![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
90 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
___ dental materials are materials designed to prevent disease OR injury to the oral tissue
|
preventive
|
|
|
Which are NOT a preventive dental material?
Fluoride gel Mouth protectors Articulating paper Sealants |
articulating paper
|
|
|
Dental fluorides are available in what 4 common forms?
|
gel, varnish, foam, rinse
|
|
|
True or False, fluoride will kill you instantly and is really dangerous and doesn't help your teeth at all
|
False
|
|
|
True or False, APF has acid in it
|
True, 0.98% phosphoric acid
|
|
|
What are the % of the components for Acidulated phosphate fluoride?
|
2% NaF
0.34% hydrogen fluoride 0.98% phosphoric acid flavoring, thickening, and coloring agents |
|
|
What does APF stand for?
|
acidulated phosphate fluoride
|
|
|
What's the overall fluoride concentration of APF?
|
about 1.22-1.32%
|
|
|
Neutral NaF has a pH of __-__ for what reason?
|
6-8
Avoid etching of restorative materials |
|
|
True or False, varnished containing 5% NaF are available
|
True
|
|
|
What dental material would likely NOT be etched by APF?
Amalgam Composite GI Compomer Hybrid Ionomer Ceramics |
Amalgam
|
|
|
What are the % of the components for Acidulated phosphate fluoride?
|
2% NaF
0.34% hydrogen fluoride 0.98% phosphoric acid flavoring, thickening, and coloring agents |
|
|
Which of these should be used twice a year?
APF 2% NaF 1.1% NaF gel/toothpaste 0.4% SnF2 gel 0.2% NaF rinse |
APF
2% NaF (These are "in office") |
|
|
What does APF stand for?
|
acidulated phosphate fluoride
|
|
|
Which of these can be used daily?
APF 2% NaF 1.1% NaF gel/toothpaste 0.4% SnF2 gel 0.2% NaF rinse |
1.1% NaF gel/toothpaste
0.4% SnF2 gel (These are "home use") |
|
|
What's the overall fluoride concentration of APF?
|
about 1.22-1.32%
|
|
|
How often can one use 0.2% NaF rinse?
|
Weekly
|
|
|
Neutral NaF has a pH of __-__ for what reason?
|
6-8
Avoid etching of restorative materials |
|
|
How often can one use 0.05% NaF, 0.24% NaF toothpaste, and 0.8% MFP?
|
Daily
|
|
|
True or False, varnished containing 5% NaF are available
|
True
|
|
|
What dental material would likely NOT be etched by APF?
Amalgam Composite GI Compomer Hybrid Ionomer Ceramics |
Amalgam
|
|
|
Which of these should be used twice a year?
APF 2% NaF 1.1% NaF gel/toothpaste 0.4% SnF2 gel 0.2% NaF rinse |
APF
2% NaF (These are "in office") |
|
|
Which of these can be used daily?
APF 2% NaF 1.1% NaF gel/toothpaste 0.4% SnF2 gel 0.2% NaF rinse |
1.1% NaF gel/toothpaste
0.4% SnF2 gel (These are "home use") |
|
|
How often can one use 0.2% NaF rinse?
|
Weekly
|
|
|
How often can one use 0.05% NaF, 0.24% NaF toothpaste, and 0.8% MFP?
|
Daily
|
|
|
APF gels are applied in (soft/hard) trays
|
soft
|
|
|
How long should APF be used in mouth?
|
4 min
|
|
|
Patient should not eat for __ min after APF application
|
30
|
|
|
Rinses are not recommended for children under __ years old
|
6
|
|
|
Neutral NaF has ___ properties
|
thixotropic
(viscosity decreases and flow increases on application of force) |
|
|
T or F, APF can stain restorations
|
FALSE! but they can etch them
|
|
|
Which of these is NOT acidic?
APF Sodium Fluoride gel Stannous Fluoride gel |
Sodium F
|
|
|
Topical fluoride is best used in conjunction with a fluoride-containing ___
|
rinse
|
|
|
True or False, rinses are good substitutes for mechanical plaque removal
|
False
|
|
|
0.12% of what is used in Peridex and Perioguard?
|
chlorhexidine
|
|
|
Listerine uses a ___ based product with methylsalicylate in alcohol
|
phenol
|
|
|
The purpose of a sealant is a (chemical/physical) barrier to bacteria
|
physical
|
|
|
What are two methods used to prepare a tooth for sealants?
|
acid etch
air abrade (with Al3O2 particles propelled by air) |
|
|
What type of sealants are recommended by the ADA council on scientific affairs?
|
resin-based
|
|
|
What are two LOW viscosity dimethacrylate monomers?
|
bis-GMA, UDMA
|
|
|
What is in sealants at 1% for opacity and enamel contrast
|
TiO2
|
|
|
Inorganic filler by up to __% by weight in sealants
|
50
|
|
|
Resin sealants can be __ or __ cured
|
cold, self
|
|
|
What are the 2 components of the 2 component curing system of resin sealants?
|
benzoyl peroxide initiator
5% tertiary amine activator |
|
|
Light cured resin sealants are a __ component system (#)
|
1
|
|
|
What is the light activated component of resin sealants?
|
camphoroquinone (diketone; photoinitiator molecule)
|
|
|
Glass ionomers are (chemically/mechanically) retained via what element?
|
chemically, Ca+
|
|
|
What has better bond strength, GI or resin-based sealants?
|
resin based sealant
|
|
|
What releases more fluoride, GI or resin sealants?
