![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
175 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define: Anatomy
|
Study of human structure
|
|
|
Define: Physiology
|
Study of human function
|
|
|
Define: Pathology
|
Study of disease
|
|
|
Define: Atom
|
Smallest non-living unit
|
|
|
Define: Molecules
|
Atoms bound together
|
|
|
Define: Cells
|
Smallest living unit
|
|
|
Define: Tissues
|
Group of cells
|
|
|
Define: Organs
|
Group of tissues
|
|
|
What are the levels of organization?
|
Atom
Molecules Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism |
|
|
What are the 11 organ systems?
|
Cardiovascular
Nervous Digestive Endocrine Reproductive Urinary Skeletal Muscular Respiratory Lymphatic/Immune Integumentary |
|
|
Define: Frontal Plane
|
Vertical plane that divides body into front and back.
|
|
|
Define: Transverse Plane
|
Horizontal plane that divides body into top and bottom.
|
|
|
Define: Sagittal Plane
|
Vertical plane that divides body into right and left.
|
|
|
Define: Dorsal
|
Back side
|
|
|
Define: Ventral
|
Belly side
|
|
|
Define: Posterior
|
Backward
|
|
|
Define: Anterior
|
Forward
|
|
|
Define: Superior
|
Up
|
|
|
Define: Inferior
|
Down
|
|
|
Define: Medial
|
Toward middle
|
|
|
Define: Lateral
|
Toward outside
|
|
|
Define: Proximal
|
Near
|
|
|
Define: Distal
|
Far
|
|
|
Define: Superficial
|
Toward outside of the body
|
|
|
Define: Deep
|
Toward inside of the body
|
|
|
What is in the axial region of the body?
|
Head and spine
|
|
|
What is in the appendicular region of the body?
|
Upper and lower extremities
|
|
|
What cavities are within the dorsal cavity?
|
Cranial and vertebral cavity
|
|
|
What is in the cranial cavity?
|
Brain
|
|
|
What is in the vertebral cavity?
|
Spinal cord
|
|
|
What divides the ventral cavity?
|
Diaphragm
|
|
|
What cavities are within the ventral cavity?
|
Thoracic/Thorax/Chest Cavity
Abdominopelvic/Abdomen |
|
|
What two areas are within the thoracic cavity and what is in them?
|
Pleura (lungs)
Mediastinum (heart) |
|
|
What is this region of the abdomen called?
| | ----------- | X | ----------- | | |
Umbilical Region
|
|
|
What is this region of the abdomen called?
| X | ----------- | | ----------- | | |
Epigastric Region
|
|
|
What is this region of the abdomen called?
| | ----------- | | ----------- | X | |
Hypogastric Region
|
|
|
What is this region of the abdomen called?
X | | X ----------- | | ----------- | | |
Hypochondriac Regions
|
|
|
What is this region of the abdomen called?
| | ----------- X | | X ----------- | | |
Lumbar Regions
|
|
|
What is this region of the abdomen called?
| | ----------- | | ----------- X | | X |
Iliac/Inguinal Regions
|
|
|
Define: Homeostasis
|
The body's ability to stay the same (maintain internal equilibrium)
|
|
|
Define: Metabolism
|
All the chemical reactions in the body
|
|
|
Name and describe the two types of metabolism.
|
Catabolism (breaking down)
Anabolism (building up) |
|
|
Define: Prone
|
Laying down belly down
|
|
|
Define: Supine
|
Laying down belly up
|
|
|
Define: Negative feedback
|
Feedback in opposite phase with (decreasing) the input
|
|
|
What are some examples of negative feedback?
|
Body temperature and glucose level
|
|
|
Define: Positive feedback
|
In a system, those changes which serve to increase the effect
|
|
|
What are some examples of positive feedback?
|
Blood clotting and child birth
|
|
|
Define: Matter
|
Anything that occupies space
|
|
|
Define: Element
|
Pure substance that can't be broken down into anything else; Consists of one kind of atom
|
|
|
Define: Subatomic particles
|
Protons (+), Neutrons, and Electrons (-)
|
|
|
Define: Compound
|
2 or more different atoms bound together
|
|
|
What is the difference between an organic and inorganic compound?
|
An organic compound contains carbon. An inorganic compound does not contain carbon.
|
|
|
Define: Atomic number
|
Number of protons and electrons
|
|
|
Define: Atomic mass
|
Number of protons and number of neurons
|
|
|
What are the most common human elements?
|
(H) Hydrogen
(O) Oxygen (N) Nitrogen (C) Carbon |
|
|
How many electrons fill the inner shell of an atom when full?
|
2
|
|
|
How many electrons fill the outer shell of an atom when full?
