![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
48 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Gur Emir. Samarkand, Uzbekistan ca. 1400 comm. Timur |

mausoleum for Timur |
|
|
Gur Emir. Samarkand, Uzbekistan ca. 1400 comm. Timur |

|
|
|
Gur Emir. Samarkand, Uzbekistan ca. 1400 comm. Timur |

|
|
|
Gur Emir. Samarkand, Uzbekistan ca. 1400 comm. Timur |

|
|
|
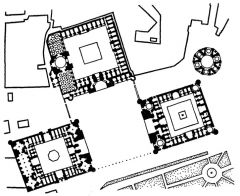
Registan Samarkand, Uzbekistan begun early 15th c. comm. Ulugh Beg |

|
|
|
Registan Samarkand, Uzbekistan begun early 15th c. comm. Ulugh Beg |
|
|
|
Shirdar Madrasa, Registan Samarkand, Uzbekistan (1616-36) comm. Ulugh Beg |

|
|
|
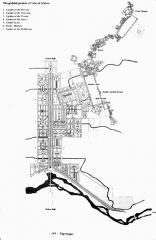
Isfahan, Iran turned capital by Shah Abbas in 1598 |

|
|
|
Isfahan, Iran turned capital by Shah Abbas in 1598 |
|
|
|
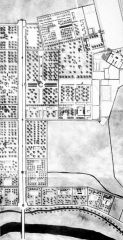
Chahar Bagh Avenue and the Chahar Bagh Garden Isfahan, Iran. comm. Shah Abbas |
|
|
|
Maydan-I Shah (Royal Square) Isfahan, Iran (1590-1602) comm. Shah Abbas |

|
|
|
Maydan-I Shah Isfahan, Iran (1590-1602) comm. Shah Abbas |

|
|
|
Maydan-I Shah Isfahan, Iran (1590-1602) comm. Shah Abbas |

|
|
|
Ali Qapu Isfahan, Iran (ca. 1600) comm. Shah Abbas |

|
|
|
Ali Qapu Isfahan, Iran (ca. 1600) comm. Shah Abbas |

|
|
|
Ali Qapu Music Room Isfahan, Iran (ca. 1600) comm. Shah Abbas |

|
|
|
Hasht Bihisht Isfahan, Iran (ca. 1670)
|

|
|
|
Masjid-I Shah (Royal Mosque) Isfahan, Iran (1611-37) |

|
|
|
Masjid-I Shah (Royal Mosque) Isfahan, Iran (1611-37) |

|
|
|
Masjid-I Shah (Royal Mosque) Isfahan, Iran (1611-37) |

|
|
|
Masjid-I Shah (Royal Mosque) Isfahan, Iran (1611-37) |

|
|
|
Masjid-I Shah (Royal Mosque) Isfahan, Iran (1611-37) |

|
|
|
Masjid-I Shah (Royal Mosque) Isfahan, Iran (1611-37) |

|
|
|
Fatehpur Sikri, India (1570s) comm. Shah Akbar after it was predicted he would have a son. Shaik Salim Chishti predicted |

|
|
|
Anup Talao Fatehpur Sikri, India (1570s) |

|
|
|
Diwan-I Khas Fatehpur Sikri, India (1570s) |

audience hall for Akbar |
|
|
Diwan-I Khas Fatehpur Sikri, India (1570s) |

audience hall for Akbar |
|
|
Diwan-I Khas Fatehpur Sikri, India (1570s) |

audience hall for Akbar |
|
|
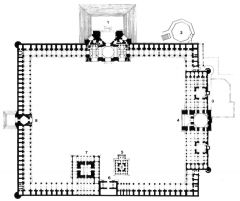
Khanqah Fatehpur Sikri, India Begun 1569 |
|
|
|
Tomb of Shaik Salim Chishti Fatehpur Sikri, India (1569-74) |

|
|
|
Tomb of Shaik Salim Chishti Fatehpur Sikri, India (1569-74)
|

|
|
|
Tomb of Shaik Salim Chishti Fatehpur Sikri, India (1569-74) |

|
|
|
Tomb of Shaik Salim Chishti Fatehpur Sikri, India (1569-74) |

|
|
|
Jali (Lattice Screens) |

|
|
|
Taj Mahal Agra, India (1632-54) comm. Shah Jahan |

|
|
|
Taj Mahal Agra, India (1632-54) comm. Shah Jahan |

|
|
|
Great Gate, Taj Mahal Agra, India (1632-54) |

|
|
|
Great Gate, Taj Mahal Agra, India (1632-54) |

|
|
|
iwan (Center arch/Gateway)
pishtaq (Ornamentation around outside) |

|
|
|
Hasht Bihisht Isfahan, Iran (ca. 1670) |

|
|
|
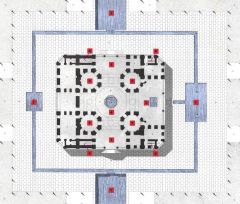
Hasht Bihisht Isfahan, Iran (ca. 1670) |
|
|
|
Hasht Bihisht Isfahan, Iran (ca. 1670) |

|
|
|
Hasht Bihisht Isfahan, Iran (ca. 1670) |

|
|
|
-The influence of the Timurids was that they did not have a pre-ordained type of architecture since they were nomadic, and therefore sought the help of the architects in the areas they captured and had them create them their own unique style |
What influence did the architecture of the Timurids have on later builders and patrons? |
|
|
-the onion and ribbed dome -Blue decorative tile -Four openings into a mosque and better known as the Four-Iwan Plan -Each Iwan surrounded by a pishtaq(rectangular frame) |
The actual characteristics that was influencing later builders |
|
|
-The four-iwan plan and pishtaq to surround it -Main focus was on the courtyard than the inside rooms(different since most mosques focused on the prayer hall) -8 paradises: Represents the eight doors to heaven(different since they just didn't have that feature) |
What distinctive mosque plan was common in Isfahan? How does it differ from previous types of mosques? |
|
|
-Many of the forms and designs come from wooden architecture in that region -Often the materials were marble, which was imported instead of red sandstone, which was common in the region -ex.: Jali or lattice screens which were originally made of wood but instead made of marble |
In what ways did the architecture of the Mughal Empire incorporate both local and imported architectural elements and concepts? |
|
|
-Red sandstone being Persian -Dome toppers and Pishtaq being Indian designs -Similar dome being that it is a double dome -The 8 paradise gardens -Italian style of inlaying precious stones into marble |
In what ways did the architecture of the Mughal Empire incorporate both local and imported architectural elements and concepts in the Taj Mahal? |

