![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

|
Mycenae, Fortified Town
-1350-1300 BCE -"Lion Gate:" principle entry composed of a relieving arch above the door, decorated with triangular stone slab of lions flanking a column. -Shaft graves, "Treasury of Atreus:" tholos tomb (beehive tomb) -Dromos: long passageway to entrance. |
|

|
Stoa of Attalus
-added in the 2nd century BCE -Kind of an ancient version of a strip mall, long rectangular structure (in this case two-stories) -roof supported by colonnade. |
|
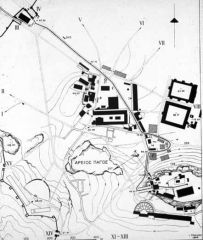
Greece:
Panathenaic Way |
-Ceremonial path from Piraeus (the port city of Athens) through Athens up to the Acropolis
-used for an annual procession in honor of Athena, the goddess who protected the city. |
|

-Main Buildings
|
Athens, Acropolis
Main Buildings: -Parthenon -Propylea -Erechtheum -Temple of Athena Nike |
|

-Sculptor:
-Column #/type: -Optical Refinements: |

Greece: Acropolis
The Parthenon - 447-432 BCE -Sculptor: Phidias -Temple to Athena Parthenos (Athena, the virgin, the goddess of wisdom/victory) -8x17 columns, doric -Optical Refinements: To the eye, a vertical column appears to be narrower in the middle than at either the top or the bottom. To counteract this, the each exterior Parthenon column has a very slight bulge in the middle. Also the upper diameter of each is slightly narrower than its base diameter, a practice called entasis. Additionally, these columns slant inward, so that they would meet, were they extended one mile into the sky. The four outside c orner columns slant inward diagonally. The three levels of the crepidoma are slightly domed in the center because to the eye purely horizontal lines would have appeared to dip in the middle. |
|

-Architect
|

Greece: The Acropolis
Propylea -Built 437-432 BCE -Architect: Mnesicles -ceremonial entrance/gatewy to the Acropolis |
|

|

Greece: The Acropolis
Erechtheum -Built 421-405 BCE -located on the most sacred site of the Acropolis. -incorporated several shrines. -highly irregular plan: north porch Ionic. South porch, "Porch of the Maidens." -caryatids: a sculpted female figure serving as an architectural support taking the place of a column or a pillar. |
|

-Architect:
|
Greece: The Acropolis
Temple of Athena Nike -449 BCE -Architect: Callicrates |
|

|
Paestum (Italy), Temple of Hera I
-ca. 530 BCE -An example of an Archaic temple -Doric columns, short and squaty -In this case, divided down the middle by a row of columns |
|

|
Hellenistic Sculpture:
Old Shepherdess, ca. 180 BCE |
|

|
Hellenistic Sculpture:
Laocoon, Rome, Vatican Museum -1st century BCE |
|

-Architects: (2)
-Column #/type: |

Greece Hellenistic Architecture:
Didyma, Turkey, Temple of Apollo -begun ca. 300 BCE; never completed -Architects: Daphnis of Miletus and Paeonius of Ephesos -10 x 21 columns -double peristyle -Ionic temple |
|

|
Greece Hellenistic Architecture:
Athens, Choragic Monument of Lysicrates -334 BCE -small freestanding monument for display of bronze triton won in choral competition -superimpostion of geometric forms, different materials, use of tholos form. |
|

|
Greece Hellenistic Architecture:
Athens, Tower of the Winds -40 BCE -Utilitarian structure with three functions: --horologion (water clock) --sundial --weathervane -ornamented on exterior with reliefs of eight winds |
|

|
The Etruscan Civilization:
Cerveteri, Italy, Necropolis ca. 650-300 BCE -"Tomb of the Chairs and Shields" |
|

|
The Etruscan Civilization:
Cerveteri, Italy, Necropolis ca. 650-300 BCE -"Tomb of the Reliefs" |
|

|

The Etruscan Civilization:
Populonia, Italy, Necropolis ca. 600 BCE |
|

|
Etruscan sarcophagus
-Two examples: one today in the Louvre Museum, Paris and one in the Villa Giulia Museum, Rome ca. 525 BCE -terra cotta (ceramic) |
|

The Etruscan Civilization
|

Etruscan sarcophagus
Two examples: Both in Archaeological Museum, Florence 2nd cent. BCE -single figures -middle aged man relaxing (Obesus Etruscus). -wealthy lady preparing for her marriage. |
|

