![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
phases of matter
states of matter |
liquid, solid, gas (for the purposes of this class)
|
|
|
Density
|
mass per unit volume
ρ=m/V symbol: Greek "rho" units: kg/m^3 |
|
|
specific gravity
|
ratio of density of a substance to the density of water
|
|
|
Pressure
|
force per unit area
P=F/A units: N/m^2 = Pa (pascal) |
|
|
Pressure in a fluid
|
P=ρgh
Pressure = density*gravity* depth under surface |
|
|
Atmospheric Pressure
|
normally 101.3kPa or
101,300 N/m^2 |
|
|
Gauge Pressure
|
The pressure above atmospheric pressure. Example: tire pressure.
|
|
|
Pascal's Principle
|
If an external pressure is applied to a confined fluid, the pressure at every point within the fluid increases by that amount.
|
|
|
Absolute presssure
|
guage pressure + atmospheric pressure
|
|
|
Pascal's Principle applied to hydraulics.
|
Pa=Pb
F/a=F/a |
|
|
Archimedes principle
|
The buoyant force on an object immersed in a fluid is equal to the weight of the fluid dispaced by that object.
|
|
|
equation of continuity
|
Since the flow rate of an incompressible fluid is constant through pipes of different diameters,
A1v1=A2v2 area * speed = area * speed |
|
|
Bernoulli's principle
|
where the velocity of a fluid is high, the pressure is low, and vice versa.
|
|
|
Bernoulli's Equation
|
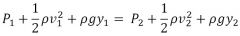
|

