![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Small Intestine Histology
|
Small intestine mucosa: simple columnar epithelium Gastric pits are in the stomach, communicate with gastric glands lined with mucous cells and specialized gastric cells:
|
|
|
How long is the small intestine? Diameter? Duodenum length? Jejunum length? Ileum length? |
Intestine is 20ft 1 inch in diameter Duodenum 10 inches Jejunum 8 feet Ileum 12 feet |
|
|
4 Layers of the stomach? Innermost to outermost |
Mucosa: simple columnar Submucosa: nerve plexus Muscularis: oblique, circle, longitudinal Serosa |
|
|
Liver
|
|
|
|
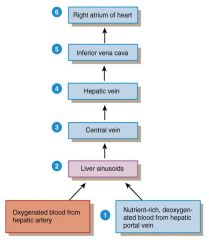
Blood supply to liver? 6 Steps |
|
|
|
Urinary System
|
4 Structures:
Functions:
|
|
|
Kidney: External Anatomy
|
|
|
|
Kidney: 3 Layers of Tissues? |
Outermost: renal fascia - thin layer of tissue that holds against posterior body wall Middle: Adipose capsule - protect from trauma Innermost: renal capsule (fibrous capsule) - dense connective tissue |
|
|
Parenchyma of Kidney Made up of two parts? Renal_________ |
1. Renal cortex = superficial layer of kidney 2. Renal medulla Inner portion consisting of the pyramids Bases facing renal cortex, apex at papilla |
|
|
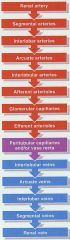
Blood into kidneys, out as urine |
|
|
|
Nephron - Two parts -Renal_________ |
1. Renal corpuscle: glomerulus and Bowman's capsule 2. Renal tubules: proximal convoluted tubules, loop of Henle, distal convoluted tubules, collecting duct |
|
|
Renal Corpuscle
|
|
|
|
hi |
bye |

