![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
88 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Which student was...
Hypertonic? Hypotonic? Isotonic? |
Student #3 - Hypertonic
Student #1 - Hypotonic Student #2 - Isotonic |
|
|
refractometer
|
instrument used to determine specific gravity
|
|
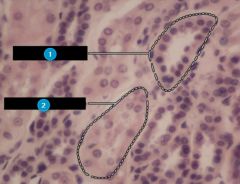
#1
|
Distal convoluted tubule
Note: Circle is well-defined |
|
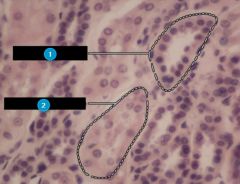
#2
|
Proximal convoluted tubule
Note: Not as prominent as DCT |
|
|
What is inside Bowman's capsule?
|
Glomerulus
|
|
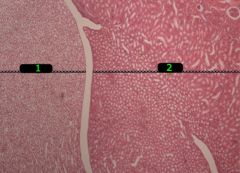
#1
|
Medulla
|
|
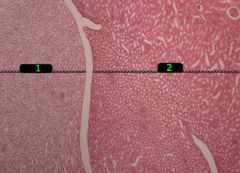
#2
|
Cortex
|
|

#1
|
Glomerulus
|
|

#2
|
Bowman's capsule
|
|

#3
|
Distal convoluted tubule
|
|

#4
|
Proximal convoluted tubule
|
|
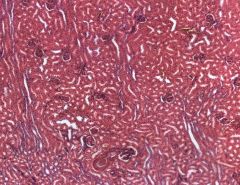
Identify this structure in the kidney.
|
Cortex
Note: Wormy, grainy, few convoluted tubules |
|
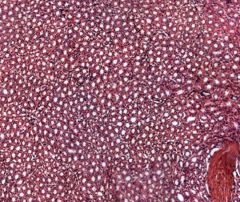
Identify this structure in the kidney.
|
Medulla
Note: Many circular structures (convoluted tubules) |
|
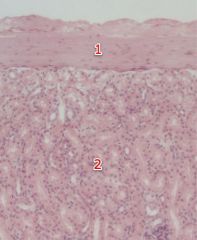
#1
|
Renal capsule
|
|
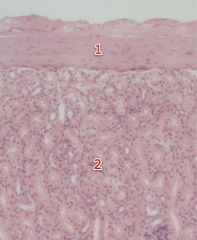
#2
|
Cortex
|
|
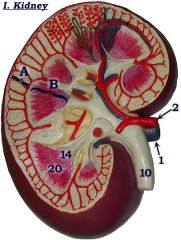
Identify A.
|
Cortex
|
|
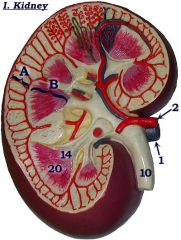
Identify B.
|
Medulla
|
|
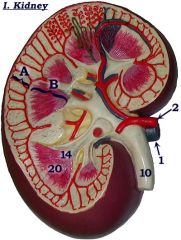
#1
|
Renal vein
|
|
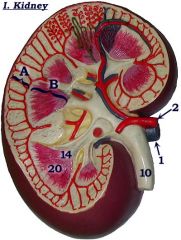
#2
|
Renal artery
|
|
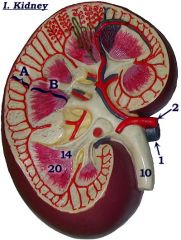
#10
|
Ureter
|
|
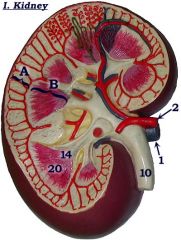
#14
|
Renal papilla
|
|
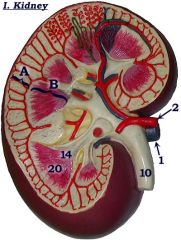
#20
|
Renal pyramid
|
|
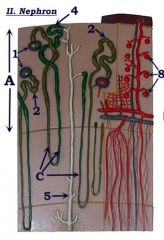
Identify A.
