![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
139 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what 2 joints are associated with elbow?
what joint is NEAR but not associated with the elbow joint? what type of joint is it? |
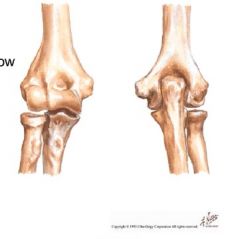
2 associated are:
humeroulnar humeroradial 1 near is: prosimal radioulnar joint type: modified hinge- relatively stable with 2 primary motions: flex/extend and aBduct |
|
what is the normal degree of valgus in the elbow joint
what causes this |
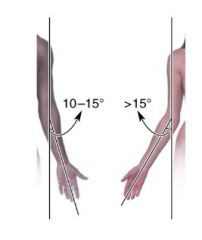
10 deg men
15 degrees women structurally caused by medial lip of the trochlea being larger than lateral lip |
|
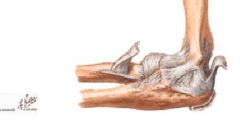
Ulnar collateral ligament is where, how many parts does it have?
|
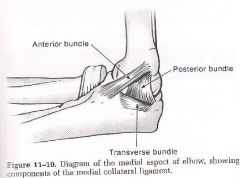
medial side
3 bundles: anterior, posterior and transverse |
|
where is the anterior bundle of the ulnar collateral ligament?
what is it responsible for? |
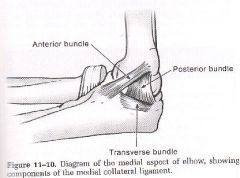
anterior and medial
goes from the medial epicondyle to the coronoid responsible for preventing valgus force and is always taut (esp in extension) is the most important and the strongest |
|
where is the posterior collateral ligament?
what is it responsible for? |
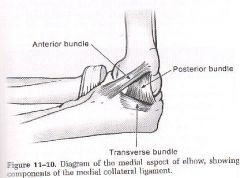
runs from medial epicondyle to olecranon, is deep to the ulnar nerve
responsible for preventing valgus force in flexion (>90degrees) |
|
where is the transverse bundle of the ulnar collateral ligament
|
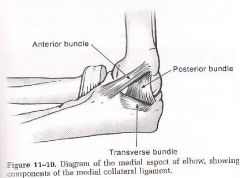
medially
runs from olecranon to coronoid (base of triangle when elbow is bent) |
|
where is the radial collateral ligament and how many parts does it have?
overall what is its function? |
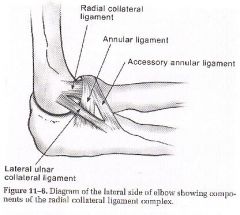
is on lateral side of elbow
has 2 parts: RCL/LUCL prevents varus stress |
|
where is the RCL (radial collateral ligament)
|
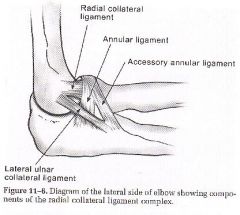
runs from lateral epicondyle to annular ligament
|
|
where is LUCL or lateral ulnar collageral ligament
what does it prevent |
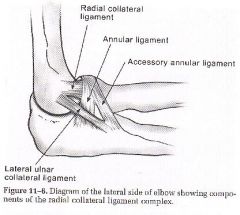
runs from lateral eipcondyle to supinator crest
prevents varus stress but specifically radial head subluxation (nursemaid's elbow) |
|
|
where is the annular (or anular) ligament?
what does it do? (she says this is reeeeealy important ligament) |
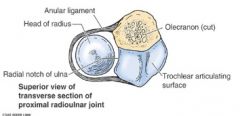
in the elbow runs from front radial notch on ulna to back radial notch of ulna
function is to allow radial head rotation and is lined with a synovial membrane |
|
where is the oblique cord? what is its function?
|
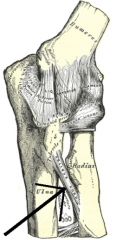
in elbow runs from lateral ulnar tuberosity to just below the tuberosity on radius
stabilizes proximal radial ulnar joint during movement and prevents downward motion of radius |
|
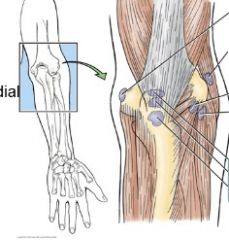
what 2 major bursas are involved in the elbow
what are their function |
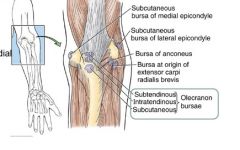
olecranon bursae (3 little guys, 2 sit deep to the tendon and 1 sits just under skin)
biceps bursa (is between biceps tendon and top part of radial tuberosity- not pictured) function- prevent friction |
|
|
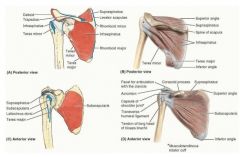
what are the 4 major ligaments that support glenohumeral joint
|
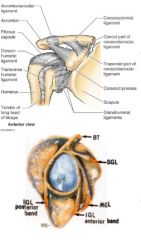
superior glenohumeral
middle glenohumeral inferior glenohumeral coracohumeral ligaments |
|
|
what are the 4 major ligaments that support glenohumeral joint
|
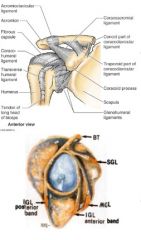
superior glenohumeral
middle glenohumeral inferior glenohumeral coracohumeral ligaments |
|
|
what are the 4 major ligaments that support glenohumeral joint
|
superior glenohumeral
middle glenohumeral inferior glenohumeral coracohumeral ligaments |
|
|
what are the 4 major ligaments that support glenohumeral joint
|
superior glenohumeral
middle glenohumeral inferior glenohumeral coracohumeral ligaments |
|
|
what are the 4 major ligaments that support glenohumeral joint
|
superior glenohumeral
middle glenohumeral inferior glenohumeral coracohumeral ligaments |
|
|
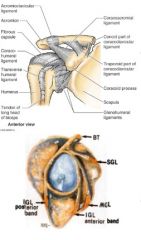
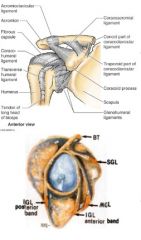
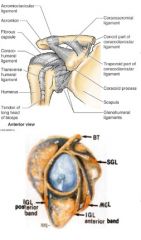
what are the 3 sections of the glenohumeral ligament and their attachments?
