![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
144 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What is anatomy?
|
Examines the structures of body parts.
|
|
|
|
What is physiology?
|
Considers the functions of body parts.
|
|
|
|
The basic unit of structure and function....
|
a cell
|
|
|
|
Human life depends on what factors?
|
water, food, oxygen, heat, pressure
|
|
|
|
What is Homeostasis?
|
The body's maintenance of a stable internal environment.
|
|
|
|
Integumentary System
|
skin, hair, nails, sweat glands, sebaceous glands
|
protects tissues, regulates temperatures, supports sensory receptors
|
|
|
Skeletal System
|
bones, ligaments, cartilage
|
provides framework, protects soft tissues, provide attachments for muscles, produce blood cells, stores inorganic salts
|
|
|
Muscular System
|
muscles
|
cause movements, maintain psture, produce body heat
|
|
|
Nervous System
|
brain, spinal cord, nerves, sense organs
|
detect changes, receive and interpret sensory information, stimulate muscles and glands
|
|
|
Endocrine System
|
glands that secrete hormones
|
control metabolic activities of body structures
|
|
|
Cardiovascular System
|
heart, arteries, capillaries, veins
|
move blood through blood vessels and transport substances throughout body
|
|
|
Lymphatic System
|
lymphatic vessels, nodes, thymus, spleen
|
returns tissue fluids to the blood, carry certain absorbed food molecules, defend against infections
|
|
|
Digestive System
|
mouth, stomach, intestines, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, esophagus
|
receive, break down, and absorb food; eliminate waste
|
|
|
Respiratory System
|
nasal cavity, pharnyx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs
|
intake and output of air, exchange gases between air and blood
|
|
|
Urinary System
|
kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, urethra
|
remove waste from blood, maintian water and electrolyte balance, store and transport waste
|
|
|
Reproductive System
|
MALE: scrotum, testes, prostate gland, urethra, penis
FEMALE: ovaries, uterine tubes, uterus, vagina, clitoris, vulva |
MALE: produce and maintain sperm cells
FEMALE: produce and maintain egg cell, support development of embryo and function in child birth |
|
|
abdominal cavity
|
liver, spleen, stomach, small intestine, gllbladder
|
|
|
|
cranial cavity
|
brain
|
|
|
|
vertebral cavity
|
spinal cord
|
|
|
|
thoracic cavity
|
lungs, heart
|
|
|
|
pelvic cavity
|
internal reproductive organs, urinary bladder, urethra
|
|
|
|
These happen in what quadrant?
stomach ulcer, kidney stone in left ureter, ruptured spleen |
LUQ
|
|
|
|
This happens in what quadrant?
gallbladder attack |
RUQ
|
|
|
|
This happens in what quadrant?
appendicitis |
RLQ
|
|
|
|
This happens in what two quadrants?
