![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
90 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Holometabolous
|
– Complete metamorphosis; Insects whose life cycle goes egg-larva-pupa-adult (e.g. beetles, flies, butterflies)
|
|
|
Hemimetabolous
|
– Simple metamorphosis; Insects whose life cycle goes egg-nymph-adult (often with >1 nymph stage) (e.g. grasshoppers, true bugs)
|
|
|
Instar
|
- each new immature stage (instars are separated by molts)
|
|
|
Ecdysis
|
– molt
|
|
|
Exoskeleton, cuticle
|
- external body covering of insects
|
|
|
Exuviae
|
– cuticle cast off after molting
|
|
|
Diapause
|
– A delay in development due to seasonal or other regular environmental conditions
|
|
|
Diel
|
– occurring at the interval of a day
|
|
|
Univoltine
|
– one life cycle (egg-adult) is completed per year (know also bivoltine, trivoltine, semivoltine)
|
|
|
Tagmosis
|
– The process by which, over evolutionary time, undifferentiated segments have fused and evolved into specific body regions (e.g. into the head, thorax, & abdomen in insects).
|
|
|
Notal, tergal
|
– top
|
|
|
Pro-
Meso- Meta- |
-Front -Back |
|
|
Sternal
|
-Bottom
|
|
|
Pleural
|
-sides
|
|
|
Pronotum
|
(top of prothorax) & same for mesonotum & metanotum
|
|
|
Prosternum
|
(mesosternum, metasternum)
|
|
|
Tergites
|
- top plates
|
|
|
Sternites
|
- bottom plates
|
|
|
Plastron
|
Air film on the surface of the body
|
|
|
Eyes vs. ocelli
|
Eyes referes to compoun eyes and ocellus referes to a simple eye consisting of a single lens
|
|
|
Labrum, clypeus, mandibles, maxillae, labium, palps, hypopharynx
|
Mouthparts
|
|
|
Scape Antenna |
- Antennal segments: paired segmental sensory organs = 1- scape: basal segement/ first joint, 2- pedicel: 2nd segment, 3- elongate segement
|
|
|
Coxa Trochanter Femur Tibia Tarsi (us) |
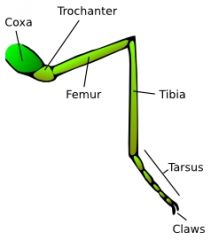
|
|
|
Cerci (cercus) vs. terminal filament
|
Cercus = terminal paired lateral slender appendages Terminal Filament = 3rd central tail filament extending from the tip of the abdomen |
|
|
Gena (genae)
|
- side of head/ sides of head
|
|
|
Occiput
|
back of head
|
|
|
Tracheal system
|
the respiratory system of an insect
|
|
|
Open tracheal system
|
Characteristic of insects that breathe air; aquatic insects must carry a store of air when they dive or connect with a stationary air source
|
|
|
Closed tracheal system
|
Gas distribution takes place through a network of internal, air-filled tubes; respiratory gas exchange through spiracles, gills, or air bubbles
|
|
|
Spiracle
|
respiratory aperture
|
|
|
Tracheae, tracheoles
|
respiratory tubes in insects (of diminishing size from tracheae to tracheoles)
|
|
|
Lotic
|
relating to moving water environment
|
|
|
Lentic
|
relating to a still water environment
|
|
|
Polypneustic
|
(poly = many; pneu = lung) – many spiracles open to the air
|
|
|
Oligopneustic
|
(oligo = few; pneu = lung) – a couple of spiracles open to the air
|
|
|
Aptneustic
|
– no open spiracles, as in some insect larvae
|
|
|
How insects breathe?
|
1. Bubble (Dytiscidae- diving beetles) 2. Air tube (Diptera larva) 3. Plastron (closely spaced hydrophobic hairs that trap air next to the body) 4. Tracheal gill 5. Cutaneous |
|
|
Gill
|
An organ that allows oxygen to pass by diffusion from water into an animal’s body
|
|
|
Plastron
|
- closely spaced hydrophobic hairs that trap air next to the body
|
|
|
Cuticle
|
– The external skeletal structure of an insect, composed of chitin and proteins, and secreted by the epidermis.
|
|
|
Integument
|
– The outer cover of an insect, composed of epidermis plus cuticle
|
|
|
Chitin
|
- a long-chain polymer of a N-acetylglucosamine, a derivative of glucose. It is the main component of the exoskeletons of arthropods.
|
|
|
Sclerotization
|
– Occurs when proteins in the cuticle cross link, which hardens the cuticle & makes it water proof.