|
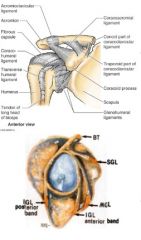
superior attached at 12-1 o'clock and runs to anatomical neck just above lesser tubercle.
middle attached at 2-3 o'clock and runs to anatomical neck just medial to lesser tubercle inferior has 2 bands anterior attached at 4-5 o'clock , posterior band is 7-9 o'clock and both run to anatomical neck just below lesser tubercle |
|
|
what is the function of the 3 sections of the glenohumeral ligament
|
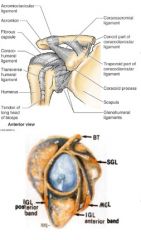
s, m, anterior inferior all prevent external rotation
superior- prevents inferior and posterior translation and aDduction middle - prevents anterior translation inferior band- limits aBduction posterior band of inferior- limits internal rotation |
|
|
where is the coracohumeral ligament and what is its function
|
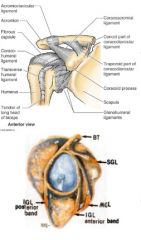
runs from coracoid process to anterior neck just above GREATER tubercle
forms almost a little cap over the top of the humerous limits external rotation, flexion, extension and prevents inferior displacement (fights gravity to keep arm in socket) |
|
|
what is the function/pull of the following muscles when the arm aBducts?
deltoid superiorspinatus inferior spinatus teres minor subscapularis |
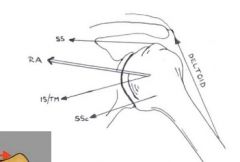
|
|
|
what are the 4 joints of the shoulder
|
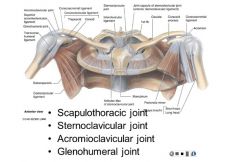
scapulothoracic
sternoclavicular acromioclavicular glenohumeral working together called scapulohumerol rhythm |
|
|
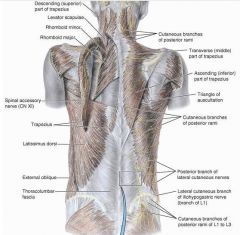
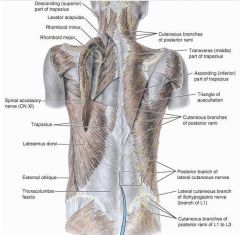
Splenis capitus
|
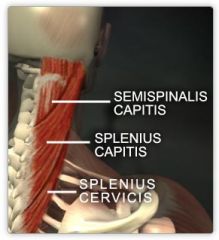
O: lower ligamentum nuchal SP T1-3
I: lateral occiput b/w superior and inferior nuchal lines A:extends and rotates the cervical spine innervation: spinal nerves C3-C4 |
|
|
splenius cervicis
|
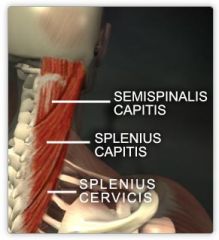
O: nuchal ligament ans spinous process of C7-T3
I: tubercles of transverse processes of C1-C3 A: laterally flex neck and rotate head to side of active muscles innervations: spinal nerves c3-c4 |
|
|
upper Trapezius
|
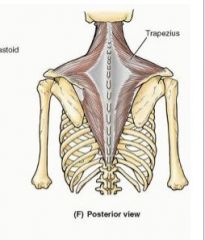
sup attachment: medial 1/3 of superior nuchal ligament, external occipital protuberance, SP:C7-T12, lumbar and sacral
inferior attachment: lateral clavicle, acromion, spine of scapula Action: elevate pectoral girdle, maintain level of shoulders against gravity or resistance innervation:cranial nerve 11 and C2 and C3 |
|
|
middle trapezius
|
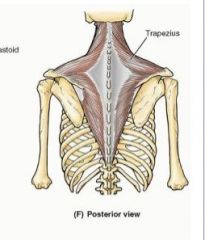
sup attachment: medial 1/3 of superior nuchal ligament, external occipital protuberance, SP:C7-T12, lumbar and sacral
inferior attachment: lateral clavicle, acromion, spine of scapula Action: retract scapula innervation: cranial nerve 11, C2, C3 |
|
|
inferior trapezius
|
sup attachment: medial 1/3 of superior nuchal ligament, external occipital protuberance, SP:C7-T12, lumbar and sacral
inferior attachment: lateral clavicle, acromion, spine of scapula Action: depress shoulders innervation: cranial nerve, C2, C3 |
|
|
together the upper and lower trapezius muscles do what?