|
8
|
|
|
Define: Ionic bond
|
One atom transfers its electron(s) to another atom
|
|
|
What is a cation?
|
A positive ion
|
|
|
What is an anion?
|
A negative ion
|
|
|
Define: Covalent bond
|
One atom shares electrons with another
|
|
|
How many bonds does Hydrogen require?
|
1
|
|
|
How many bonds does Oxygen require?
|
2
|
|
|
How many bonds does Nitrogen require?
|
3
|
|
|
How many bonds does Carbon require?
|
4
|
|
|
What is a non-polar covalent bond?
|
A covalent bond in which electrons are shared equally and there are no poles (charges)
|
|
|
What is a polar covalent bond?
|
A covalent bond in which electrons are shared unequally with one positive and one negative pole
|
|
|
What is a hydrogen bond?
|
A bond that connects 2 polar molecules with the positive pole of one attracted to the negative pole of another
|
|
|
What are the 6 properties of water?
|
Surface tension
High heat capacity - thermal stability High evaporative heat loss Solvent Very reactive Cushioning (CSF, etc.) |
|
|
Differentiate between hydrophilic and hydrophobic.
|
Hydrophilic - dissolves in water
Hydrophobic - cannot dissolve in water |
|
|
What do salts do in water?
|
Dissolve and dissociate into ions
|
|
|
Define: Acid
|
A substance that donates a hydrogen ion when dissolved in water
|
|
|
Define: Base
|
A substance that accepts a hydrogen ion when dissolved in water
|
|
|
What chemical reaction results in producing chemical compounds and water?
|
Synthesis/Anabolic Reactions/Dehydration Synthesis
|
|
|
What chemical reaction results in breaking chemical reactions by interacting with water?
|
Decomposition/Catabolic Reactions/Hydrolysis
|
|
|
Define: Monomer
|
One unit
|
|
|
Define: Dimer
|
Two units
|
|
|
Define: Polymer
|
Many units
|
|
|
What is a chemical equation demonstrating dehydration synthesis?
|
Monomer 1 + Monomer 2 --> Dimer + Water
|
|
|
What is a chemical equation demonstrating hydrolysis?
|
Dimer + Water --> Monomer 1 + Monomer 2
|
|
|
What is the chemical equation for carbohydrates?
|
CH2O
|
|
|
Name three monosaccharides.
|
Glucose, Fructose, and Galactose
|
|
|
Name three disaccharides.
|
Maltose, Sucrose, and Lactose
|
|
|
How is maltose formed?
|
Glucose + Glucose --> Maltose + Water (via dehydration synthesis)
|
|
|
How is sucrose formed?
|
Fructose + Glucose --> Sucrose + Water (via dehydration synthesis)
|
|
|
How is lactose formed?
|
Galactose + Glucose --> Lactose + Water (via dehydration synthesis)
|
|
|
What is a polysaccharide?
|
Polymer of glucose
|
|
|
Name three polysaccharides and where they are found.
|
Glycogen - stored in human muscle and liver
Starch - plants Cellulose - plants |
|
|
Name three lipids.
|
Triglycerides (fats)
Phospholipids Steroids |
|
|
What is the structure of a glycerol molecule?
|
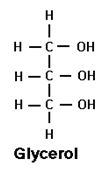
|
|
|
What are three types of fatty acids?
|
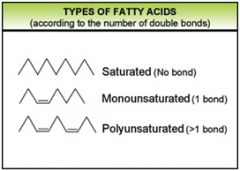
Saturated, Monounsaturated, and Polyunsaturated
|
|
|
What is the structure of a fatty acid?
|
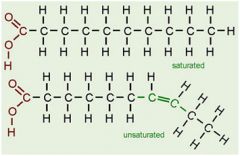
|
|
|
What is the chemical equation that demonstrates how triglycerides are formed?
|
Glycerol + 3 fatty acids --> triglyceride + 3 Water
|
|
|
What chemical equation illustrates dehydration synthesis?
|
Monomer 1 + Monomer 2 --> Dimer + Water
|
|
|
What chemical equation illustrates hydrolysis?
|
Dimer + Water --> Monomer 1 + Monomer 2
|
|
|
What are the 3 types of carbohydrates?
|
Monosaccharides, Disaccharides, and Polysaccharides
|
|
|
What are the 3 monosaccharides and what is their chemical makeup?
|
Glucose, Fructose, and Galactose
6(CH2O) |
|
|
Glucose + Glucose --> __________ + Water
|
Maltose
|
|
|
Fructose + Glucose --> __________ + Water
|
Sucrose
|
|
|
Galactose + Glucose --> __________ + Water
|
Lactose
|
|
|
What is a polysaccharide?
