![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
218 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Gonads |
The primary sex organs: ovaries or testes |
|
|
Secondary Sex Organs |
Male: ducts, glands and penis (deliver sperm) Female: uterine tubes, uterus and vagina (receive sperm and nourish fetus) |
|
|
Secondary sex characteristics |
Pubic, armpit and facial hair, scent glands, body morphology and low voices in males |
|
|
Mesonephric (Wolffian) Ducts |
Develop into male reproductive system Paramesonephric ducts degenerate |
|
|
Paramesonephric (Mullerian) Ducts |
Develop into female reproductive tract Mesonephric ducts degenerate |
|
|
SRY |
Sex-determining Region of Y gene Grows testes and secretes testosterone Degenerates mullerian ducts Without SRY, a female develops |
|
|
Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome |
Genetically male (XY) Testosterone is secreted, but no receptors for it. No masculinizing effects occur |
|
|
Somatic Cells |
Diploid cells. 46 chromosomes. 23 pairs. Also known as autosomes. |
|
|
Sex Chromosomes |
Also known as Gametes. One pair of 23 chromosomes. Either X or Y. Produced by Meiosis. |
|
|
Prophase I of Meiosis I |
DNA membrane dissolves and spindles emerge |
|
|
Metaphase I of Meiosis I |
Homologous chromosomes line up along the center and crossing over occurs. Microtubules attach |
|
|
Anaphase I of Meiosis I |
Each pair of homologous chromosomes are divided as they are pulled to opposite sides of the cell |
|
|
Telophase of Meiosis I |
The cell divides resulting in 2 Haploid cells |
|
|
Purpose of Meiosis I |
One diploid cell becomes two haploid cells |
|
|
Tetrad |
Two homologous chromosomes are attached at a centromere, each with two sister chromatids totaling 4. |
|
|
Purpose of Meiosis II |
To create 4 unique haploid daughter cells (gametes) from 2 haploid cells. Each gamete contains one sister chromatid instead of a whole chromosome |
|
|
What is the vertical division of the scrotum called? |
The median septum made up of the tunica albuginea |
|
|
What is contained in the spermatic cord? |
The ductus deferens, testicular artery and vein (Pampiniform plexus), autonomic nerves, lymphatics and the cremaster muscle |
|
|
Pampiniform plexus |
Veins ascending near the testicular artery allow heat exchange to flow away from the testicles |
|
|
Cremaster muscle |
An extension of the internal obliques that pull testes up as a protective reflex and to regulate temperature |
|
|
Dartos muscle |
Smooth muscle that wrinkles the skin decreasing the surface area of the scrotum to minimize heat loss |
|
|
Tunica Vaginalis |
The pushed out parietal peritoneum. Called serosa in adults. Creates a lubricating fluid to protect against friction |
|
|
Cryptorchidism |
One or both testes do not descend into the scrotum. Results in sterility and increased risk of cancer. Most descend spontaneously. |
|
|
Torsion |
Twisting of the testes or ovaries which cuts off blood supply |
|
|
Seminiferous Tubules |
Contain sperm in all their stages of development |
|
|
Leydig Cells |
Surround the seminiferous tubules and secrete testosterone |
|
|
Sertoli Cells |
Also known as Sustentacular cells. Form BTB. Control or inhibit sperm production through the production of FSH and Inhibin. Produce fluid and release sperm into lumen. |
|
|
Type A daughter cells in Spermatogenesis |
Are a product of Mitosis. Identical daughter cells. One (A) stays behind to replace parent |
|
|
Type B daughter cells in spermatogenesis |
One daughter spermatogonium (B) crosses BTB to become a Primary spermatocyte that will undergo Meiosis and become a Secondary Spermatocyte. |
|
|
Spermiogenesis |
Spermatid discards cytoplasm and sprouts a flagelate tail. |
|
|
Spermiation |
Release of a sperm cell from a Sertoli cell |
|
|
Reduction Phase |
Going from 2n to n |
|
|
When does the centriole become the basal body? |
When the flagella is produced |
|
|
What is contained within the acrosome? |
Hyaluronidase and Protease enzymes for penetrating the egg cell |
|
|
What is the purpose of the midpiece of the sperm? |