|
rotate spinous process of scapula superiorly
bilateral contraction with fixed shoulders extends neck unilateral contraction produces lateral flexion to same side |
|
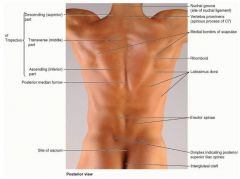
ID:
nuchal groove superior, middle, inferior trapezius rhomboid erector spinae superior iliac spine |
|
|
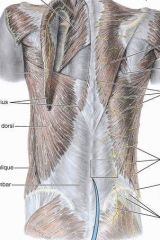
rhomboid major
|
O: SP T2-T5
I: medial border of scapula A: retract and rotate scapula innervation: dorsal scapular, C4, C5 |
|
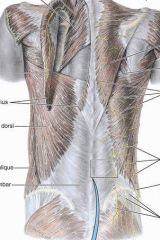
rhomboid minor
|
O: SP C7 & T1
I: medial end of scapula A: retract and rotate scapula innervation: dorsal scapular, C4, C5 |
|
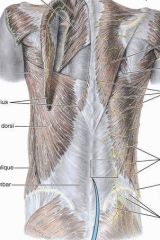
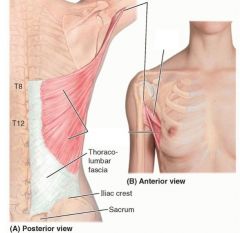
latissimus dorsi
|
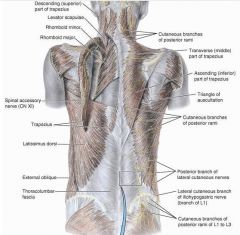
O:SP of inferior thoracic iliac crest and inferior 3 or 4 ribs
I: floor of intertubercular groove of humerous A: extension, aDduction, medial rotation innervation: thoracodorsal |
|
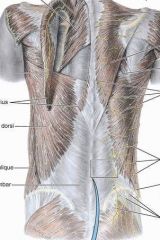
levator scapulae
|
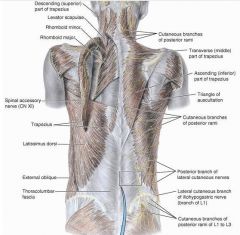
O: posterior tubercles of TP of C1-C4
I: medial border of scapula A: elevates scapula innervation: dorsal scapular C5 and cervical C3,C4 |
|
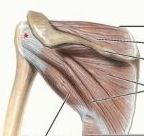
supraspinatus
|
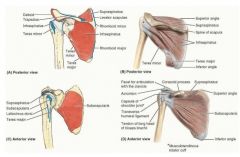
proximal: supraspinous fossa of scapula
distal: superior facet of greater tubercle of humerus A: aBduction of arm innervation: suprascapular nerve C5, C6 |
|
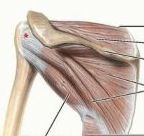
infraspinatus
|
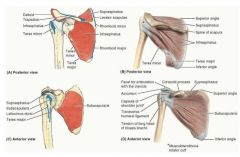
proximal: infraspinous fossa of scapula
distal: middle facet of greater tubercle of humerous a: lateral rotation of arm innervation: subscapular nerve, C5, C6 |
|
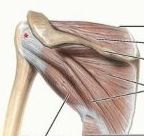
teres minor
|
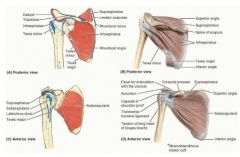
proximal: middle part of lateral border of scapula
distal: inferior facet of greater tubercle of humerus A: lateral rotation of arm innervation: axillary nerve C5 |
|
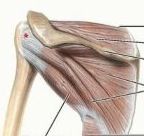
subscapularis
|
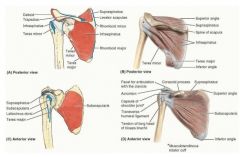
proximal: subscapular fossa of scapula
distal: lesser tubercle of humerus A: medial rotation of arm, helps hold humerus in glenoid cavity innervation: subscapular nerve (C5-C6) |
|
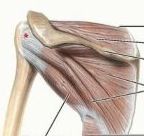
what are the muscles in the rotator cuff
|
supraspinatus
infraspinatus teres minor subscapularis |
|
|
serratus anterior
|
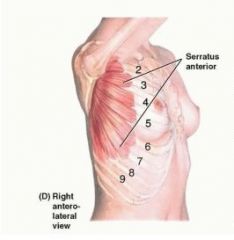
proximal: external surfaces of lateral parts of 1-8th ribs
distal: anterior surface of medial border of scapula A: protracts scapula and holds it against thoracic wall, rotates scapula innervation: long thoracic nerve |
|
|
pectoralis major
|
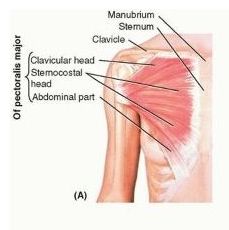
proximal:
clavicular head: anterior surface of medial half of clavicle sternocostal head: anterior surface of sternum, superior six costal cartilages, aponeurosis of ext oblique muscle distal: lateral lip of intertubercular sulcus of humerus A: aDduction and medial rotation of humerus innervation: lateral and medial pectoral nerve |
|
|
pectoralis minor
|
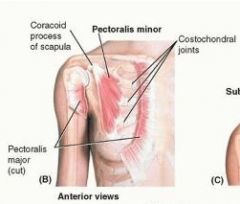
proximal: 3rd-5th ribs near costal cartilage
distal: medial border and superficial surface of teh coracoid process of the scapula A: stabilizes scapula by drawing it inferiorly and anteriorly against thoracic wall innervation: medial pectoral nerve |
|
ID
teres major latissimus dorsi |
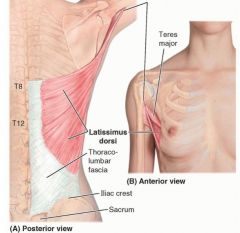
|
|
|
anterior deltoid
|
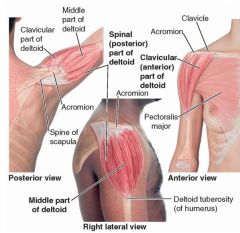
proximal: lateral third of clavicle, acromion and spine of scapula
distal: deltoid tuberosity of humerus action: flexes and medially rotates the arm innervation: axillary nerve (C5-C6) |
|
|
middle deltoid
|
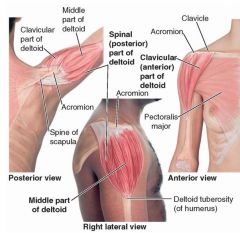
proximal: lateral third of clavicle; acromion and spine of scapula
distal: deltoid tuberosity of humerus A: aBducts arm innervation: axillary nerve (C5-C6) |
|
|
posterior deltoid
|
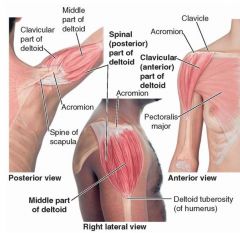
proximal: lateral 1/3 of clavicle; acromion and spine of scapula
distal: deltoid tuberosity of humerus A: extends and laterally rotates the arm innervation: axillary nerve (C5-C6) |
|
|
teres major
|
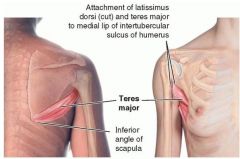
proximal: posterior surface of inferior angle of scapula