|
Cortex
|
|
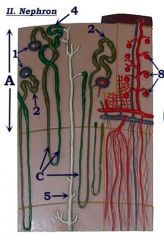
#1
|
Renal corpuscle
|
|
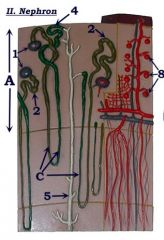
#2
|
Proximal convoluted tubule
Note: Attached to renal corpuscle |
|
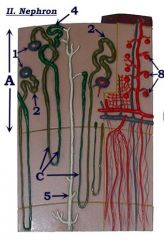
Identify C.
|
Loop of Henle (nephron loop)
|
|
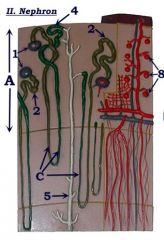
#4
|
Distal convoluted tubule
|
|
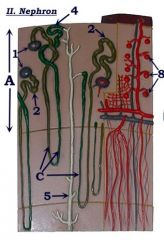
#5
|
Collecting duct
|
|
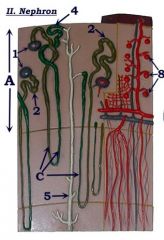
#8
|
Glomerulus
|
|
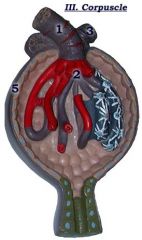
#1
|
Afferent arteriole
Note: Always thicker than efferent arteriole |
|
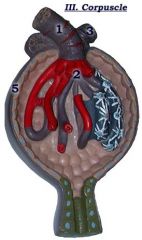
#2
|
Glomerulus
Note: Middle of renal corpuscle |
|
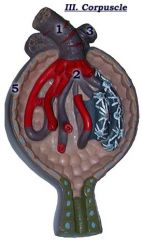
#3
|
Efferent arteriole
Note: Thinner than afferent arteriole |
|
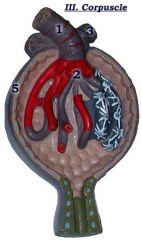
#5
|
Bowman's capsule
|
|
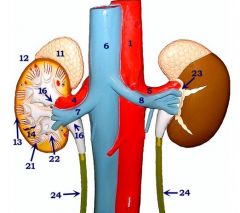
#1
|
Abdominal a.
|
|
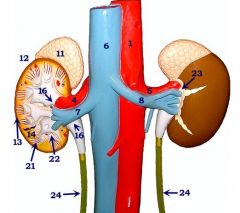
#6
|
Inferior vena cava
|
|
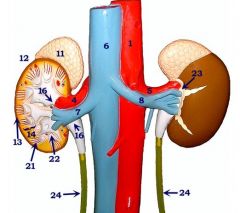
#4
|
Right renal a.
|
|
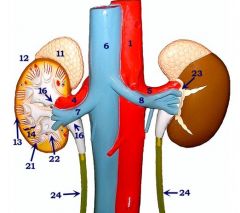
#7
|
Right renal v.
|
|
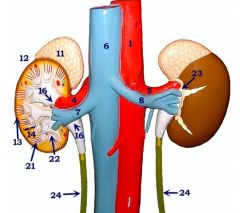
#5
|
Left renal a.
|
|
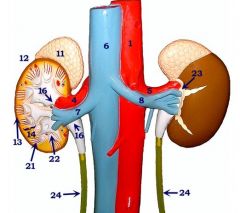
#8
|
Left renal v.
