![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
85 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
T-cells Lymphocytes
|
|

|
Monocytes
|
|
|
B-cells Lymphocytes
|
|

|
Basophils
|
|

|
Neutrophils
|
|

|
Platelets
|
|

|
Eosinophils
|
|

|
Erythrocytes
|
|
|
insufficient oxygen is transported to the body's cells
|
anemia
|
|
|
failure of the bone marrow to produce adequate RBC
|
aplastic anemia
|
|
|
inadequate iron supply to manufacture hemoglobin
|
iron-deficiency anemia
|
|
|
inherited condition in which protein portion of hemoglobin folds incorrectly when oxygen levels are low, so oxygen is unable to properly bind with the hemoglobin
|
sickle cell anemia
|
|
|
increase in RBC
|
polycythemia
|
|
|
decrease in WBC below normal range
|
leukopenia
|
|
|
increase in WBC above normal range
|
leukocytosis
|
|
|
cancerous condition involving overproduction of abnormal WBC
|
leukemia (know 4 kinds)
|
|
|
1. distribution- O2, metabolic waste, hormones
2. regulation- body temp, pH, fluid volume 3. protection- preventing blood loss and infection |
Functions of Blood
|
|
|
non-living fluid matrix
makes up 55% blood composed of 90% water and over 100 different solutes (nutrients, gases, wastes, hormones, protein, inorganic ions, product of cell activity) |
Blood Plasma
|
|
|
living blood cells
makes up 45% blood formed in red bone marrow composed of erythrocytes, leukocytes, and platelets |
formed elements
|
|
|
Most common formed element in the blood. 4-6 million RBC/ mm3 of blood
• Formed through a process called erythropoiesis • At maturity, have no nucleus or any other cellular organelles • Biconcave shape (edges thicker than middle) |
Erythrocyte (RBC)
|
|
|
transport O2 and CO2
|
Erythrocyte Function
|
|
|
Number of erythrocytes per unit of blood
• Normal RBC count: • Males = 5.1-5.8 mill/mm3**** • Females = 4.3-5.2 mill/mm3**** • Major factor contributing to blood viscosity |
Total RBC Count
|
|
|
Spherical, nucleated cells
General Function: Defense and Immunity Able to leave the blood and enter other body tissues Come in 5 Specific Types Total WBC count: Number of leukocytes per unit of blood Normal 4800-10,800/ mm3 blood**** Differential WBC count: The percentage of the different types of leukocytes present in the blood |
Leukocytes (WBC)
|
|
|
1.Granulocytes – Leukocytes that contain granules for chemical defense
2.Agranulocytes – Leukocytes that lack cytoplasmic granules Five (6) Types: • Neutrophils • Lymphocytes – T-cells – B-cells • Monocytes • Eosinophils • Basophils |
Two Categories of Leukocytes
|
|
|
50% -‐ 70% of the Leukocytes 3000-‐7000 cells/mm3 blood
• Mul8-‐lobed nucleus (oQen tri-‐ lobed) • Granulocytes: Cytoplasmic granules stain purple-‐pink |
neutrophil
|
|
|
• 25% -‐ 45% of the Leukocytes • 1500-‐3000 cells/mm3 blood
• Agranulocytes -T-‐Cell • Round nucleus takes up most of the cytoplasm -B-‐Cell • Large bean-‐shaped nucleus |
lymphocyte
|
|
|
3% -‐ 8% of the Leukocytes 100-‐700 /mm3 blood
• Largest leukocyte with a large U or Kidney-‐shaped nucleus • Agranulocytes |
monocyte
|
|
|
2% -‐ 4% of the Leukocytes 100-‐400 / mm3 blood
• Bi-‐lobed nucleus and red granules • Granulocytes: Cytoplasmic granules stain orange-‐red |
eosinophil
|
|
|
0.5-‐ 1% of the Leukocytes 20-‐50 /mm3 blood
• Bi-‐lobed nucleus (U or S shaped) and blue cytoplasmic granules • Granulocytes |
basophil
|
|
|
150,000-‐400,000 /mm3
blood • Not true cells – formed from the breakup of large cells called Megakaryocytes • Granules stain deep purple |
Platelets (Thrombocytes)
|
|
|
percentage of whole blood made up of erythrocytes
Normal Hematocrit: • Males.......... 42-52% • Females....... 37-47% -above-polycythemia, below-anemia |
hematocrit
|
|
|
Polycythemia,
Congestive heart failure, Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), Dwelling at high altitude, |
Causes of Increased Hemoglobin