The Etruscan Civilization
|
Etruscan funerary urn; Chiusi, Archaeological Museum
-2nd cent. BCE |
|

The Etruscan Civilization
|
Etruscan funerary urn, "The Old Folks"
-2nd cent. BCE |
|

|
Perugia, Port Augusta, Etruscan gate
-300 BCE -round-headed arch used in a monumental manner -barrel vaulting -composed of voussoirs (wedge-shaped stone used in building an arch) -Frieze of Ionic pilasters above. |
|
|
Basilica of Trajan
|
Rome:(inside Forum of Trajan)
-100 CE. -Trabeated structural system -nave -aisles -clerestory -apse |
|

|

Rome, Basilica of Maxentius and Constantine
- 307-312 CE -arcuated structural system with trabeated (post&lintel) decoration. |
|

|

Rome, Markets of Trajan
-100 CE -macellum: an ancient Roman indoor market that normally sat alongside the forum and basilica. -exedra: a semicircular recess, often crowned by a half-dome, which is usually set into a building's facade. An exedra may also be expressed by a curved break in a colonnade, perhaps with a semi-circular seat. -taberna: a single room shop covered by a barrel vault within great indoor markets of ancient Rome. Each taberna had a window above it to let light into a wooden attic for storage and has a wide doorway. |
|

|

Lepcis Magna, Libya, Theater
-1st cent. CE -cavea (seating) -orchestra -scaenae frons ("front of stageset") |
|

|

Rome, Theater of Marcellus
-1st cent. BCE |
|
|
Colosseum
|
Rome:(Flavian Amphitheater)
-80 CE |
|

|

Rome, Forum Boarium, "Temple of Vesta"
(actually dedicated to Hercules Victor) -1st cent BCE -round tholos type temple -Hellenistic architecture. cf. Delphi, Tholos Temple(current photo), 4th cent BCE |
|

|

Rome, Forum Boarium, "Temple of Fortuna Virilis"
-early 2nd cent. BCE -constructed of concrete, travertine, tufa, and stucco. -Axial orientation -elevated on platform |
|

|
Rome, Pantheon
-118-128 CE -commissioned by the emperor Hadrian -Dedicated to all of the gods -meant to be approached on axis -Dome made of concrete -Peir and arch style of support -coffers: name of the squares on the dome interior. -Dome diameter equal to the height (perfect sphere) |
|

|

Rome, "Mausoleum of Augustus"
-28 BCE -cf. Etruscan tumulus tombs -Built inside city walls -lined w/ a circle of cypress trees. -280 ft. in diameter |
|

|
Rome, Tomb of Caius Gestius
-1st cent. BCE -cf. Egyptian Pyramids -steep pyramid, 120 ft. high -concrete faced with marble |
|

|
Rome, Catacomb of Callixtus
-3rd cent. BCE -Loculus: a recess large enough to receive a human corpse. Covered by plaque. Usually for working class. (halocaust bunkbeds) -Tufa |
|

|

Rome, Catacomb of St. Agnese fouri le mura
- 200-500 CE -cubiculum: for wealthier families that could afford a room/cubical for the family to be burried in. -Arcosolium: (from Lat. arcus, "arch", and solium, "a sarcophagus") is an architectural term applied to an arched recess used as a burial place for the father of the family in a cubiculum. -(Current photo) Via Latina Catacombs - fresco decoration: painting technique; putting wet paint on plaster |
|

|
Roman City Gate:
Turin, Italy -ca. 16 BCE |
|

|
Roman City Gate:
Trier, Germany, "Porta Nigra" -late 3rd cent. CE -pier and arch structural system (arcuated) with an overlaid post and lintel decorative system (trabeated). |
|

Triumphal Arches
|
Pula, Istria (today Croatia), Arch of the Sergius Family
- 29-27 BCE |
|

Triumphal Arches
|
Orange, France, "Triumphal Arch"
-ca. 21 CE |
|

|

Aqueduct of Nimes (France) and the Pont du Gard
-ca. 50 CE -Construction of the Pont du Gard (bridge): limestone ashlars, dry-laid (no mortor) -projecting stones and voussoirs* used to support wood centering* (formwork) -canal above top level of arches (ca. 150 ft. above top of the foundation) -bridge is only one segment of the aqueduct which winds 30 miles, drops ca. 45 ft. -regulating basin -castellum (water tower/reservoir). (current photo) |