It contains Mitochondria that produce ATP for flagellar movement |
|
|
What chemical is responsible for the start of puberty? |
A surge of pituitary gonadotropins |
|
|
When does puberty officially end? |
The first menstrual period in girls and the first ejaculation of viable sperm in boys |
|
|
When does adolescence officially end? |
When a person attains full adult height |
|
|
Precocious Puberty |
Early onset puberty |
|
|
What is GnRH and where is it released? |
Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone from the Hypothalamus |
|
|
What effect does LH have in males? |
Stimulates Leydig cells to produce Testosterone |
|
|
What effect does FSH have in males? |
Stimulates Sertoli cells to secrete androgen-binding protein to stimulate spermatogenesis when it interacts with testosterone |
|
|
How is Testosterone levels maintained? |
A negative feedback loop based in the hypothalamus which measures the level in the blood supply. |
|
|
What effect does Inhibin have in males |
Slows sperm production by stimulating the anterior pituitary gland to release less FSH and LH |
|
|
Efferent ductules |
transport sperm from rete testes to epididymus |
|
|
Epididymus |
Site of sperm maturation and storage (1-2 months) |
|
|
Ductus Deferens |
Passes from scrotum to seminal vesicle. Undergoes peristalsis during orgams |
|
|
Ejaculatory Duct |
Ductus deferens + Seminal vesicle Passes through the prostate into urethra |
|
|
Histology of Epididymus |
Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium Smooth muscle |
|
|
Histology of Ductus Deferens |
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium Thick smooth muscle |
|
|
Direct vs Indirect Inguinal Hernia |
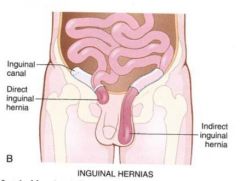
Direct breaks through the side of the inguinal canal and goes out the superficial ring Indirect goes in the deep ring and out the superficial ring |
|
|
What does the membranous urethra pass through? |
The urogenital diaphragm |
|
|
Seminal Vesicles |
Produce an alkaline viscous fluid to neutralize vaginal acid and male urethral fluid. Fluid includes: Fructose (ATP) Prostaglandins (Stimulate peristalsis in uterus) Fibrin (coagulate semen) |
|
|
Prostate Gland |
Produces alkaline fluid that increases sperm motility and viability. Includes: Citric Acid for ATP Enzymes for decoagulation |
|
|
Bulbourethral (Cowper's) Gland |
Secretes alkaline pre-ejaculate during arousal. Lubricates urethra. |
|
|
What's in Semen? |
A mixture of sperm, seminal fluid (60%), prostatic fluid (10%), fructose, fibrinogen, fibrinolysis (liquefies), prostaglandins and spermine |
|
|
Spermine |
Stabilizes sperm pH |
|
|
Crura |
Attaches penis to hip bones and flexes during orgasm |
|
|
What is the main erectile tissue? |
The corpus cavernosa paired muscles |
|
|
Muscle at the base of the penis |
Ischiocavernosus bulbospongiosus |
|
|
Definition of excitement |
Vasocongestion of genitals Myotonia - involuntary flexing of skeletal muscles Increased HR, BP and respiration |
|
|
What nervous system response causes erection? |
Parasympathetic response secretes Nitric Oxide which vasodilates and relaxes Trabecular muscles. |
|
|
What nervous system response causes ejaculation? |
Sympathetic response expels sperm by stimulating contractions |
|
|
Detumescence |
When the penis becomes flaccid after ejaculation from sympathetic restriction of pudendal arteries |
|
|
What are some physical factors that could cause erectile dysfunction? |
Diabetes, vascular or neurological disturbances, drugs (alcohol, stimulants, nicotine, antidepressants, etc.) |
|
|
How does viagra work? |
Increases the effects of nitric oxide by causing the vasodilation of penile arteries |
|
|
What makes up the vulva |
The vagina and external genitalia |
|
|
4 Layers of the ovaries |
Germinal epithelium Tunica albuginea Cortex - follicle growth Medulla - blood vessels, connective tissue and lymphatics |
|
|
4 Reproductive Ligaments and purposes |
Broad - Attaches uterus to sides of pelvic wall Round - Attaches uterus to inguinal canal Ovarian - Attaches ovaries to uterus Suspensory - Attaches uterus to the lumbar wall |
