![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
54 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
37C to F |
98F |
|
|
|
100C |
212F |
|
|
|
Four broad categories of tissues. |
•Nervous tissue - brain, spinal cord, nerves •Muscle tissue - cardiac, smooth, skeletal •Epithelial tissue - skin surface, lining of gi tract organs, hollow organs •Connective tissue - fat, bone, tendon |
|
|
|
Three types of mucle tissue |
•Cardiac •Smooth •Skeletal |
|
|
|
Type of muscle in hollow organs and blood vessels |
Smooth muscle |
|
|
|
Six different types of connective tissue |
•Adipose (fat) •Blood •Hyaline Cartilage •Bone •Dense Connective tissue •Areolar connective tissue |
|
|
|
Epithelial tissue is avascular |
Blood doesn't go through the wall but under it instead. |
|
|
|
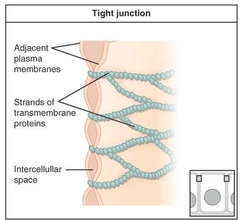
Tight Junction |
|
|
|
|
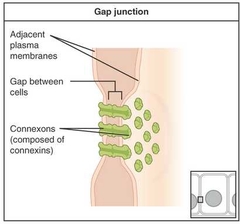
Gap Junction |
|
|
|
|
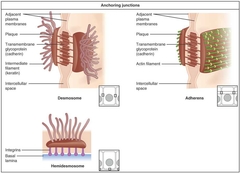
Anchoring Junction |
|
|
|
|
Simple Squamous Epithelium |

|
|
|
|
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium |

Asorbtion and secretion of molecules. |
|
|
|
Simple Columnar Epithelium |

The structure is to provide a barrier against non specific movement of lumenal substances. |
|
|
|
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium |

|
|
|
|
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium |

|
|
|
|
Stratified Columnar Epithelium |

|
|
|
|
Transitional Epithelium |

|
|
|
|
Squamous |
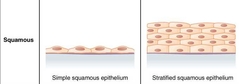
|
|
|
|
Cuboidal |
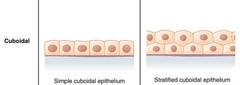
|
|
|
|
Columnar |
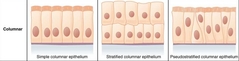
|
|
|
|
Apical |
The part of the cell or tissue which faces an open space. |
|
|
|
Basal Lamina |
Thin extracellular layer that lies underneath epithelial cells and seperates them from other tissues. |
|
|
|
Basement Membrane |
Im epithelial tissue, a thin layer of fibrous material that anchors the epithelial tissue to the underlying connective tissue; made up of the balas lamina and reticular lamina. |
|
|
|
Lumen |
Free space. |
|
|
|
Stratified Squamous Epithelium |

Protects against pysical and chemical wear and tear by having multiple stacks. |
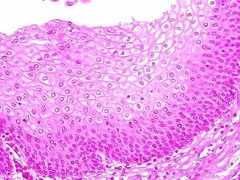
|
|
|
Differnce of cilia and microvilla |
•Cilia are longer •Cilia are motile •Cilia are used to move cell bodies and microvilla are used to in the absorbtion process |
|
|
|
Adipose |
Function: insulation, energy storage, padding. |
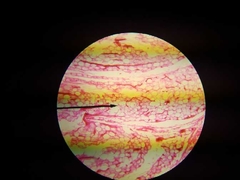
|
|
|
Blood |
Plateletes - clog broken blood vessels. RBC - transport of oxygen. WBC - Immune system. |
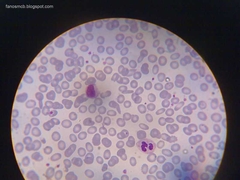
|
|
|
Hyaline Cartilage |
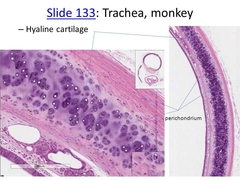
•Most common type of cartilage. •Provides compression cushion •Provides a flexable sternocostal articulations where the ribs attach to the sternum. •Provides structural support for c-shaped rings of the trachea. •Fetal skeleton starts as this which later ossifies turing into bone. |
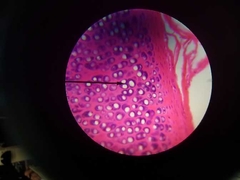
|
|
|
Bone |
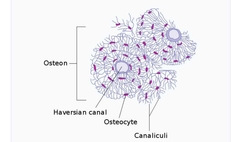
•Osteocyte (lacunae) •Lamellae - tree rings •Periosteum - the membrane that covers the outer surface of all bones except at the joints of long bones. •Endosteum - a thin vascular membrane of connective tissue that lines the inner surface of bony tissue. •Nutrient Foramina - the external opening for the enterance of blood vessels in a bone. •Perforating (sharpey's) fiber - a matrix of connective tissue that connects the periosteum to bone. |
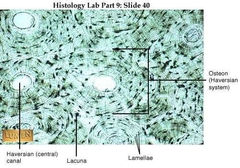
|
|
|
Dense Connective Tissue |
•Regular and irregular have have densely packed collagen protein fibers for strength. •dense regular connective tissue - majority of the protein fibers running in the same direction. Found in tendons where the stress is in a straight line between two points. •Dense irregular connective tissue - protein fibers oriented in different directions. Found in ligaments and aponeuroses where the stress can come from many different directions. |
|
|
|
Areolar Connective Tissue |
•This tissue is loose and stretchy. •Fewer collagen fibers and more elastic protein fibers than dense con t. •Found between organs, cushioning and holding them in place. •Flexible and anchors epithelium to deeper tissues. |
|
|
|
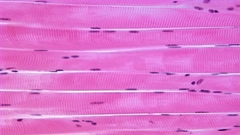
Skeletal Muscle |
•Identified by very large, and long, cells with regular traverse striations when viewed in a longitudinal section. •You will not see the striations where the muscle cells have been cut transversely. |
|
|
|
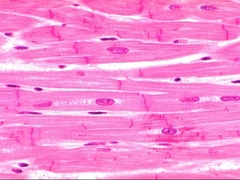
Cardiac Muscle |
•This tissue is also striated like skeletal muscle but cardiac cells are shorter, branching and are connected to each other by intercalated disks which appear as a dark line or band between cells. The intercalated disks contain gap junctions. |
|
|
|
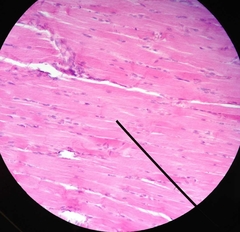
Smooth Muscle |
Look for it in the stomach, veins, arteries, and intestines. Hollow organs. |
|
|
|
Nerve Tissue |
•A nueron is a nerve cell. A nerve is a collection of many indivdual axons bundled together in a common sheath. •In veins and arteries, there are nerve fiber bundles. |

