![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Types of cartilage
|
- hyaline cartilage
- fibrocartilage - elastic cartilage |
|
|
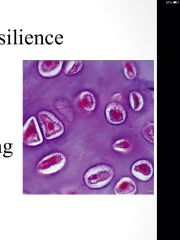
Hyaline cartilage
- function - fibers - where? |
Function: support, flexibility, resilience
Fibers: fine collagen Where: articular(end of long bones), costal, larynx and airways, nose |
|
|
Hyaline cartilage
|
|
|
Elastic cartilage
- function? - fibers? - location? |
Function: bending/flexibility
Fibers: collagen and elastic Location: external ear and epiglottis |
|
|
Fibrocartilage
-function? -fibers? -location? |
Function: absorbs shock, resist stretching
Fibers: thick collagen Locations: meniscus, intervertebral disks, pubic symphysis |
|

|
Fibrocartilage
|
|
|
Types of cartilage growth
|
Appositional
Interstitial Calcification |
|
|
Appositional growth
|
-outside in
-cells in the perichondrium secrete matrix against the external face of existing cartilage |
|
|
Interstitial growth of cartilage
|
-inside-out
-lacunae bound chondrocytes inside the cartilage divide and secrete the new matrix, expanding the cartilage from within |
|
|
Function of bones
|
Support, protect, movement, mineral storage, blood cell formation
|
|
|
Axial vs appendicular
|
Axial: skull, vertebrae, rib cage
Appendicular: upper and lower limbs, shoulders, hips |
|
|
Shape of bones
|
-Long bones- longer than they are wide
-Flat bones- sternum, scapula, skull, ribs -Short bones(sesamoid): cube, inside tendons -irregular: odd shaped (vertebrae) |
|

Compact vs spongy bone
|
Compact- dense outer layer
Spongy- honeycomb filled with yellow marrow |
|
|
Epiphyses
|

|
|
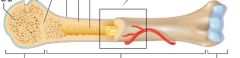
Label
|
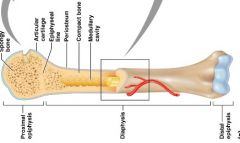
|
|
|
Bones membranes
|
-Periosteum
-endosteum |
|
|
Periosteum
|
-Two layers
-outer layer is dense regular connective tissue -inner layer consists of osteoblasts and osteoclasts -richly supplied with blood, nerve fibers, and lymphatic vessels |
|
|
Endosteum
|
-Delicate layers that cover internal bone surfaces
-contains osteoblasts and osteoclasts -covers trabeculae of spongy bone -lines canals of compact bone |
|
|
Types of bone cells
|
-osteogenic cells:bone stem cell, gives rise to osteoblasts
-osteoblasts: bone-building cells -osteoclasts: bone digesting cells (resorption) -osteocytes: mature bone cells, maintain bone matrix |
|
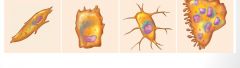
1) 2) 3) 4)
|
1)osteogenic cell
2)osteoblast 3) osteocytes 4) osteocyte |
|
|
Structure of short, irregular, and flat bones
|

|
|
|
Hematopoietic tissue (red merrow) location in adults and infants
|
-Infants: found in medullary cavity and all areas of spongy bones
-Adults: found in diploe of flat bones(hip and sternum), and head of femur and humerus |
|
|
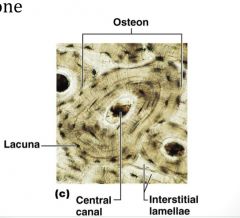
|

