![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the 4 main categories of casting defects
|
distortion
surface roughness/irregularities/discoloration porosities incomplete/missing detail |
|
|
What 3 things cause distortion?
|
improper manipulation of wax
improper handling of wax pattern uneven movement of pattern walls |
|
|
What is defined as relatively finely spaced surface imperfections whose height, width and direction establish the surface pattern
|
surface roughness
|
|
|
surface roughness of casting is (lesser/greater) than that of pattern
|
greater
|
|
|
surface roughness of casting depends on particle size of ____ and its ability to reproduce surface detail
|
investment
|
|
|
True or false, improper manipulation can lead to surface roughness AND surface irregularities
|
True
|
|
|
What is defined as isolated imperfections like nodules that do not characterize the total surface area?
|
surface irregularities
|
|
|
Surface irregularities can interfere with what step in the crown fitting process?
|
seating
|
|
|
What defect results in small nodules?
|
air bubbles
|
|
|
What defect results in minute ridges or veins?
|
water films
|
|
|
What defect results in fins or spines, or surface roughness?
|
rapid heating rates
|
|
|
What defect results in voids or porosity, or a tenacious carbon coating?
|
underheating
|
|
|
True or False, liquid:powder ratio does not affect surface roughness or irregularities
|
False
|
|
|
(prolonged/shortened) heating as well as (high/low) heating temperature result in surface roughness
|
prolonged, high
|
|
|
What is considered 'high' casting pressure? (in MPa)
|
above 0.14 MPa
|
|
|
True or False, the composition of the investment material can create surface roughness and irregularities
|
True
|
|
|
What is caused by solidification shrinkage of alloy before casting is completely filled?
|
localized shrinkage porosity
|
|
|
Where does localized shrinkage porosity usually occur?
|
near the sprue-casting junction in the interior (sometimes exterior)
|
|
|
Localized shrinkage porosity is created by a __ __ on the mold wall where molten alloy impinges
|
hot spot
|
|
|
The hot spot is the (first/last) to solidify
|
last
|
|
|
Hot spots result in what?
|
suck back porosity
|
|
|
What is caused by solidification shrinkage of fine grain alloys before microvoids can segregate to the liquid pool
|
Microporosity
|
|
|
Microporosity usually appear as small irregular voids within the body of the ___
|
casting
|
|
|
Microporosities occur if the casting temperature is too (high/low)
|
low
|
|
|
Pinhole and gas inclusion porosities are usually __ in shape
|
spherical
|
|
|
Which are larger, pinhole or gas porosities?
|
gas
|
|
|
(pinhole/gas) porosities are due to dissolution of gasses in molten metals [like Cu, Ag, Pt, Pd] that re expelled on solidification
|
pinhole
|
|
|
(pinhole/gas) porosities are due to entrapment of gas in molten metal
|
gas
|
|
|
Castings severely contaminated with gasses like sulfer are usually what color when removed from investment? Will pickling clean these?
|
black
no, not easily |
|
|
What causes subsurface porosities?
|
unknown; but might be caused by the simultaneous nucleation of solid grains and gas bubbles at the first moment that the alloy freezes at the mold walls
|
|
|
How can subsurface porosities be diminished?
|
control rate at which molten metal enters mold
|
|
|
An entrapped-air porosity is also known as what?
|
back-pressure porosity
|
|
|
Entrapped-air porosity can produce large (concavities/convexities) at cavity surface of crown or MOD casting
|
concavity
|
|
|
What is caused by the inability of air in the mold to escape through pores in the investment?
|
entrapped-air porosities
|
|
|
What is caused by a pressure gradient that displaces air pocket towards the end of the investment via the molten sprue and button?
|
entrapped-air porosities
|
|
|
If solidification occurs BEFORE the entrapped air can escape, you get what defect? Is this found on the outside or inside of casting?
|
entrapped-air porosity, outside
|
|
|
Incidence of entrapped air porosities is (increased/decreased) in dense modern investment
|
increased
|
|
|
Incidence of entrapped air porosities is (increased/decreased) by an increase in mold density produced by vacuum investing
|
increased
|
|
|
Incidence of entrapped air porosities is (increased/decreased) by tendency for the mold to clog with residual carbon when the low-heat technique is used
|
increased
|
|
|
Factors that (slow/speed up) the venting of gases can cause entrapped-air
|
slow
|
|
|
What 4 things eliminate entrapped-air porosities?
|
proper burnout
adequate mold and casting temp sufficiently high casting pressure proper liquid/powder ratio |
|
|
Thickness of investment between to of pattern and end of casting is less than or equal to __mm
|
6mm
|
|
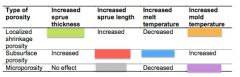
Label all colors with either "increased", "decreased", or "no effect"
|

decreased - green, red, orange, purple
increased - blue grey - no effect |
|
|
If molten alloy is somehow prevented from filling the mold, this results in what?
|
incomplete casting
|
|
|
What two things can prevent alloy from filling mold?
|
insufficient venting of mold
high viscosity of fused metal |
|
|
If the alloy is heated too (high/low), it will be too viscous and not properly fill the mold
|
low
|
|
|
If the casting pressure is too (high/low), you get a dull, rounded, and incomplete margins
|
low
|
|
|
If you don't completely eliminate all wax residue, this can result in what?
|
incomplete casting
|
|
|
When too many combustion products remain in the mold and fill pores in investment material, you have (increased/decreased) venting of air
|
decreased
|
|
|
Contact of molten alloy with moisture or wax particles produces and explosion and creates __ pressure, preventing filling of mold
|
back
|
|
|
Incomplete elimination of wax results in (dull/shiny), incomplete, rounded margins die to what gas in the residual wax?
|
shiny, carbon monoxide
|