bowel sounds |
RLQ, LLQ
|
|
|
|
NASAL
|
NOSE
|
|
|
|
ORAL
|
MOUTH
|
|
|
|
CERVICAL
|
NECK
|
|
|
|
ACROMIAL
|
SHOULDER
|
|
|
|
AXILLARY
|
ARMPIT
|
|
|
|
ABDOMINAL
|
ABDOMEN
|
|
|
|
ANTEBRACHIAL
|
FOREARM
|
|
|
|
BRACHIAL
|
ARM
|
|
|
|
ANTECUBITAL
|
FRONT OF ELBOW (anterior)
|
|
|
|
PELVIS
|
PELVIS
|
|
|
|
CARPAL
|
WRIST
|
|
|
|
PALMAR
|
PALM
|
|
|
|
DIGITAL
|
FINGER/TOE
|
|
|
|
PUBIC
|
GENITAL REGION
|
|
|
|
PATELLAR
|
KNEE (anterior)
|
|
|
|
CRURAL
|
LEG
|
|
|
|
PEDAL
|
FOOT
|
|
|
|
TARSAL
|
ANKLE
|
|
|
|
FRONTAL
|
FOREHEAD
|
|
|
|
ORBITAL
|
EYE
|
|
|
|
BUCCAL
|
CHEEK
|
|
|
|
MENTAL
|
CHIN
|
|
|
|
STERNAL
|
BREASTBONE
|
|
|
|
THORACIC
|
CHEST
|
|
|
|
MAMMARY
|
BREAST
|
|
|
|
UMBILICAL
|
NAVEL
|
|
|
|
COXAL
|
HIP
|
|
|
|
INGUINAL
|
GROIN
|
|
|
|
FEMORAL
|
THIGH
|
|
|
|
FIBULAR
|
SIDE OF THE LEG
|
|
|
|
CEPHALIC
|
HEAD
|
|
|
|
OTIC
|
EAR
|
|
|
|
OCCIPITAL
|
BACK OF HEAD/BASE OF SKULL
|
|
|
|
ACROMINAL
|
SHOULDER
|
|
|
|
VERTEBRAL
|
SPINAL COLUMN
|
|
|
|
SCAPULAR
|
SHOULDER BLADE
|
|
|
|
BRACHIAL
|
ARM
|
|
|
|
DORSAL
|
BACK
|
|
|
|
OLECRANAL
|
BACK OF ELBOW
|
|
|
|
LUMBAR
|
LOIN / LOWER BACK
|
|
|
|
SACRAL
|
BETWEEN HIPS
|
|
|
|
GLUTEAL
|
BUTTOCK
|
|
|
|
PERINEAL
|
REGION BETWEEN THE ANUS AND GENITALS
|
|
|
|
FEMORAL
|
THIGH
|
|
|
|
POPLITEAL
|
BACK OF KNEE
|
|
|
|
SURAL
|
CALF
|
|
|
|
PLANTAR
|
SOLE
|
|
|
|
The backbone is ______ to the belly.
(dorsal or ventral) |
dorsal
|
|
|
|
The breastbone is ______ to the heart.
(dorsal or ventral) |
ventral
|
|
|
|
The diaphram is _____ to the stomach.
(inferior or superior) |
inferior
|
|
|
|
The shoulder is _____ to the elbow.
(distal or proximal) |
proximal
|
|
|
|
The bladder is _____ to the hips.
(medial or lateral) |
medial
|
|
|
|
The ribs are _____ to the lungs.
(medial or lateral) |
lateral
|
|
|
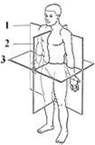
Name the Planes.....
|
1. Coronal Plane
2. Sagital Plane 3. Transverse Plane |
|
|
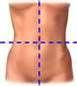
Name the Quadrants...
|
RUQ
RLQ LUQ LLQ |
|
|
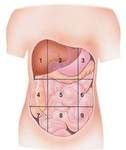
Name the Body Regions...
|
1. right hypochondriac
2. epigastric 3. left hypochondriac 4. right lumbar 5. umbilical 6. left lumbar 7. right iliac 8. hypogastric 9. left iliac |
|
|
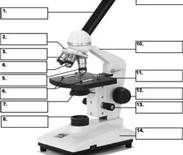
Label the Microscope
|
1. eyepiece
2. rotating nosepiece 3. scanning objective (low) 4. medium objective 5. high objective 6. stage clips 7. iris diaphram 8. projection lens 9. ocular lens 10. arm 11. stage 12. coarse adjustment 13. fine adjustment 14. base |
|
|
|
Cells with specialized characteristics are....
|
differentiated
|
|
|
|
Three major parts of a cell...
|
nucleus, cytoplasm, and the cell membrane
|
|
|
|
What is the outermost layer of a cell?
|
cell membrane
|
|
|
|
What allows the cell to receive and respond to incoming messages?
|
signal transduction
|
|
|
|
Cytoplasm also contains abundant protein rods and tubules that form supportice framework called.....
|
the cytoskeleton
|
|
|
|
The contents of a cell including the gel-like cytosol and organelles, excluding the nucleus, enclosed by the cell membrane is .....