|
GI
|
|
|
Ideal sealants should do 9 awesomely awesome things
|
These are pretty self-explanatory... look them up if you want
One had one is that they should NOT form an O2 inhibited layer |
|
|
Sealants are retained by what type of retention?
|
micromechanical
|
|
|
Why are fissures difficult to fill?
|
air and debris are trapped at bottom of fissures
|
|
|
What is the equation for rate of penetration?
|
r(PC)/2l
r - radius of fissure l - length |
|
|
What does the PC = in the rate of penetration equation?
|
γ(cosθ)/2(η)
γ = surface tension θ = contact angle η = viscosity of sealant |
|
|
Which has a LONGER working time, chemically or light-activated sealants?
|
light-activated
|
|
|
Chemically-activated sealants have the following compared to light-activated
(shorter/longer) working time (shorter/longer) polymerization time (less/more) expensive (does/doesn't) require mixing |
shorter, longer, less, does
|
|
|
(chemical/light) activated sealants should be stored in dark containers
|
light
|
|
|
A greater C value will lead to (more/less) pulling of the restoration away form the walls of a restoration
|
more
|
|
|
Which of these will NOT cause sensitivity to teeth in a typical situation?
Warm water on enamel Movement of fluid in dentin tubules Osmotic pressure changes Cold on exposed pulp |
Warm water on enamel
|
|
|
True or False, simple evaporation of water from dentin by air blasts can cause sensitivity
|
True
|
|
|
What are two ways that OTC desensitizing agents work?
|
PLUGGING open tubules via chemical OR mechanical
Desensitizing the actual nerve |
|
|
Which of these is not considered a desensitizing agent
fluoride potassium oxalate ferric oxalate dentin bonding agents Al3O2 |
Al3O2
|
|
|
(potassium/sodium) nitrate is a nerve depolarizer
|
potassium
|
|
|
Amorphous (calcium/aluminum) phosphate mineralizes the opening of dentinal tubules
|
calcium
|
|
|
True or False, GI sealants can act as desensitizing agents
|
True
|
|
|
By what mechanism do mouth protectors actually protect the mouth?
|
Absorb impact energy
|
|
|
Injury occurs (more/less) often when mouth protector is used
|
less
|
|
|
Which of these is NOT a response of the teeth when trauma occurs?
pulpitis enamel hardening pulpal necrosis reabsorption hemorrhage pulp canal obliteration |
enamel hardening
|
|
|
Mouth protectors are also known as ___
|
mouthguards
|
|
|
According to Dr. Khajotia, what are the three common types of mouth protectors?
|
stock
mouth-formed custom-made |
|
|
Anita Job goes to Walmart and grabs a mouthpiece from the sports section. What kind is it?
stock mouth-formed custom-made |
stock
|
|
|
Justin Case wanted to make sure he had the best mouth piece available for football season. He should get a ___ mouth protector.
stock mouth-formed custom-made |
custom-made
|
|
|
Mouth protectors are made of ___ polymers
|
thermoplastic
|
|
|
What are some of the materials that custom-made mouth protectors are made from?
|
polyethylene-poly(vinyl acetate) [EVA]
rubber latex polyurethane vinyl plastisol |
|
|
Ned N. Munee was looking for the cheapest mouth protector. He decided to rank them from MOST to LEAST expensive... can you help him?
mouth-formed stock custom-made |
custom-made
mouth-formed stock |
|
|
Put these steps for making mouth protectors in order:
finish form thermoplastic material on cast impressions of arch pour cast in disinfected impression |
impression
pour form thermoplastic finish |
|
|
Many injuries result from the (maxilla/mandible) being driven into the other
|
mandible
|
|
|
True or False, mouth protectors concentrate forces on posterior teeth because they are the strongest
|
FALSE! they distribute force over the entire arch
|
|
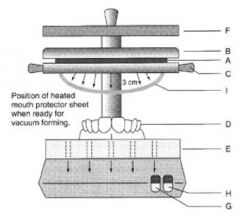
Label!
|
A mouth protector sheet
B upper clamp C lower clamp D model E perforated support plate F heater G vacuum switch H heater switch I sag of 3cm permitted before vacuum is switched on |
|
|
Which of these do NOT need to be taken into consideration when making a mouth protector?
-Does pt have ortho? -Does pt have teeth still erupting that you need to make space for? -Does pt have frenum in the way? -Will all teeth contact the mouth protector? |
NONE!
You must consider all 4 of these things! |
|
|
EVA has the following compared to polyurethane
(lower/higher) initial strength (lower/higher) hardness (lower/higher) more energy absorption (lower/higher) water sorption requires (lower/higher) processing temp |
ALL lower
|
|
|
EVA has the following compared to vinyl plastisol
(lower/higher) strength (lower/higher) hardness (lower/higher) energy absorption (lower/higher) processing difficulty |
higher, higher, higher, lower
|
|
|
T or F, gagging, poor taste, irritation and speech impairment are common downfalls of custom made protectors
|
False, these are NOT common
|
|
|
T or F, only stock mouth protectors will stain
|
False, they can all stain
|
|
|
What are the three main causes of mouth protector breakdown?
|
biting, tearing, general deterioration
|
|
|
T or F, pressure and heat can actually lead to permanent deformation of mouth protectors
|
True
|
|
|
You should clean mouth protectors in (cool/hot) water
|
cool
|
|
|
It's ok to scrub mouth protectors with abrasive dentifrices
|
Nope
|
|
|
T or F, you can use alcohol and denture cleaning products on mouth protectors
|
False
|
|
|
True or False, mouth protectors do not need any special storage treatment
|
False, store in a rigid container
|