distal: medial lip of intertubercular sulcus of humerus A: aDducts and medially rotates arm innervation: subscapular nerve |
|
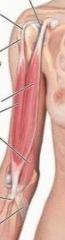
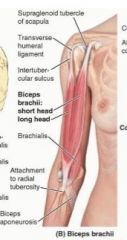
biceps brachii (short head)
|
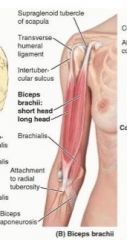
proximal: tip of coracoid process of scapula
distal: tuberosity of radius and fascia and forearm via bicipital aponeurosis A: supinates forarm and, when supine, flexes forearm also resists dislocation of shoulder innervation: musculocutaneous (c5,6,7) |
|
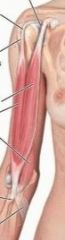
biceps brachii (long head)
|
proximal: supraglenoid tubercle of scapula
distal: tuberosity and radius and fascia of forearm via bicipital aponeurosis A: supinates forearm and, when supine, flexes forearm innervation: musculocutaneous (c5,6,7) |
|
|
coracobrachialis
|
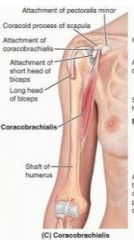
proximal: tip of coracoid process of scapula
distal: middle 1/3 of medial surface of humerus A: helps flex and adduct arm, resists dislocation of shoulder innervation: musculocutaneous (c5,6,7) |
|
|
brachialis
|
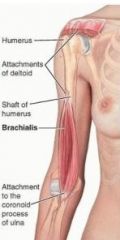
proximal: distal 1/2 of anterior surface of humerus
distal: coronoid process and tuberosity ulna A: flexes forearm in all positions innervation: musculocutaneous (C5,6) and radial nerve (C5,7) |
|
|
triceps brachii (long head)
|
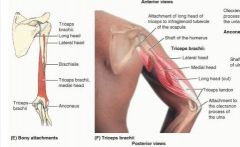
proximal: infraglenoid tubercle of scapula
distal: proximal end of olecranon of ulna and fascia of forearm A: chief extensor of forearm, resists dislocation of humerus innervation: radial nerve (C6,7,8) |
|
|
triceps brachii (medial head)
|
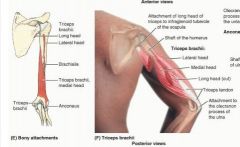
proximal: posterior surface of humerus, inferior to radial groove
distal: proximal end of olecranon of ulna and fascia of forearm A: chief extensor of forearm Innervation: radial nerve (C6,7,8) |
|
|
triceps brachii (lateral head)
|
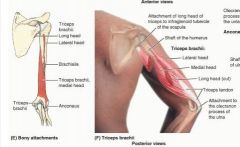
proximal: posterior surface of humerus, superior to radial groove
distal: proximal end of olecranon of ulna and fascia of forearm A: chief extensor of forearm Innervation: radial nerve (C6,7,8) |
|
|
anconeus
|
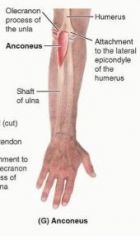
proximal: lateral epicondyle of humerus
distal: lateral surface of olecranon and superior part of posterior surface of ulna A: assists triceps in extending forearm; stabilizes elbow, may aBduct ulna during pronation innervation: radial nerve (C7,8, T1) |
|
|
brachioradialis
|
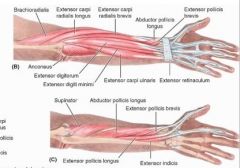
proximal: proximal 2/3 of supraepicondylar ridge of humerous
distal: lateral surface of distal end of radius proximal to styloid process A: relatively weak flexion of forearm innervation: radial nerve (C5,6,7) |
|
|
extensor carpi radialis longus
|
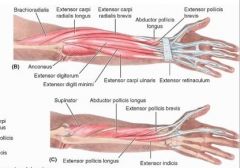
proximal: lateral supraepicondylar ridge of humerus
Distal: dorsal aspect of base of 2nd metacarpal A: extend and aBduct hand at the wrist joint; active during fist clenching innervation: radial nerve (C6,7) |
|
|
extensor carpi radialis brevis
|
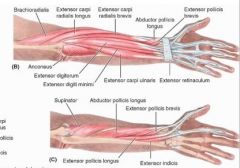
proximal: lateral epicondyle of humerus
distal: dorsal aspect of base of 3rd metacarpal A: extend and aBduct hand at the wrist joint; active during fist clenching innervation: radial nerve (c6,7) |
|
|
extensor digitorum
|
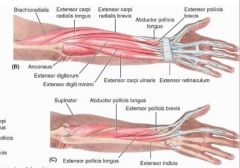
proximal: lateral epicondyle of humerus
distal: extensor expansions of medial 4 digits A: extends medial four digits primarily at metacarpophalangeal joints innervation: radial nerve (c7, c8) |
|
|
extensor digiti minimi
|
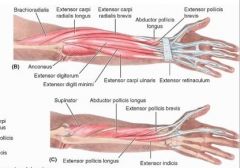
proximal: lateral epicondyle of humerus
distal: extensor expansion of 5th digit A: extends 5th digit innervation: radial nerve (C7,8) |
|
|
extensor carpi ulnaris
|
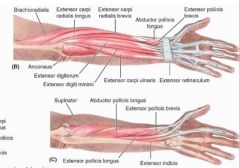
proximal: lateral epicondyle of humerus; posterior border of ulna via shared aponeurosis
distal: dorsal aspect of base of 5th metacarpal A: extends and aDducts hand at wrist joint innervation: radial nerve (C7,8) |
|
|
supinator
|
proximal: lateral epicondyle of humerus; radial collateral and anular ligaments; supinator fossa; crest of ulna
distal: lateral, posterior, and anterior surfaces of proximal 1/3 of radius A: supinates forearm; rotates radius to turn plam anteriorly or superiorly innervation: radian nerve (C7,8) |
|
|
