![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Nucleus
|
round structure near center of the cell; contains DNA
|
|
|
Chromatin
|
DNA in threadlike form, dispersed throughout the nucleus
|
|
|
Chromosomes
|
Chromatin coiled and condensed, in this form for cell division
|
|
|
Nucleoli
|
small round bodies in the nucleus, composed of proteins and RNA. Assembly sites for ribosomes.
|
|
|
Nuclear envelope
|
Double-layered porous membrane that binds the nucleus. Has nuclear pores to permit passage of proteins and RNA.
|
|
|
Plasma Membrane
|
Separates cell contents from surrounding environment. Made of a phospholipid bilayer with dispersed protein molecules. Has selective permeability.
|
|
|
Microvilli
|
Fingerlike projections or folds in the plasma membrane that increases surface area to increase absorption of materials and binding of signaling molecules.
|
|
|
Cytosol
|
Fluid cytoplasmic material inside the cell.
|
|
|
Organelles
|
Metabolic machinery of the cell including ribosomes, ER, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, peroxisomes, mitochondria, cytoskeletal elements, and centrioles.
|
|
|
Ribosomes
|
Tiny spherical bodies composed of RNA and protein; sites of protein synthesis; free floating or attached to rough ER
|
|
|
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
|
Membranous system of tubules. Rough ER- studded with ribosomes; tubules provide storage and transport of the proteins made; external face synthesizes phospholipids and cholesterol
Smooth ER- site of steroid and lipid synthesis, lipid metabolism, and drug detoxification |
|
|
Golgi Apparatus
|
Stack of flattened sacs with bulbous ends and associated small vesicles; plays a role in packaging proteins or other sub.s for export from the cell and in packaging lysosomal enzymes
|
|
|
Lysosomes
|
Membranous sacs containing digestive enzymes (acid hydrolases); digests worn-out organelles and foreign sub.s that enter the cell; can destroy entire cell if ruptured
|
|
|
Peroxisomes
|
Membranous sacs containing oxidase enxymes that detoxify harmful substances, incl. free radicals
|
|
|
Mitochondria
|
Rod-shaped bodies w/ a double-membrane wall; inner membrane is thrown into cristae; contains enzymes that oxidize foodstuffs into ATP; the "powerhouse of the cell"
|
|
|
Centrioles
|
Paired, cylindrical bodies lie close to the nucleus; direct the formation of the mitotic spindle during cell division; form bases of cilia and flagella
|
|
|
Inclusions
|
Other substances stored in the cytoplasm, incl. glycogen granules, lipid droplets, pigment granules, various crystals, water vacuoles, and ingested foreign materials.
|
|
|
Cytoskeletal elements
|
Microfilaments- formed of actin, important in cell motility
Intermediate filament- stable, composed of proteins, resist mechanical forces on a cell Microtubules- form internal structure of centrioles and determine cell shape |
|
|
Interphase
|
Period from cell formation to cell division. 4 subphases:
G1 (gap 1)-vigorous growth & metabolism G0- gap phase in cells that will no longer divide (permanent) S (synthetic)- DNA replication G2 (gap 2)- prep for division |
|
|
Mitosis
|
Nuclear division
|
|
|
Cytokinesis
|
Division of the cytoplasm. Ring of actin microfilaments contracts to form a cleavage furrow. 2 daughter cells are pinched apart. Begins in late anaphase and continues through and beyond telophase.
|
|
|
Meiosis
|
A specialized type of nuclear division that occurs in the reproductive organs. Results in 4 daughter cells with half the chromosomes.
|
|
|
Early Prophase
|
Chromosome become visible, each with two chromatids joined at a centromere with cohesin(an adhesive protein). The nucleoli disappear. Centrosomes separate and migrate toward opposite poles. Mitotic spindles and asters form around the centrioles.
|
|
|
Late Prophase
|
Nuclear envelope fragments. Kinetochore microtubules attach to kinetochore of centromeres and draw them toward the equator of the cell. Polar microtubules are linked in the center and, pushing against each other, they assist in forcing the poles apart.
|
|
|
Metaphase
|
Centromeres of chromosomes are aligned at the equator. This plane midway between the poles is called the metabolic plate. The enzyme separase cleaves cohesin, separating the chromatids.
|
|
|
Anaphase
|
Centromeres of chromosomes split simultaneously- ea. chromatid becomes a chromosome. Chromosomes (V-shaped) are pulled toward poles by motor proteins of kinetochores. Polar microtubules cont. forcing the poles apart.
|
|
|
Telophase
|
Begins when chromosome movement stops. The two sets of chromosomes uncoil to form chromatin. New nuclear membranes form around each chromatin mass. Nucleoli reappear. Spindle disappears.
|
|
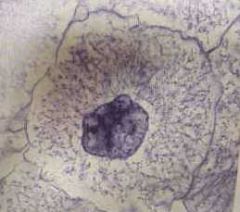
|
Interphase
|
|
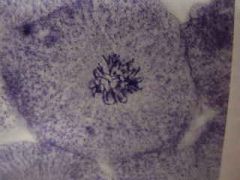
|
Late prophase
|
|

|
Metaphase
|
|
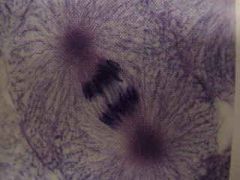
|
Anaphase
|
|

|
Telophase/ Cytokinesis
|
|
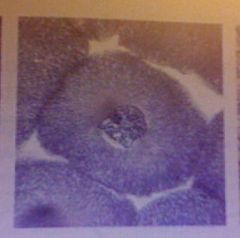
|
Early prophase
|