|
|
|
Anemia, Hyperthyroidism, Cirrhosis of the liver, Renal disease, Systemic lupus Erythematous Severe hemorrhage
|
causes of decreased hemoglobin
|
|
|
Male 13-18 g/100 ml blood Female 12-16 g/100 ml blood
|
normal blood hemoglobin
|
|
|
when antibodies cross the placenta blood barrier and attack the erythrocytes of the fetus
|
erythroblastosis fetalis
|
|
|
Between 100- 200 mg/deciliter of blood
|
desirable blood levels
|
|
|
Between 200- 239mg/dl of blood
|
borderline high cholesterol
|
|
|
Over 240mg/dl
Increased risk of cardiovascular disease. |
High Cholesterol = Hypercholesterolemia
|
|
|
Below 100 mg/dl
hyperthyroidism, liver disease, inadequate absorption of nutrient from the intestine. Linked to depression, anxiety. |
Low Cholesterol = Hypocholesterolemia
|
|
|
1. Myeloid (granulocytic) from myeloid cells
2. Lymphocytic from Lymphyocytes 3. Acute (quick advancing) from stem cells 4. Chronic (slow advancing) from later stage cells |
types of leukemia
|
|
|
• Function:
During an acute infection, phagocytosis of bacteria and fungi followed by enzymatic destruction |
neutrophil
|
|
|
• Function:
Attack viruses & tumors |
T-cell lymphocyte
|
|
|
• Function:
When stimulated by bacteria or toxins, they differentiate into plasma cells. These plasma cells then produce and secrete antigen-‐ specific antibodies |
B-cell lymphocyte
|
|
|
• Function:
Phagocytosis: Differentiate into macrophages in issues for phagocytosis |
monocyte
|
|
|
• Functions:
– Attack parasitic worms – Play a complex role in allergy and asthma – Lessens the severity of allergic reactions |
Eosinophil
|
|
|
• Function:
– Releases histamine and other mediators of inflammation – Contains Heparin (blood thinner) – Increases allergic reactions |
basophil
|
|
|
• Function:
– Seal small openings in blood vessels – Instrumental in blood clotting |
platelets
|
|
|
Can receive from A+, A-, O+, O-
|
A+ blood
|
|
|
Can receive from B+, B-, O+, O-
|
B+ blood
|
|
|
Can receive from A+ A- B+ B- O+ O- AB+ AB-
|
AB+ blood
|
|
|
Can receive from O+ O-
|
O+ blood
|
|
|
Can receive from A- O-
|
A- blood
|
|
|
Can receive from B- O-
|
B- blood
|
|
|
Can receive from A- B- AB- O-
|
AB- blood
|
|
|
Can receive from O-
|
O- blood
|
|
|
has A antigens and B antibodies
|
A blood
|
|
|
has B antigens and A antibodies
|
B blood
|
|
|
has A and B antigens and no antibodies
|
AB blood
|
|
|
has no antigens and A and B antibodies
|
O blood
|
|
|
bird
|
|
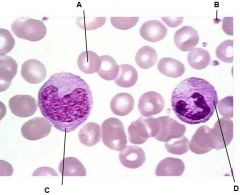
What is A?
|
Erythrocyte
|
|
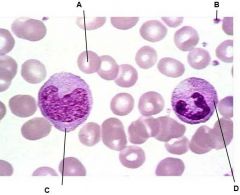
What is B?
|
Platelets
|
|
|
camel
|
|
|
cat
|
|
|
crab
|
|
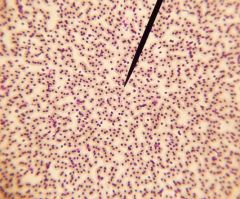
|
fish
|
|
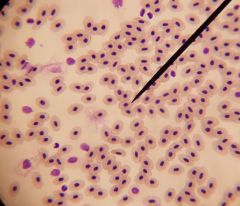
|
frog
|
|
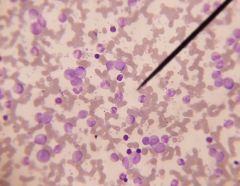
|
granulocytic leukemia
|
|
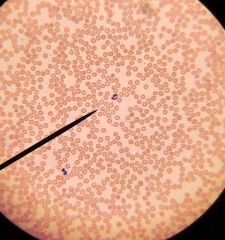
|
normal human
|
|
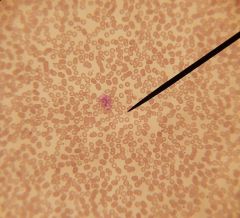
|
normal human
|
|
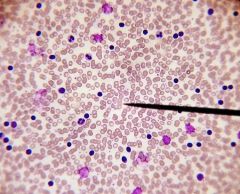
|
lymphatic leukemia
|
|
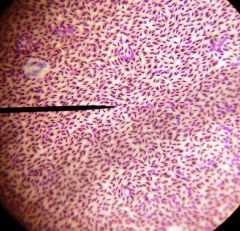
|
bird
|
|
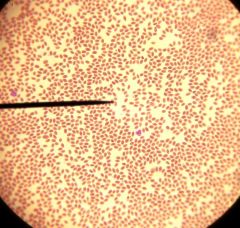
|
camel
|
|
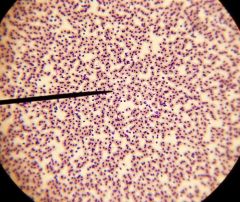
|
fish
|
|
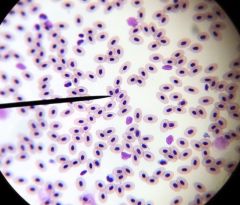
|
frog
|
|
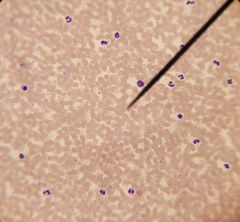
|
polycythemia
|
|
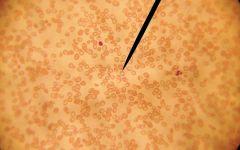
|
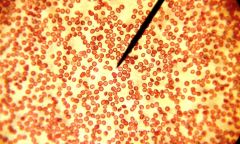
sickle cell
|
|
|
sickle cell
|
|
|
LAL found in ______ blood
|
crab
|
|
|
clumped RBC
|
rouleaux formation
|
|
|
when antibodies cross the placenta blood barrier and attack the erythrocytes of the fetus
|
erythroblastosis fetalis
|
|
|
given to mom shortly before or after birth of first Rh+ baby it will prevent mom from making antibodies
|
rhogam
|
|
|
Mom’s Antibodies will attack and lyse 2nd fetus’ blood
|
hemolysis
|
|
|
nucleated RBC found in which animals?
|
fish, bird, frog
|
|
|
no RBC found in which animal?
|
crab
|