|
|
|
Sclerite
|
– A portion of the cuticle that has been sclerotized. Each sclerite forms a separate plate.
|
|
|
hemolymph
|
1. Transports hormones 2. Transports nutrients 3. Removes wastes 4. Carries hemoglobin in a few species (e.g. some aquatic diptera), but otherwise does not transport oxygen. That is left to the tracheal system. 5. Buffers against dehydration. |
|
|
How did insects evolve?
|
Evidence indicates that insects colonized land and then re-evolved freshwater aquatic lifestyles. Insects did not colonize freshwater directly from saltwater.
|
|
|
How many times did recolonization of freshwater occur?
|
- many different times in insects. It did not just occur once. Therefore, not all aquatic insects are one another’s closest relatives. (Repeat evolutionary colonization of freshwater habitat would suggest that there were a lot of ecological opportunities for insects in such habitat.)
|
|
|
Protura
|
evolutionarily primitive hexapods
|
|
|
Diplura
|
evolutionarily primitive hexapods
|
|
|
archaeognatha
|
- old jaw
|
|
|
Pterygota
|
- Subclass of Insecta; "winged insects"
|
|
|
Paleoptera
|
- Infraclass of Insecta; Cannot fold wings back on abdomen
|
|
|
Neoptera
|
- Infraclass of Insecta; Fold wings back onto abdomen
|
|
|
Odonata
|
(Odon, a tooth) = dragonflies and damselflies; ~5500 species
|
|
|
Ephemeroptera
|
(Ephemero, brief; ptera, wing) = mayflies; ~2500 species.
|
|
|
Plecoptera
|
(Pleco, pleat; ptera, wing) = stoneflies; ~1200 species.
|
|
|
Hemiptera
|
(Hemi, one-half; ptera, wing) = true bugs; ~82,000 species. Sometimes this order is treated as two orders: Heteroptera & Homoptera.
|
|
|
Coleoptera
|
(Coleo, sheath; ptera, wing) = beetles; ~375,000 species.
|
|
|
Trichoptera
|
(Tricho, hair; ptera, wing) = caddisflies; ~7,000 species. Related to butterflies.
|
|
|
Lepidoptera
|
(Lepido, scale; ptera, wing) = butterflies and moths; ~175,000 species.
|
|
|
Diptera
|
(Di, two; ptera, wing) = true flies; ~125,000 species.
|
|
|
Phylum
|
Arthopoda ("jointed"/"leg")
|
|
|
Subphylum
|
Hexapoda
|
|
|
Class
|
Insecta
|
|
|
Hexapoa
|
six / legs
|
|
|
Shredder
|
Feeds on living vascular plants
|
|
|
Scraper
|
Feedson periphyton
|
|
|
Predator
|
Feeds on live animals
|
|
|
Piercer
|
Pierces plants and sucks nutrients
|
|
|
Gathering Collector
|
Feeds on decomposing material
|
|
|
Filtering Collector
|
Filters organisms from water
|
|
|
Surface film/ Pleuston
|
Water's surface
|
|
|
Hyperheic zone
|
the region of a stream where there is interchange between ground and surface water; can extend outward from the banks
|
|
|
Littoral zone
|
a region of pond or lake shallow enough for light penetration to the bottom
|
|
|
Limnetic
|
the surface portion of still, deep water; photosynthesis occurs in plants (e.g. algae) floating in this zone, but light does not penetrate to the bottom (or else it would be littoral)
|
|
|
Profundal
|
below the limnetic
|
|
|
CPOM, FPOM
|
coarse and fine organic particulate matter
|
|
|
Benthic/ Benthos
|
The bottm of a body of water (adj. benthic)
|
|
|
Periphyton
|
organisms (algae, cyanobacteria, heterotrophic microbes) and detritus attached to submerged surfaces in aquatic ecosystems.
|
|
|
Allochthonous
|
originating in a place other than where found. In a stream, allochthonous detritus would come as inputs from the terrestrial habitat.
|
|
|
Direct Aerial Descent (DAD)
|
An origin of insect wings
|
|
|
Sailing
|
An origin of insect wings
|
|
|
How old is the first arthopod
|
Appeared ~500 mya in the Cambrian
|
|
|
When were the first insect fossils
|
- Archeognatha (=bristletails); appeared 400 mya in the Devonian
|
|
|
What/when were the first fossils of aquatic insects?
|
Ephemeroptera (mayflies); from 300 mya in the Carboniferous
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