|
|
Corona Radiata |
Granulosa cells that directly touch the egg and the zona pellucida |
|
|
Zona Pellucida |
Clear area between oocyte and granulosa cells |
|
|
Atresia |
The degeneration of the majority of oogonia |
|
|
Histology of Uterine Tubes (3 Layers) |
Mucosa - ciliated columnar epithelium with secretory cells Muscularis - Circular and longitudinal (2) undergo peristalsis Serosa - outer membrane |
|
|
Histology of cervix |
Stratified squamous (same as vagina) |
|
|
Anteflexion |
The uterus normally projects forward and over the bladder |
|
|
Retroflexion |
Uterus tilts slightly less forward |
|
|
Histology of the Uterus (3 layers) |
Endometrium (inner) - simple columnar. Stratum functionalis and stratum basalis Myometrium - 3 layers of smooth muscle Perimetrium (outer) - Visceral peritoneum |
|
|
Progression of uterine arteries |
Uterine - Arcuate - Radial - Straight - Spiral ONLY straight and spiral reach the endometrium ONLY spiral respond to progesterone |
|
|
Hormones involved in the first half of your period |
Estrogen and FSH |
|
|
Radical Hysterectomy |
Removes uterus, tubes, ovaries, part of the vagina, pelvic lymph nodes and supporting ligaments |
|
|
Complete Hysterectomy |
Removes the uterus and cervix |
|
|
Functional Cyst |
Grows each month and disappears with your cycle |
|
|
Histology of Vagina (3 layers) |
Mucosal Layer (inner) - stratified squamous. Glycogen breakdown to produce acidity Muscularis - Thin smooth muscle Adventitia - Loose connective tissue that attaches vagina to other organs |
|
|
Pudendum (vulva) |
Is the external genitalia including: Mons pubis Labia (majora and minora) Clitoris Bulb of vestibule (erectile tissue) |
|
|
Cooper's (suspensory) Ligaments |
Attach breast to skin and muscle. |
|
|
Fibrocystitis |
Cysts and thickening of alveoli. Most common cause of breast lumps. Caused by lack of progesterone or too much estrogen |
|
|
Which hormones does the anterior pituitary produce? |
FSH and LH |
|
|
Tanner Stages (3) |
The development of secondary sex organs Thelarche - Breasts Pubarche - Growth of pubic and armpit hair, apocrine and sebaceous glands Menarche - First menstrual period |
|
|
Hormones secreted by the Corpus Luteum |
Progesterone - prepares uterus and mammary glands Relaxin - Facilitates implantation in the relaxed uterus Inhibin - stops release of FSH |
|
|
Follicular (Proliferative) Phase |
First two weeks of cycle. AKA Menstrual Phase. Period occurs and endometrium is lost and replaced. Follicles grow. |
|
|
Luteal (Secretory) Phase |
Second two weeks of cycle. Corpus Luteum increases estrogen and progesterone which thicken endometrium which is lost again if pregnancy does not occur |
|
|
What causes the stratum functionalis to die off? |
Declining levels of progesterone cause constriction of spiral arteries in the endometrium leading to tissue death |
|
|
Follicular Phase in Ovary |
FSH stimulates the maturation of multiple follicles and ends with ovulation |
|
|
Proliferative Phase in Uterus |
Occurs concurrently with Follicular phase in ovaries. Endometrium thickens from increased estrogen |
|
|
Postovulatory Phase - Uterus and Ovaries |
Last 14 days. In the Ovaries (Luteal) - Formation of corpus albicans and increase in LH and FSH With fertilization - Embryo secretes hCG to maintain corpus luteum In the Uterus (Proliferative) - Menstrual cycle With fertilization - Thickening of endometrium and formation of glands and vascularization |
|
|
Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder (PDD) |
More severe form of PMS dominated by mood symptoms |
|
|
Estrogen's effect on GnRH, FSH and LH |
High: Promotes Medium: Inhibits Low: Promotes |
|
|
Causes of Dysmenorrhea |
Uterine tumors, ovarian cysts, endometriosis, or IUD |
|
|
Orgasmic Platform |
Outer 1/3 of vagina |
|
|
Hormones in oral contraception |
Estrogen and Progesterone |
|
|
Norplant Hormones |
Progestin |
|
|
Depo-Provera Shot Hormones |
Progesterone |
|
|
Vaginal ring |
Combination of Progestin and estrogen |
|
|
Physiological methods of birth control |