|
cytoplasm
|
|
|
|
What is cytokinesis?
|
Division of the cytoplasm during the cell cycle.
|
|
|
|
Tiny, spherical structures composed of protein and DNA?
|
ribosomes
|
|
|
|
Complex organelle composed of membrane-bound flattened sacs, elongated canals, and fluid-filled vesicles?
|
Endoplasmic Reticulum
|
|
|
|
Endoplasmic Reticulum that lacks ribosomes?
|
smooth edoplasmic reticulum
|
|
|
|
Endoplasmic Reticulum that has ribosomes?
|
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
|
|
|
|
Membranous sacs that store and transport substances within a cell?
|
vesicles
|
|
|
|
A stack of half a dozen or so flattened, mebranous sacs called cisternae is.....which refines, packages, and delivers proteins synthesized on the rough ER.
|
Golgi apparatus
|
|
|
|
Elogated, fluid-filled sac; "power house of the cell"....
|
mitochondria
|
|
|
|
Cellular energy....
|
ATP.....or adenosine triphosphate
|
|
|
|
"garbage disposals" of the cell....
|
lysosomes
|
|
|
|
The nucleus is enclosed in a double-layered _______ which consists of an inner and an outer bilayer membrane.
|
Nuclear Envelope
|
|
|
|
Known as the "little nucleus" and is a small, dense body largely composed of RNA and protein.
|
Nucleolus
|
|
|
|
______consists of a cells 46 chromosomes.
|
Chromatin
|
|
|
|
The 3 movements of substances in and out of cells use physical (passive) transport are....
|
diffusion, osmosis, filtration
|
|
|
|
The tendency of atoms, molecules, and ions in a liquid or air solution to move from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration is called ____
|
diffusion
|
|
|
|
The movement of water across a selectively permeable membrane is ______
|
osmosis
|
|
|
|
Cells will not change size in an _________
|
isotonic solution
|
|
|
|
Cells will shrink in a _______
|
hypertonic solution
|
|
|
|
Cells will swell in a ________
|
hypotonic solution
(salt sucks) |
|
|
|
This process is used to seperate solids from water______
|
filtration
|
|
|
|
Movement against a concentration gradient that requires energy is _____
|
active transport
|
|
|
|
The series of changes a cell undergoes, from the time it forms till the time it divides, is called_______
|
cell cycle
|
|
|
|
A cell cycle is considered in three phases_____
|
interphase, mitosis, cytokinesis
|
|
|
|
____ is sometimes called cellular reproduction.
|
mitosis
|
|
|
|
4 phases of mitosis are?
|
prophase
metaphase anaphase telephase |
|
|
|
The study of tissues .....
|
histology
|
|
|
|
What are the 4 major types of tissues?
|
epithelia, connective, muscle, nervous
|
|
|
|
_______tissue is found throughout the body. It covers organs, lines the body cavities, and lines hollow organs. Has a free end and a basement membrane.
|
Epithelia
|
|
|
|
Single layer of thin, flattened cells.
|
Simple squamous
|
|
|
|
Single layer of cube-shaped cells.
|
Simple cubodial
|
|
|
|
Appear stratified or layered, but they are not.
|
Pseudostratified Columnar
|
|
|
|
Tissue that forms the inner lining of the urinary bladder.
|
Transitional
|
|
|
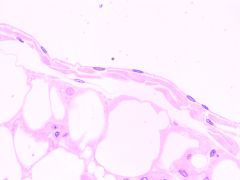
Name the tissue.
