![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
10 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Name the three types of particle in an atom. State the relative mass and charge of each particle.
|
>Proton - mass 1, charge +1
>Neutron - mass 1, charge 0 >Electron - mass 1/1840, -1 |
|
|
How are the particles in an atom arranged?
|
Protons and neutrons in central nucleus held by strong nuclear force. Electrons orbit nucleus in shells (electrostatic force).
|
|
|
How many electrons do the first shells hold?
|
2n squared / n = number of shell
1st = 2 2nd = 8 3rd = 18 |
|
|
Write the shorthand for 9 electrons.
|
2,7,
|
|
|
Draw the electron arrangement diagram of an atom with 16 electrons.
|
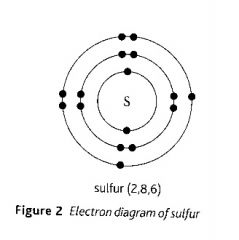
|
|
|
Define the term mass number, A.
|
The sum of the protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom.
|
|
|
Define the term atomic number, Z.
|
The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom.
|
|
|
Define the term Isotope.
|
Atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons.
|
|
|
Why do isotopes of the same element have identical chemical properties?
|
They have the same number and arrangement of electrons.
|
|
|
What does a mass spectrometer measure?
|
Relative atomic masses
Relative molecular masses |