abductor pollicis longus
|
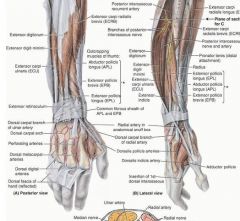
proximal: posterior surface of proximal halves of ulna, radius, and interosseous membrane
distal: base of 1st metacarpal A: aBducts thumb and extends it at carpometacarpal joint innervation: posterior interosseous nerve (C7,8) |
|
|
extensor pollicis brevis
|
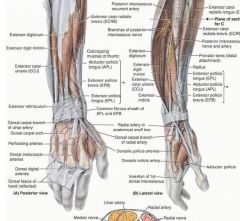
proximal: posterior surface of distal third of radius and interosseous membrane
distal: dorsal aspect of base of proximal phalanx of thumb A: extends proximal phalanx of thumb at metacarpophalangeal joint; extends carpometacarpal joint innervation: posterior interosseous nerve (C7,8) |
|
|
what are the 11 muscles of the posterior forearm
|
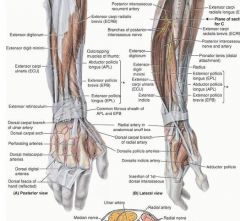
➢ Brachioradialis
➢ Extensor carpi radialis longus ➢ Extensor carpi radialis brevis ➢ Extensor digitorum ➢ Extensor digiti minimi ➢ Extensor carpi ulnaris ➢ Supinator ➢ Abductor pollicis longus ➢ Extensor pollicis longus ➢ Extensor pollicis brevis ➢ Extensor indicis |
|
|
extensor indicis
|
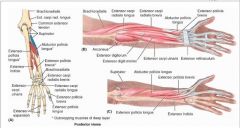
proximal: posterior surface of distal 1/3 of ulna and interosseous membrane
distal: extensior expansion of 2nd digit (pointer finger) A: extends 2nd digit innervation: posterior interosseous nerve (C7, C8) |
|
|
pronator teres (superficial and deep head)
|
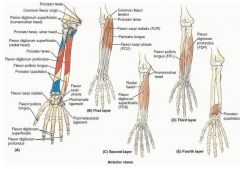
proximal: coronoid proccess
distal: middle convexity of lateral surface of radius A: pronates and flexes forearm at elbow innervation: median nerve (C6,7) |
|
|
flexor carpi radialis
|
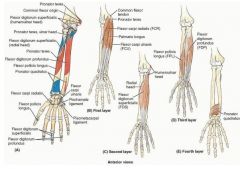
proximal: medial epicondyle of humerus
distal: base of 2nd metacarpal A: flex and aBduct hand at wrist innervation: median nerve (C6,7) |
|
|
palmaris longus
|
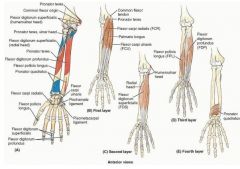
proximal: medial epicondyle of humerus
distal: distal 1/2 of flexor retinaculum and apex of palmar aponeurosis A: flexes hand at wrist and tenses palmar aponeurosis inneration: median nerve (C7,8) |
|
|
flexor carpi ulnaris
|
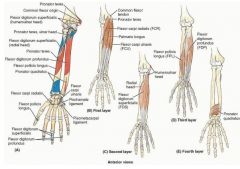
proximal: medial epicondyle of humerus and olecranon
distal:pisiform, hook of hamate, 5th metacarpal A: flexes and aDducts hand at wrist innervation: ulnar nerve (C7,8) |
|
|
flexor digitorum superficialis
|
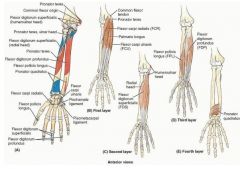
proximal: medial epicondyle of umerus and anterior border of radius
distal: shafts of middle phalanges of medial 4 digits A: flexes middle phalanges at proximal interphalangeal joints of middle 4 digits, flexes proximal phalanges at metacarpophalangeal joints innervation: median nerve (C7, C8, T1) |
|
|
flexor digitorum profundus
|
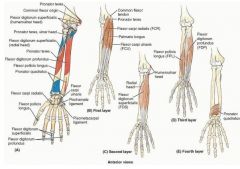
proximal: proximal 3/4 of medial and anterior surface of ulna and interosseous membrane
distal: bases of distal phalanges of fingers A: flexes distal phalanges at distal interpharangeal joints innervation: ulnar nerve (C8, T1) and median nerve (C8, T1) |
|
|
flexor pollicis longus
|
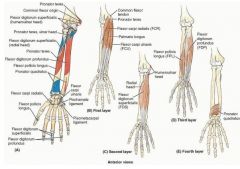
proximal: anterior surface of radius and interosseous membrane
distal: base of distal phalanx of thumb A: flexes thumb innervation: anterior interosseous nerve, from median nerve (C8, T1) |
|
|
pronator quadratus
|
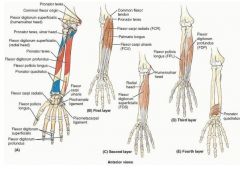
proximal: distal 1/4 of anterior surface of ulna
distal: distal 1/4 of anterior surface of radius A: pronates forearm- hold radius and ulna together innervation: anterior interosseous nerve from median nerve (C8, T1) |
|
|
what muscles are considered anterior forearm
|
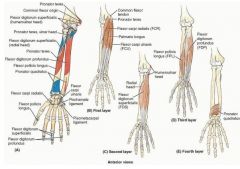
pronator teres
flexor carpi radialis palmaris longus flexor carpi ulnaris flexor digitorum superficialis flexor digitorum profundus flexor pollicis longus pronator quadratus |
|
|
abductor pollicis brevis
|
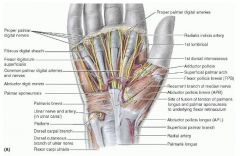
proximal: flexor retinaculum and tubercles of scaphoid and trapezium
distal: lateral side of base of proximal phanlanx of thumb A: aBducts thumb, helps oppose it innervation: median nerve (C8, T1) |
|
|
flexor pollicis brevis
|
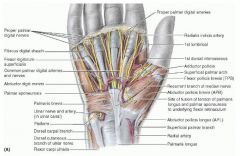
proximal: flexor retinaculum and tubercles of scaphoid and trapezium
distal: lateral side of base of proximal phalanx of thumb A: flexes thumb innervation: median nerve (C8, T1) |
|
|
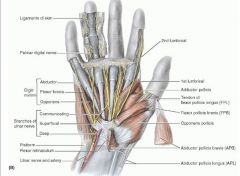
abductor digiti minimi
|
