|
Indirect gain system |
Similar to direct gain except thermal mass is not in direct sunlight. Mass is heated during the day by room air temperature and related sunlight |
|
|
Thermal storage wall |
I.e. trombe wall placed directly behind a South facing glass wall and collects energy during the day, release at night |
|
|
Roof ponds |
Store heat in large water filled bags on the roof. At night, insulation placed over the bags at which lose heat into the building |
|
|
Flat plate collectors |
Network of pipes located on an absorbitive black surface with low emissivity below a covering of glass or plastic |
|
|
Focusing collectors |
Parabolic shaped reflectors that focus incoming radiation to a single pipe. Operate at higher temp than flat plate. Must be continuously aimed at the sun |
|
|
Photovoltaic (PV) cells |
Crystalline-most common Polycrystalline- less expensive but less power Thin-film cells- 1/3 power of crystalline. ideal to integrate with variety of materials |
|
|
Balance point temp |
Outdoor temp at which a building transitions from a heating need to a cooling need |