Rhythm method - Periodic abstinence near ovulation Sympto-thermal - abstinence during ovulation signs Coitus interruptus - Withdrawal |
|
|
Dilation and Curettage (D&C) |
Suction, saline infusion, scraping to kill embryo |
|
|
RU 486 |
Also called Plan B or the morning after pill. Antiprogestin causes immediate menstruation |
|
|
Most common cause of female infertility |
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). Other causes include ovarian disease, tubal obstruction, inadequate or excessive body fat. |
|
|
In Vitro Fertilization |
Oocytes (from mother) removed and implanted with sperm, then replaced in uterus (of mother) |
|
|
Embryo transfer |
Artificial insemination of DONATED oocyte and then implanted in infertile mother |
|
|
Gamete Intrafallopian Transfer (GIFT) |
Sperm is implanted in fallopian tubes. Fertilization occurs in vivo. |
|
|
Respiratory changes during pregnancy |
Increase in tidal volume Decrease in expiratory reserve Increase in minute respiratory volume |
|
|
HELLP Syndrome |
Hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, low platelets |
|
|
Eclampsia |
Preeclampsia + proteinuria + seizures |
|
|
Pregnancy Induced Hypertension (PIH) |
High BP Preeclampsia if proteinuria |
|
|
Blastocyst Phase |
1-2 weeks |
|
|
Embryo Phase |
3-8 weeks |
|
|
Fetus Phase |
9-38 weeks |
|
|
Human Chorionic Somatomammotropin (HCS) |
Human placental lactogen. Secreted from placenta. Decreases mother's glucose usage and increase release of fatty acids |
|
|
Progesterone in pregnancy |
Secreted from the placenta and corpus luteum. Prevents FSH and LH from stimulating follicular development. Stops menstruation. Thickens endometrium. Develops acini in breasts |
|
|
Hyperemesis Gravida (HG) |
Morning sickness during first few months |
|
|
Nutrients needed by the fetus |
Protein, iron, calcium, vitamin K (hemorrhage), Folic acid (neural tube defects) and phosphates |
|
|
Chloasma |
Mask of pregnancy. Blotchy darkening over the nose and cheeks |
|
|
Braxton Hicks |
AKA false labor. Weak contractions that occur throughout gestation. |
|
|
Hormonal changes near full term |
Posterior pituitary gland releases more oxytocin and uterus produces more receptors. (stimulates contractions). Fetus produces cortisol which enhances estrogen and prostaglandin secretion which both stimulate oxytocin (dilate cervix) |
|
|
What is the difference between true and false labor? |
Both have uterine contractions, but true labor's are at regular intervals and includes cervical dilation due to the presence of prostaglandins |
|
|
Positive feedback loop of labor |
Cervical stretch - oxytocin - uterine contraction - cervical stretch |
|
|
What is the source of labor pains? |
Myometrial ischemia and cervical stretching |
|
|
Early Dilation Stage |
Widening of cervical canal by thinning of the cervix, rupture of fetal membranes and loss of amniotic fluid |
|
|
Late Dilation Stage |
Fully dilated, time to push |
|
|
Expulsion Stage |
Time from when baby's head enters vagina until fetus is expelled |
|
|
Placental Stage of Birth |
Contractions continue until the placenta is expelled |
|
|
Dystocia |
Difficult labor due to fetal position or size |
|
|
Puerperium |
First six weeks after delivery |
|
|
Involution |
Pertaining to the shrinkage of the uterus after parturition Autolysis by lysosomal enzymes produces lochia Promoted by breast-feeding |
|
|
Lochia |
Vaginal discharge after parturition |
|
|
Hormones involved in lactation |
Estrogen - Stimulates duct growth Progesterone - Stimulates acini growth HPL and Prolactin - Stimulate milk production Oxytocin - Stimulates milk ejection |
|
|
Colostrum |
Breast milk containing 1/3 less fat, thinner and contains IgA antibiotics |
|
|
Nursing effect on ovulation |
Inhibits GnRH to reduce ovarian cycling |
|
|
What hormone spikes during breast-feeding? |
Prolactin |
|
|
What physiological effect causes milk ejection? |
The contraction of myoepithelial cells surrounding lactiferous gland acinus |
|
|
Benefits of breastfeeding |
