![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define the term structural formula.
|
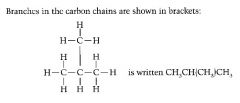
Shows the unique arrangement of atoms in a molecule in a simplified form, without showing all the bonds.
|
|
|
Define the carbon bond in alkanes and alkenes?
|
> -enes have a double carbon bond,
> -anes do not |
|
|
Define how many carbons are in alkanes and alkenes?
|
>MEPB
1C = Meth 2C = Eth 3C = Prop 4C = But 5C = Pent 6C = Hex 7C = Hep 8C = Oct 9C = Non 10 = Dec |
|
|
Define the prefixes used in organic chemistry to locate branches.
|
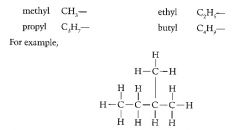
Prefixes are added to describe changes that have been made to root molecule.
|
|
|
What is a functional group?
|
An atom or group of atoms in an organic molecule that are responsible for the characteristic of that molecule.
|
|
|
Define the 6 suffixes used in organic chemistry.
|
>Alkane= -ane as in methane
>Alkene-= -ene as in methene >Halogenalkanes= fluor-, chloro-, bromo-, iodo-, >Alcohols (-OH) = -ol as in methanol, CH3OH >Aldehydes (-CHO) = -al as in ethanal CH3CHO >Ketones (-COR) = -one as in propanone CH3COCH3 >Carboxylic acids (-COOH) = -oic acid as in ethanoic acid CH3COOH |
|
|
What are structural isomers?
|
Molecules that have the same molecular formula but whose atoms are arranged differently.
|
|
|
Define an homologous series.
|
A set of organic compounds with the same functional group. The compounds differ in the length of their hydrocarbon chains.
|
|
|
What are the three ways in which structural isomerism can occur?
|
>Positional isomerism - same functional group attached to main chain at different points
>Functional group isomerism - functional groups that are different >Chain isomerism - different arrangement of hydrocarbon chain (branching) |
|
|
Stereoisomers
|
Compounds with the same structural formula but have a different arrangement in space
|
|
|
Two types of stereoisomerism
|
Z-isomers= 'cis' isomer, where non-hydrogen groups are on the same side of molecule
E-isomers= 'trans' isomer, where non-hydrogen groups are on opposite of molecule |