|
Simple squamous
|
|
|
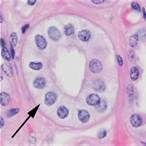
Name the tissue
|
Simple Cubodial
|
|
|
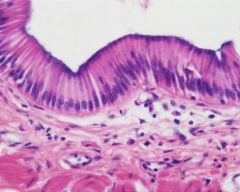
Name the tissueS
|
Simple Columnar
|
|
|
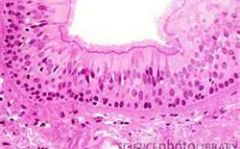
Name the tissue
|
Pseudostratified Columnar
|
|
|
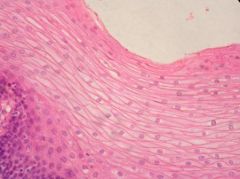
Name the tissue
|
Stratified Squamous
|
|
|
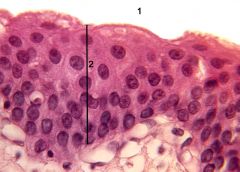
Name the tissue
|
Transitional
|
|
|
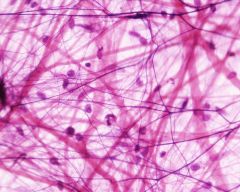
Name the connective tissue
|
Loose connective (areolar)
|
|
|
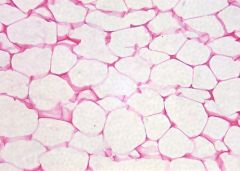
Name the connective tissue
|
Adipose
|
|
|

Name the connective tissue
|
Elastic
|
|
|
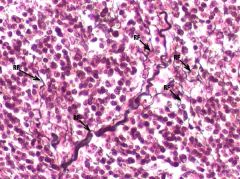
What type of tissue?
|
Reticular Connective
|
|
|

What type of tissue?
|
Dense Regular Connective
|
|
|
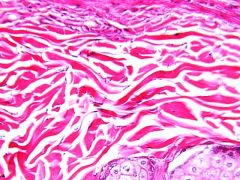
What type of tissue?
|
Dense Irregular Connective
|
|
|
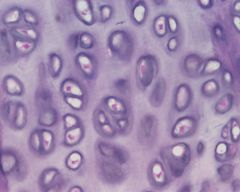
What type of tissue?
|
Hyaline Cartilage
|
|
|

What type of tissue?
|
Elastic Connective
|
|
|
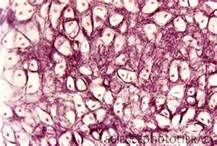
What type of tissue?
|
Elastic Cartilage
|
|
|
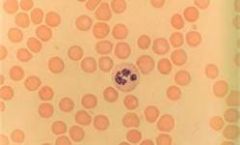
What type of tissue?
|
Blood
|
|
|
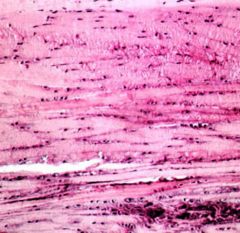
What type of tissue?
|
Fibrocartilage
|
|
|
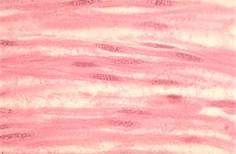
What type of muscle?
|
Smooth Muscle
|
|
|
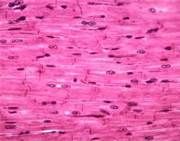
What type of muscle?
|
Cardiac muscle
|
|
|
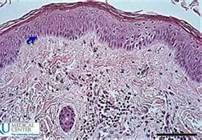
Identify the layers of skin!
|
Epidermis, Dermis, Hypodermis
|
|
|
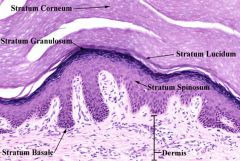
Label the 5 layers of Epidermis
|
Stratum Corneum-top layer
Stratum Lucidum-between Corneum and Granulosum (on soles and palms) Startum Granulosum-beneath Corneum Stratum Spinosum-beneath granulosum Stratum Basale-deepest layer |
|
|
|
What are the two sweat glands called?
|
Eccrine Gland and Aprocrine Gland
|
|
|
|
What is the gland that produces sebum?
|
Sebaceous Gland
|
|
|
|
What is sebum?
|
Oily substance that is excreted into the hair follicle that keeps hair pliable and somewhat waterproof.
|
|