WBC - breakdown bacteria in gut, macrophages produce lysosomes, antibodies Decreased incidence of disease later in life Bonding time Child drinks what they need |
|
|
Cystocele |
Prolapsed bladder moves into vagina |
|
|
Rectovaginal Fistula |
A fusion and passageway created between the vagina and rectum |
|
|
Chlamydia |
Bacteria caused. Asymptomatic. Causes infertility from scarring (PID) |
|
|
Gonorrhea |
Bacteria caused. Discharge. Blind newborn if infected. Second most common cause of PID |
|
|
Syphilis |
Bacteria caused. Painless sores (chancres). Affects all organs eventually including the brain (neurosyphilis) |
|
|
Genital Herpes |
Virus caused. Incurable. Painful blisters |
|
|
Genital Warts |
Virus caused (HPV). Associated with cervical cancer. There IS a vaccine |
|
|
Testicular Cancer |
Most common among younger men. Problem with spermatongonia in seminiferous tubules. Becomes a mass. |
|
|
Endometriosis |
Uterine tissue is expelled from the uterine tubes and grows elsewhere in the body. Responds to monthly hormones causing breakdown and bleeding. May lead to scarring and infertility |
|
|
Most common male cancer |
Prostate cancer |
|
|
Most common female cancer |
Breast cancer |
|
|
Symptoms of Breast Cancer |
Palpable lump Skin puckering Nipple drainage Orange peel skin |
|
|
Risk Factors of breast cancer |
Family history, aging, estrogen and progesterone exposure, BRCA 1 and BRCA 2 mutations, ionizing radiation, carcinogens, alcohol, smoking and high fat intake |
|
|
2nd most common killer of women |
Ovarian Cancer |
|
|
Risk factors for ovarian cancer |
Over 50, white, family history, nullparity, first pregnancy after 30, high fat, low fiber diet, low vitamin A, asbestos and talc |
|
|
Cervical Cancer |
Squamous cell carcinoma. Change in shape of the cervix. Slow growing. Detected in Pap smears |
|
|
Fungus that causes a yeast infection |
Candida albicans |
|
|
Risk factors for yeast infection |
Recently on antibiotics, common in diabetics |
|
|
Neonatal Period |
42 days after birth. 6 weeks |
|
|
Antiperistalsis |
The sperm contain prostaglandins that stimulate peristalsis in the uterine tubes to pull sperm towards egg. |
|
|
How is the egg pulled into the uterine tube |
Egg is pulled into uterine tube via negative pressure and cilia transport |
|
|
How long is capacitation? |
Ten hours |
|
|
What is the acrosomal reaction? |
ZP3 (zona pellucida) glycoproteins bind with the sperm head it triggers the release of hyaluronidase and acrosin |
|
|
Describe the fast and slow block to polyspermy |
Fast block: Oocyte membrane depolarization (1-3 secs) Slow block: Cortical reaction. Granulosa cells release Ca+ to harden the zona pellucida (now fertilization membrane) |
|
|
How are fraternal twins formed? |
Two eggs, two sperm |
|
|
How are identical twins formed? |
One egg, one sperm. Cell splits but may share placenta |
|
|
What can cause ectopic pregnancies? |
PID, multiple D&C procedures (Asherman's syndrome), tubal surgery, history of smoking (paralyzes cilia) |
|
|
Amnion |
Purpose: Shock absorption, regulates body temp Made of: Maternal filtrate and fetal urine |
|
|
Amniocentesis |
Taking a sample of the amniotic fluid |
|
|
Chorion |
Becomes placenta Trophoblast + Extraembryonic mesoderm Produces hCG |
|
|
When does organogenesis occur? |
The Embryonic period |
|
|
When does organ maturation occur? |
The fetal period |
|
|
Allantois |
An outpocketing of the yolk sac that later becomes the umbilical cord |
|
|
Ectoderm gives rise to.. |
Nervous system, special sensory organs |
|
|
Endoderm gives rise to.. |
GI tract and Lower respiratory tract |
|
|
Mesoderm gives rise to.. |
Skin, muscle, bones, organs, blood |
|
|
Trophoblastic Nutrition |
Fetus is nourished by the digestion of endometrial cells for the first 8 weeks |
|
|
Placental Nutrition |
Fetus is nourished by the mother's blood stream through the placenta after 8 weeks |
|
|
Chorionic Villi |
Extensions of cytotrophoblast into endometrium to "digest" mother's blood |
|
|
Placental Sinus (lacunae) |
Mother's blood surrounds chorionic villi |
|
|
Decidua Basalis |