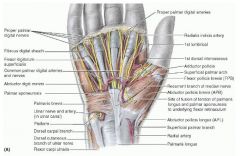
proximal: pisiform
distal: medial side of base of proximal phalanx of 5th digit A: aBduction of 5th digit, flexion of 5th digit's proximal phalanx innervation: ulnar nerve (C8, T1) |
|
|
flexor digiti minimi
|
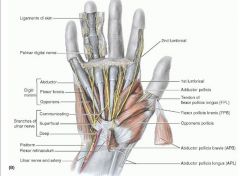
proximal: hook of hamate and flexor retinaculum
distal: ulnar side of base of proximal phalanx of pinkie A: flexes pinky innervation: ulnar nerve (C8, T1) |
|
|
opponens digiti minimi
|
proximal: hook of hamate and flexor retinaculum
distal: medial border of 5th metacarpal A:Draws 5th metacarpal anteriorly and rotates it, bringing little finger (5th digit) into opposition with thumb innervation: ulnar nerve (C8, T1) |
|
|
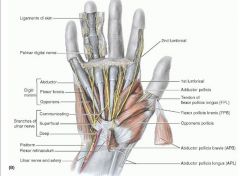
aDductor pollicis (oblique head)
|
proximal: Oblique head: bases of 2nd and 3rd metacarpals, capitate, and adjacent carpals
distal: Medial side of base of proximal phalanx of thumb A: Draws 1st metacarpal laterally to oppose thumb toward center of palm and rotates it medially innervation: ulnar nerve (C8, T1) |
|
|
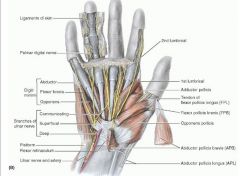
aDductor pollicis (transverse head)
|
proximal: anterior surface of body of 3rd metacarpal
distal: Medial side of base of proximal phalanx of thumb A: Draws 1st metacarpal laterally to oppose thumb toward center of palm and rotates it medially innervation: ulnar nerve (C8, T1) |
|
|
lumbricals
|
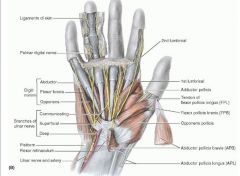
innervation 1st and 2nd: median nerve (C8 and T1)
innervation 3rd and 4th: ulnar nerve (C8, T1) A: flex metacarpophalangeal joints of fingers |
|
|
palmar interossei muscles
|
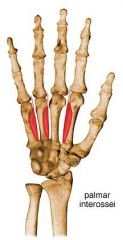
proximal: palmar surfaces of 2nd, 4th, 5th metacarpals
distal: bases of proximal phalanges; extensor expansions of 2nd, 4th, 5th digit A: aDduction of 2nd, 4th, 5th digit innervation: ulnar nerve (C8, T1) |
|
|
dorsal interossei
|
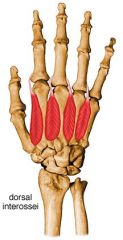
proximal: adjacent sides of 2 metacarpals
distal: bases of proximal phalanges A: aBduct 2nd - 4th digits from axial line innervation: ulnar nerve (C8, T1) |
|
|
trace the path of C5, C6, C7, C8 and T1 through the trunks, divisions, cords and nerves
|
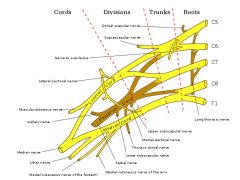
|
|
|
the superior (upper) trunk is the union of
|
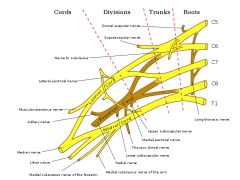
C5 and C6 roots
|
|
|
the middle trunk is
|
a continuation of C7 root
|
|
|
the inferior lower trunk is
|
a union of C8 and T1 roots
|
|
|
trace the path of the median nerve
|
travels in medial surface anterior in brachium through cubital fossa medial to biceps tendon and brachial artery, is between te two heads of pronator teres, runs deep to FDS above FDP
then gives off anterior interosseus branch and enters carpal tunnel |
|
|
what gives off anterior interosseous nerve
|
median nerve
|
|
|
trace the path of the musculocutaneous neve
|
pierces coracobrachialis and runs deep to biceps brachii but above brachialis, gives rise to lateral cutaneous nerve
|
|
|
what gives off the lateral cutaneous nerve of the forearm
|
musculocutaneous nerve
|
|
|
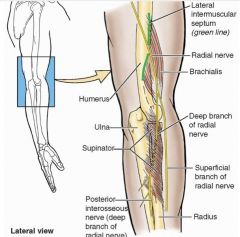
trace the path of the radial nerve
|
travels anterior to long head of triceps and passes through triangular interval to the posterior brachium, pierces lateral intermuscular septum, crosses elbow anteriorly deep to brachioradialis and dives into superficial and deep branches, deep brach continues into posteriar interosseous
|
|
|
what gives off the superficial and deep radial nerve
|
radial nerve
|
|
|
what gives off the posterior interosseous nerve
|
continuation of the deep radial nerve
|
|
|
describe the path of the ulnar nerve
|
travels down the posterior medial aspect of teh arm behind the medial epicondyle through cubital tunnel, runs through the 2 heads of FCU then with the artery goes deep to FCU, lastly it passes superficial to flexor retinaculum via ulnar canal
|
|
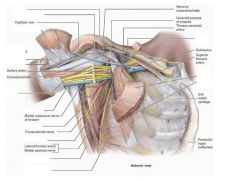
ID the following:
deltoid musculocutaneous nerve pectoralis major pectoralis minor biceps brachii long and short coracobrachialis median nerve ulnar nerve teres major subscapularis lattissimus dorsi serratus anterior long thoracic nerve |
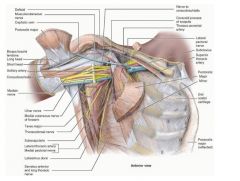
|
|
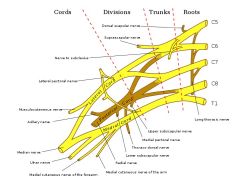
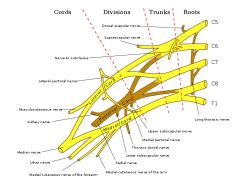
ID the following