|
Polymer of glucose
|
|
|
What are 3 polysaccharides and where are they found?
|
Glycogen (human muscle & liver)
Starch (plants) Cellulose (plants) |
|
|
What are the 3 types of lipids?
|
Triglycerides (fat)
Phospholipids Steroids |
|
|
What are the 3 fatty acids and what differentiates them?
|
Saturated fatty acid - all single bonds
Monounsaturated fatty acid - one double bond Polyunsaturated fatty acid - more than one double bond |
|
|
Glycerol + 3 fatty acids --> __________
|
Triglyceride + 3 water
|
|
|
Glycerol + 2 fatty acids --> __________
|
Diglyceride + 2 Water
|
|
|
Glycerol + 1 fatty acid --> ___________
|
Monoglyceride + 1 water
|
|
|
1 glycerol + 2 fatty acids + 1 phosphate group --> ____________
|
Phospholipid + 3 Water
|
|
|
What is cholesterol?
|
A steroid used to synthesize other steroids
|
|
|
What are some steroids?
|
Testosterone
Estrogen Progesterone Vitamin D Bile Salts Cortisone Aldosterone |
|
|
What is the structure of cholesterol?
|
Four interlocking steroid rings
|
|
|
What is the structure of an amino acid?
|
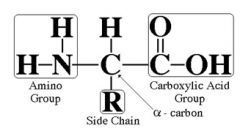
|
|
|
Amino Acid + Amino Acid --> _________
|
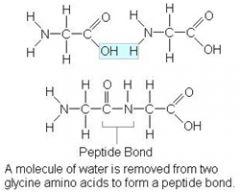
Dipeptide + Water
|
|
|
Dipeptide + Amino Acid --> __________
|
Tripeptide + Water
|
|
|
10 amino acids -->
|
Decapeptide + 9 Water
|
|
|
Name and define the 4 levels of protein structure.
|
Primary - sequence of amino acids that form a polypeptide chain
Secondary - Hydrogen bonds within the molecule (between O and H) cause pleats or helices Tertiary - 3D structure resulting from hydrophilic R groups going to the outside and hydrophobic R groups going to inside Quaternary - exists when there are more than 1 polypeptide chain |
|
|
What is an enzyme?
|
A catalyst that lowers activation energy required for a reaction to occur
|
|
|
Define: Cell
|
The smallest living thing
|
|
|
Define: Cell Theory
|
All living thing consist of cells
|
|
|
Define: Nuclear Envelope
|
Specialized membrane with nuclear pores
|
|
|
Define: Chromatin
|
DNA and proteins (unwound) during interphase
|
|
|
Define: Chromosomes
|
DNA and proteins (condensed) during mitosis
|
|
|
What must occur before mitosis?
|
Chromosome Duplication/DNA Replication
|
|
|
What is DNA?
|
Deoxyribonucleic acid; polymer of nucleotides
|
|
|
What makes up a nucleotide?
|
Phosphate, Sugar, Base
|
|
|
What are the four bases present in DNA?
|
Adenine
Thymine Guanine Cytosine |
|
|
How do the four bases in DNA pair up?
|
A <--> T
G <--> C |
|
|
What is a chromatid?
|
One side of a duplicated chromosome
|
|
|
What is ATP?
|
A nucleotide (adenine, ribose, 3 phosphates)
|
|
|
What is the process of DNA replication?
|
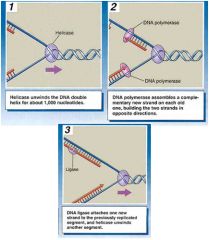
1. DNA unwinds
2. DNA polymerase - enzyme 3. Semiconservative replication - base pairing creates new strand |
|
|
Define: Transcription
|
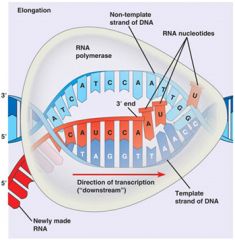
DNA is used to make RNA
|
|
|
What is RNA?
|
Ribonucleic Acid; Polymer of nucleotides
|
|
|
What are 2 differences between DNA and RNA?
|
RNA is single stranded, while DNA is double stranded.