|
|
|
Atery, Vein, Nerve |
•Artery - thicker wall and abumdant smooth muscle. •Vein - thinner wall and usually collapsed. Less smooth muscle. •Nerve - Cut transversely. |
|
|
|
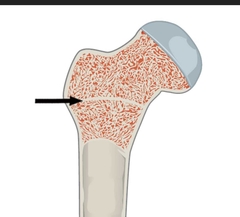
Epiphyseal line |
•a plate of hyaline cartilage found in children and adolescents, located in the metaphysis at the ends of each long bone. •The site of new bone growth. |
|
|
|
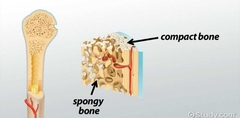
Compact and Cancellous (spongy) Bone |
|
|
|
|
Stratrum Basale |
the deepest layer of the five layers of the epidermis, the outer covering of skin in mammals. |
|
|
|
Papillary layer |
•The squiggly lines between the derimis and epidermis. •the uppermost layer of the dermis. It intertwines with the rete ridges of the epidermis and is composed of fine and loosely arranged collagen fibers. |
|
|
|
Arrector Pili Muscle |
small muscles attached to hair follicles in mammals. Contraction of these muscles causes the hairs to stand on end, known colloquially as goose bumps. |

|
|
|
Hair Root and Shaft |

|
|
|
|
Sebaceous (oil) Gland |
•Empties into hair follicle. •Lubricates the skin and hair. |

|
|
|
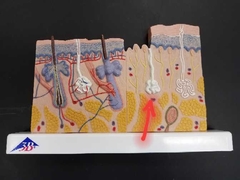
Suboriferous Glands (most common iseccrine sweat gland) |
•Duct empties to skinn •Homeostasis. |
|
|
|
Meissner/tactile corpuscles |
•in the dermal papillae. •Sensitive to touch. |

|
|
|
Merkel Cells/tactile disks |
•Hooked to cells in the epidermil. •Sensitive to light touch. •Merkel Cell is attached to the tactile disk. |
|
|
|
Pacinian/Lamellar Corpuscles |
•In the dermal/hypodermal boundry and sensitive to pressure. |
|
|
|
Free nerve endings |
Very sensitive to pain and light touch. |
|
|
|
Melanocyte |
Cell found in the stratum basale of the epidermis that produces melanin. |
|
|
|
Langerhans (dendritic) Cell |
Specialized dendritic cell found in the stratum spinosum that functions as a macrophage. In skin infections, the local langerhan cells take up the process microbial antigens. |
|
|
|
Stratum Spinosum |
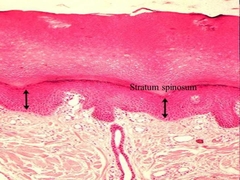
|
|
|
|
Basal Cell Carcinoma |
•Most common skin cancer. •Begins in the basal cells. |
|
|
|
Melanoma |
•Most dangerous. •Comes from melancytes. |
|