C4 C5 C6 C7 C8 T1 long thoracic nerve suprascapular nerve lateral pectoral medial pectoral musculocutaneous axillary radial median nerve ulnar nerve medial bracheal cutaneous |
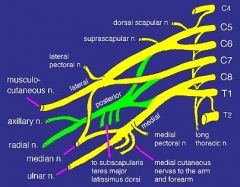
|
|
|
what nerve comes off the nerve roots
|
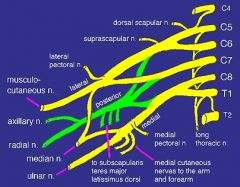
long thoracic nerve
|
|
|
what neve(s) comes off a nerve trunk
|
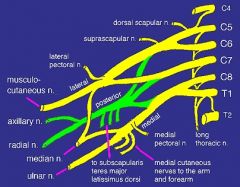
suprascapular
|
|
|
what nerve(s) com off the posterior cord (made of fibers from C5-T1)
|
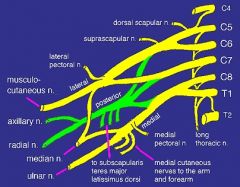
upper subscapular
lower subscapular thoracodorsal |
|
|
what nerve(s) come off the lateral cord (fibers from C5-C7)
|
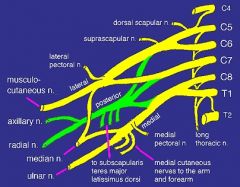
lateral pectoral nerve
|
|
|
what makes up the superior trunk
|
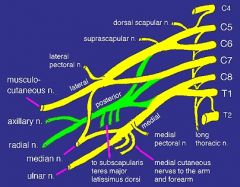
nerve roots C5, C6
|
|
|
what makes up mid trunk
|
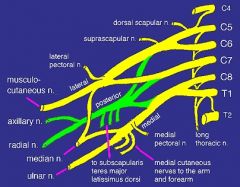
C7
|
|
|
what makes up inferior trunk
|
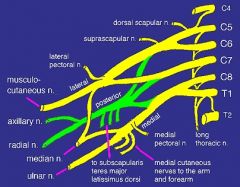
nerve roots C8, T1
|
|
|
what makes up lateral cord
|
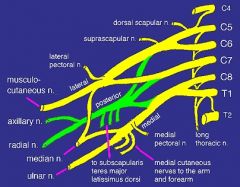
anterior division of the superior and middle trunk
|
|
|
what makes up the posterior cord
|
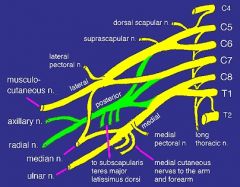
posterior divisions of the superior, middle and inferior trunk
|
|
|
what makes up medial cord
|
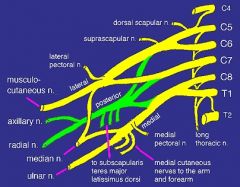
anterior division of the inferior trunk
|
|
|
the sternoclavicular joint is what type of joint?
what 3 ligaments are involved? what type of movement? |
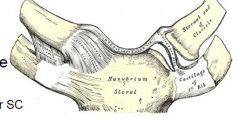
saddle joint with articular disc and fibrous capsule
3 ligaments are: anterior posterior sternoclavicular lig costoclavicular lig interclavicular lig very sturdy joint = little movment |
|
|
what bones articulate to make up the acromioclavicular joint
|
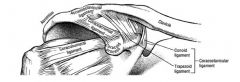
clavicle and acromion of scapula
|
|
|
what type of joint is teh acromioclavicular joint?
what major ligaments are involved and what do they do? |
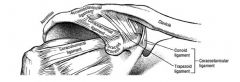
is a plane joint
acromioclavicular lig coracolavicular lig (conoid and trapezoid- these are most important ones and they make sure the clavicle doesn't move away from the scapula) |
|
|
what is the only joint holding the arm onto the body
what ligaments assist this? |
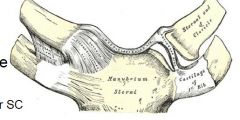
the sternoclavicular joint
the ant/post SC ligaments involved prevent 'distraction' or pulling away of the clavicle the costoclavicular ligament prevents distraction and elevation the interclavicular ligament prevents lateral distraction and depression |
|
|
what is the motion at the AC joint
|
elevation and depression, upward and downward rotation of scapula
|
|
|
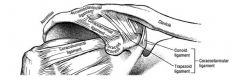
the two best ligaments to support the AC joint are?
what does the other ligament there do and what is it? |
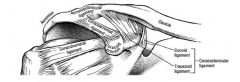
the 2 in the coracoclavicular joint
the conoid and trapezoid ligaments prevent elevation of clavicle and medial distraction of scapula don't actually cross joint itself the acromioclavicular ligament actuall goes from clavicle to acromion and prevents distraction |
|
|
what type of joint is the scapulothoracic joint
what does it allow |
it's really not- no ligaments, no bursa etc
allows for greater range of motion at shoulder, without it we couldn't move above 60 degrees |
|
|
what allows your scapula to move
|
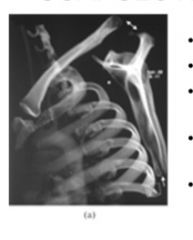
combo of movement of AC joint and SC joint
not truely the scapuulothoracic joint |
|
|
what is the glenoid labrum and its function
|
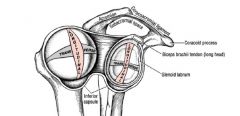
triangular shaped fibrous lip around glenoid rim
it helps provide stability to GH joint by creating a cup around the glenoid fossa, keeps the humoral head from rolling out of the fossa |
|
|
the joint capsule of GH joint is how big?
has how many openings? where's the weak point? |
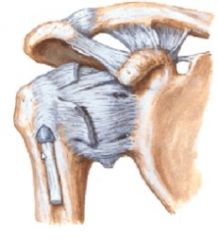
2x size of head of humerus is a very loose capsule to allow more ROM
has 2 openings- long head of biceps into capsule and subscapular bursa created by synovial membrane coming out of capsule is weak inferiorly- clinically significant b/c it's easy to have inferior dislocations |
|
|
joint capsule is super duper special according to Lday b/c....
|
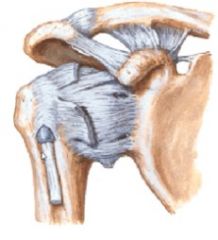
long head of bicep actually goes INTO the joint.
