![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
10 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Appendages of the skin - Hair - Skin glands - Nails |
|
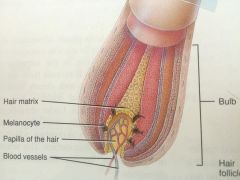
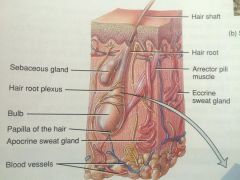
Hair Follicle |
Follicle is an invaginating tube that connects with epidermis but dips into the dermis and sometimes the hypodermis. Follicle Wall Stratified Squamous Epithelium Not considered part of epidermis! Hair bulb Bottom of hair follicle contains papilla Papilla of hair follicle Dermal tissue (loose CT) pushed up into the hair follicle with blood vessels to nourish the growing hair follicle. The papilla increases surface area to reach more cells. |
|
|
Hair or pili |
Strand of hair = pilus filament of keratinized cells that grow from hair follicle. New cells from the hair base (matrix) are added to the bottom of the hair root. Existing cells of the hair root are pushed upward. As cells are being pushed upward they become keratinized and die. |
|
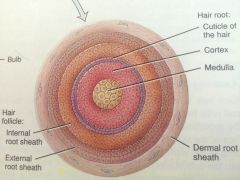
Hair Layers |
3 hair layers: Medulla - core 2 - 3 rows of cells tightly smashed together Cortex - makes up most of hair shaft Cuticle - outer most layer single layer of thin flat cells that are heavily keratinized |
|
|
Different types of hair |
Follicles have different rates of activity, will produce different size hairs. Baldness is hair follicle death. Follicles have life cycles, lose hair and follicle goes into rest. Then restarts to develop new hair. Melanocytes located in hair matrix of the bulb will deposit melanin into kerotinocytes of cortex and medulla of the hair. More melanin gives darker hair color. Hair becomes gray because of progressive decline in melanin production. White hair results from the lack of melanin and the accumulation of air bubbles in the hair development. Straight hair follicle with produce straight hair. Follicle can twist in dermis to give curly hair. Follicle shape changes hair. |
|
|
Arrector pili muscles |
Smooth muscle extends from the superficial dermis to the dermal root sheath on the side of the hair follicle. Normally hair comes out of skin at an angle Under stress (cold or fright), the arrector pili muscle contracts so the hair stands perpendicular to the skin. "goose bumps" Evolutionary use, caveman used for heat retention or to scare predators. |
|
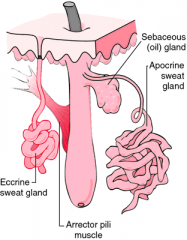
Skin Glands |
simple cuboidal epithelium produce and secrete |
|
|
Sebaceous holocrine gland |
bag connected to hair follicles, lies in the dermis and usually opens it the neck of the hair follicle. Found all over body except hands and soles of feet because hair is absent. Secretes oily substance (sebum) - skin oil, prevents excessive evaporation of water from the skin - oils keeps skin soft and pliable - coats surface of hairs, prevents from drying and becoming brittle |
|
|
Eccrine sudoriferous sweat gland |
coiled tubular glands that project through dermis and epidermis distributed through the skin in most regions of the body produces sweat (water and electrolytes) help regulate body temperature (thermal regulation) through evaporation secretes sweat through pore on surface of skin |
|
|
Apocrine sudoriferous sweat gland |
simple coiled tubular glands found in patches of hair (facial, pubic, armpit) secretory portion of sweat glands is located mostly in subcutaneous layer excretory duct opens into hair follicles produce sweat (water, electrolytes, lipids and proteins (pheromones)) Pheromones signal attractiveness to other members of the species Sweat is odorless but when interact with bacteria, it will metabolize its components causing body odor. |