RNA uses Uracil in place of Thymine |
|
|
What are 3 types of RNA?
|
mRNA - messenger
rRNA - ribosomal tRNA - transfer |
|
|
Define: Gene
|
Piece of DNA that codes for RNA
|
|
|
What is mRNA?
|
Strand of RNA that consists of codons that code for a single amino acid
|
|
|
What is rRNA?
|
Used to make ribsomes
|
|
|
What is tRNA?
|
used to carry amino acids; each codon has a specific tRNA
|
|
|
What is a ribosome?
|
rRNA + protein; made in nucleus and exit through pores
|
|
|
What is translation?
|
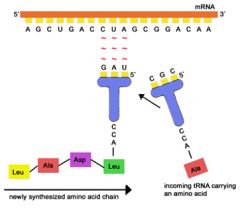
protein synthesis/using RNA to make protein
|
|
|
Where does translation occur?
|
Ribosomes in rough endoplasmic reticulum
|
|
|
Define: Plasma Membrane
|
divides extracellular space (outside) from intracellular space (cytoplasm)
|
|
|
What is the structure of a phospholipid?
|
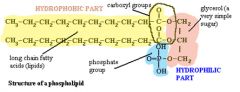
|
|
|
What is the function of cholesterol and where is it found?
|
Stabilizes membrane
Found in hydrophobic part of phospholipid bilayer |
|
|
What are the 5 types of proteins?
|
R - Receptors (binding site)
E - Enzymes C - Carriers (bind to what is trying to get across & carrier it) C - Channels (opening/portal) C - Cell-to-Cell Attachment |
|
|
What are the 3 primary components of a plasma membrane?
|
Phopholipid bilayer, cholesterol, proteins
|
|
|
Define: Passive Process
|
no energy is needed from ATP
|
|
|
Define the 2 types of passive processes
|
Diffusion - spread of particles from high concentration to low concentration
Osmosis - diffusion of water |
|
|
Define: Simple diffusion
|
substances go right through
|
|
|
Define: Facilitated diffusion
|
carrier in membrane or channel/port (usually for small ions)
|
|
|
Define: Isotonic
|
same concentration inside and out; no movement
|
|
|
Define: Hypotonic
|
water less concentrated than the cell; causes hemolysis (water goes into cell and it bursts)
|
|
|
Define: Hypertonic
|
water more concentrated than the cell; causes crenation (water goes out of cell and it shrivels up)
|
|
|
Define: Active process
|
energy required from ATP
|
|
|
Define: Active transport
|
Using ATP to move substances across the plasma membrane
|
|
|
Give an example of active transport.
|
Na+/K+ pump - one protein pumps K+ (kids) in and Na+ (neighbors) out
|
|
|
Define: Secondary active transport
|
proteins which piggyback other things back into the cell with the Na+
|
|
|
Define: Exocytosis
|
particles leave the cell via a vesicle (made by Golgi apparatus) which fuses with the plasma membrane
|
|
|
Define the 3 types of Endocytosis.
|
Phagocytosis - cell "eats" solids such as bacteria
Pinocytosis - cell "drinks" a droplet of something Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis - endocytosis except the "stuff" won't be eaten unless there are receptors |
|
|
Define: Resting Membrane Potential
|
There are more K+ channels than Na+ channels (more K+ diffusing out than Na+ diffusing in); result is cell negative inside and positive outside
|
|
|
What are the 4 classifications of tissues?
|
Epithelial
Connective Muscle Nervous |
|
|
Arrange types of tissues in order of mitosis (highest to lowest)
|
Epithelial
Connective Muscle (not in muscle fibers) Nervous (maybe) |
|
|
Define the two types of glands.
|
Endocrine - secretions go into the blood
Exocrine - secretion go outside the body (goblet cell, multicellular) |
|
|
What is the most abundant tissue type?
|
Connective tissue
|
|
|
Define: Membranes
|
Epithelial tissue with their underlying connective tissue
|
|
|
Define the 3 types of membranes.
|
Cutaneous - skin
Mucous - lines body cavities that open to the outside (respiratory, reproductive, digestive, urinary, eyes) Serous - lines internal body cavities (pleura, pericardium, peritoneum) |
|
|
Where is the visceral layer found?
|
Serous membrane lining area closest to the organ
|
|
|
Where is the parietal layer found?
|
Serous membrane lining area farthest from the organ
|
|
|
The following are indicative of what tissue type:
Classified by shape and arrangement Cells packed close together Avascular Microvilli & cilia Found in glands |
Epithelial
|
|
|
"Cells in a matrix" indicates what tissue type?
|
Connective
|
|
|
What are the 5 connective tissues?
|
Cartilage, bone, blood, loose, dense
|
|
|
The following are indicative of what tissue type:
Contractile Generate body heat |
Muscle
|
|
|
What are the 3 types of muscle tissue?
|
Striated (skeletal, voluntary)
Smooth (involuntary) Cardiac |
|
|
The following are indicative of what tissue type:
Neurons Glial (supporting) cells |
Nervous
|