it reinforces the stability and helps prevent humerus from moving anteriorly |
|
|
what is the significance of teh axillary pouch of the GH joint
|
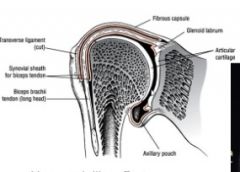
has a hammock-like effect that allows for movment of humerus when in resting position
PREVENTS inferior translation during overhead movment by cradling the head of the humerus |
|
|
what is the subacromial space and what is found there?
what clinical issue can be caused if it is too small? |
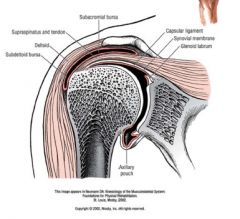
contains:
supraspinatus subacromial bursa long head bicep tendon superior joint capsule can have impingement of shoulder if it is too small with the LH of biceps tendon or the supraspinatus getting caught |
|
|
what are the 3 variations of the acromian process and what is the significance
|
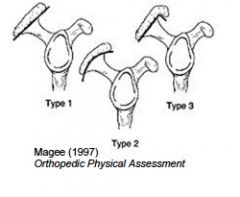
type 1: flat - least likely to have tears
type 2: curved, slightly more likely to have tears type 3: hooked, highly associated with RTC tears and also with bone spurs |
|
|
what bones articulate at the wrist?
|
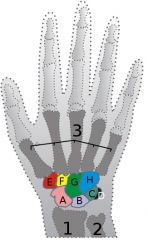
radius articulates with scaphoid, lunate and triquetrum= radiocarpal joint
these in turn articulate with trapezium, trapezoid, capitate and hamate = midcarpal joint these in turn articulate with the metacarpals = carpometacarpal joint |
|
|
which muscles cause palmar flexion at wrist
|
C8 Root Motor groups
Flexor Carpi Radialis Palmaris Longus Flexor Carpi Ulnaris Flexor Digitorum Superficialis - all Flexor Digitorum Profundus - all |
|
|
which muscles cause extension at the wrist
|
C7 Root Motor groups
Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis Extensor Carpi Ulnaris |
|
|
which muscles cause ulnar deviation at the wrist
|
Extensor Carpi Ulnaris
|
|
|
which muscles cause radial deviation at the wrist
|
Abductor Pollicis Longus
Flexor Carpi Radialis Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis |
|
|
which muscles pronate the forearm
|
C7 Root motor groups
Pronator Quadratus Pronator Teres |
|
|
which muscles supinate the forearm
|
C6 Root motor groups
Biceps Brachii Supinator |
|
|
what ligaments support the wrist
|
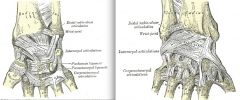
the palmar and dorsal radiocarpal ligaments, and the ulnar and radial collateral ligaments.
the pisometacarpal and palmar and dorsal carpometacarpal ligament |
|
|
what is the TFCC
|
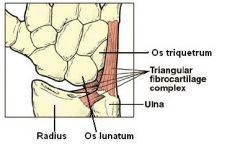
The triangular fibrocartilaginous comples is an articular discus that lies on the pole of the distal ulna.
The primary functions of the TFCC: To cover the ulna head by extending the articular surface of the distal radius Load transmission across the ulnocarpal joint and partially load absorbing Allows forearm rotation by giving a strong but flexible connection between the distal radius and ulna. It also supports the ulnar portion of the carpus |
|
|
what would happen if the ulna articulated with the triquetrum
|
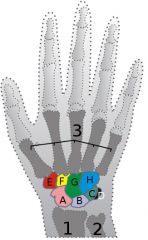
we wouldn't have as much ROM with ulnar deviation
|
|
|
what articulates at the metacarpophalngeal joint
what movement is there? |
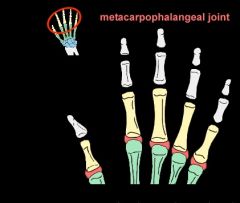
The metacarpophalangeal joint is the articulation between the convex metacarpal head proximally and the concave base of the first phalanx distally. These articulations are condyloid with the movemnts of flexion / extension and abduction / adduction.
|
|
|
what is the function of the collateral ligaments at MCP joint
|
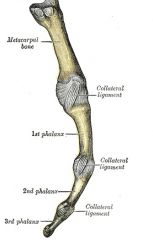
stability at the joint
collateral ligaments are taut in flexion but lax in extension |
|
|
why can you only aBduct MCP in extension but not in flexion
|
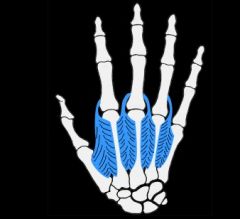
because the dorsal interossi muscle responsible for aBduction inserts on the extensior expansion which is stretched when in flexion
|
|
|
what articulates at IP joint?
what type of joint? movment? |
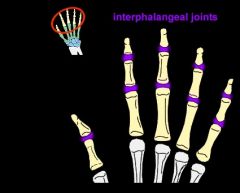
adjacent middle and distal phalanges
is a hinge joint that allows flexion and limited extension |
|
|
what is the palmar plate
|
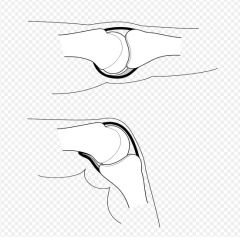
in MCP and IP joints these ligaments reinforce joint capsules
|
|
|
what is the extensor expansion
|
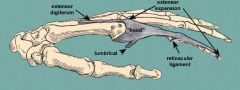
refers to the special connective attachments by which the extensor tendons insert into the phalanges.
These flattened tendons (aponeurosis) of extensor muscles span the proximal and middle phalanges. At the distal end of the metacarpal, the extensor tendon will expand to form a hood, which covers the back and sides of the head of the metacarpal and the proximal phalanx. |
|
|
what muscles insert into the extensor expansion
|
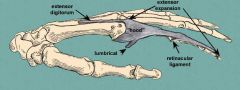
lateral bands pass on either side of the proximal phalanx and stretch all the way to the distal phalanx. The lumbricals of the hand, extensor indicis muscle, dorsal interossei of the hand, and palmar interossei insert on these bands.
|