Endometrium touching the chorionic villi. Forms maternal portion of placenta |
|
|
Decidua Capsularis |
Opposite the placenta. Surrounds the amnion and chorion |
|
|
Decidua Parietalis |
The endometrium of the uterus except at the point of connection to the placenta |
|
|
Which viruses can pass through the placenta? |
HIV, rubella, measles, chickenpox, polio, encephalitis |
|
|
Placenta Previa |
Placenta covers the cervical os. May lead to spontaneous abortion or increased maternal mortality. Sudden bright red blood in 3rd trimester |
|
|
Placental abruption |
Small or large separation of placenta from the uterus. Causes: trauma, tobacco or alcohol use, hypertension |
|
|
Rhogam |
Given to Rh negative mothers in case of blood mixing or trauma so that immune system does not attack possible Rh positive baby |
|
|
Uses of ultrasound |
Determine fetal age, viability, growth, position, head size, twins, maternal abnormalities and size of pelvic outlet |
|
|
Chorionic Villus Sampling |
Sample placenta. 1-2% mortality. Used for chromosomal analysis |
|
|
Placental Hormones |
Relaxin - Relaxes pelvic ligaments and prevents contractions Estrogen and Progesterone - Maintain uterine lining hCS - decreases maternal glucose usage and increases protein synthesis hPL - Prepare mammary glands for lactation CRH - Produces fetal cortisol (lung maturation) |
|
|
Corticotropin Releasing Hormone (CRH) |
Increases fetal cortisol to produce Type II Pneumocytes (secrete surfactant) for lung development. Also helps time birth |
|
|
What could cause a false positive/negative pregnancy? |
Excess protein or blood in urine Molar pregnancy (trophoblast w/o fetus) Uterine cancer Steroids, diuretics, hormones and thyroid drugs |
|
|
Premature infants may suffer from.. |
Respiratory distress syndrome Inability to thermoregulate Underdeveloped digestive system Immature liver leading to jaundice |
|
|
What causes the baby to take it's first breath? |
Increased CO2 after umbilical cord is cut |
|
|
Symptoms of fetal alcohol syndrome, smoking and x-rays |
Cardiac and CNS defects, anencephaly, cleft lip/palate, ADHD |
|
|
Mutagen |
Any agent that alters DNA or chromosome structure |
|
|
What is the most common genetic disorder? |
Nondisjunction which causes aneuploidy |
|
|
Triplo-X Syndrome |
XXX makes an infertile female with mild intellectual impairment |
|
|
Klinefelter Syndrome |
XXY - Sterile male, underdeveloped testes. Tall, feminine |
|
|
Turner's Syndrome |
X - Sterile female. Webbed neck and no secondary sexual features |
|
|
Trisomy-21 |
Down syndrome. Short stature, flat face, epicanthal fold on eyes, large tongue, stubby fingers and mental retardation |
|
|
Inheritance |
Passing on a trait from one generation to the next |
|
|
Translocation |
Crossing over of non-homologous chromosomes |
|
|
Incomplete Dominance |
Intermediate phenotype Ex. Red + White = Pink Ex. Sickle Cell Anemia |
|
|
Codominance |
When multiple genes are expressed equally Ex. ABO Bloodtype |
|
|
Multiple-Allele Inheritance |
The majority of traits. A gene with more than two alternate forms |
|
|
Polygenic Inheritance |
Majority of traits. Trait controlled by multiple alleles Ex. skin color, eye color, height |
|
|
Pleiotropy |
One gene affects multiple phenotypic traits Ex. Albinism + crossed eyes |
|
|
Epistasis |
One gene allows the expression of other genes Ex. Testosterone gene activates balding gene |
|
|
Sex-linked Traits |
Genes found only on the X-chromosome. Ex. Muscular Dystrophy, color-blindness |
|
|
X-Chromosome Inactivation |
One of the two X chromosomes in females in silenced. Typically no physical traits |
|
|
Fragile X Syndrome |
Defective gene on X chromosome causes mental retardation |
|
|
Leading cause of death from 18-34 |
Accidents, homicide, suicide, AIDS |
|
|
Leading cause of death after 55 |
Heart disease, cancer, stroke, lung disease |
|
|
Senescence |
Decreased function |
|
|
Theories on why we age |
Free radicals damage macromolecules Collagen becomes cross-linked Limit to number of times cells can regenerate |
|
|
Progeria |
Genetic disorder characterized by accelerated aging |