|
|
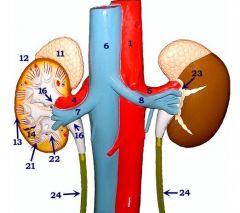
#23
|
Perirenal fat
|
|
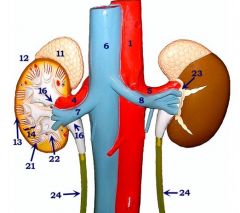
#11
|
Adrenal gland
Note: Left/right |
|
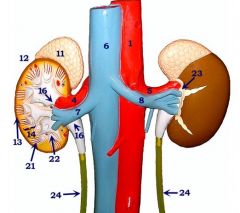
#12
|
Kidney
Note: Left/right |
|
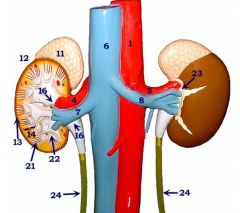
#13
|
Cortex
|
|
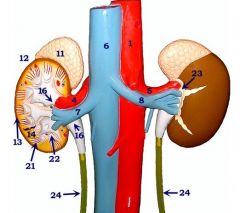
#14
|
Medulla
|
|
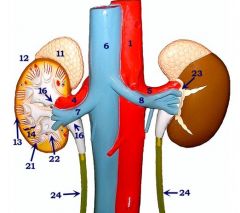
#16
|
Renal pelvis
Note: This part always looked "caved in" |
|
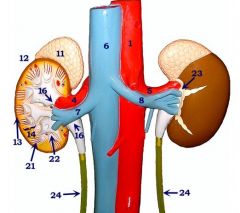
#21
|
Renal pyramid
|
|
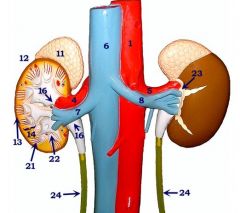
#22
|
Renal papilla
|
|
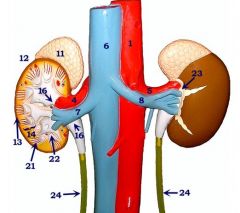
#24
|
Ureters
|
|
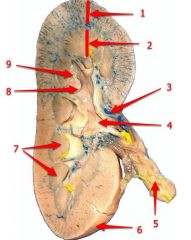
#1
|
Cortex
|
|
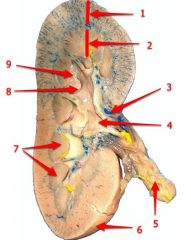
#2
|
Medulla
|
|
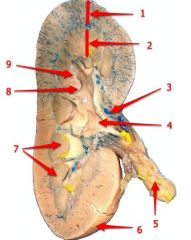
#3
|
Hilum
|
|
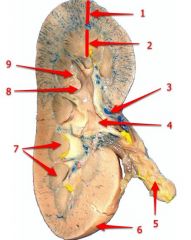
#4
|
Renal pelvis
|
|
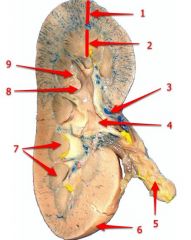
#5
|
Ureter
|
|
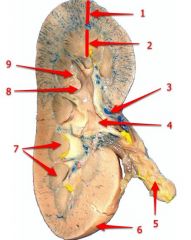
#6
|
Renal capsule
|
|
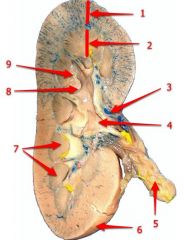
#7
|
Renal pyramid
|
|
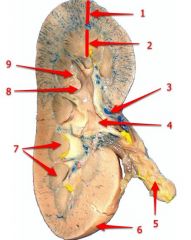
#8
|
Major calyx
|
|
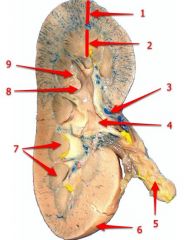
#9
|
Minor calyx
|
|
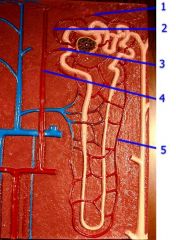
#1
|
Peritubular capillary
|
|
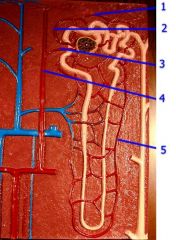
#5
|
Vasa recta
Note: Intertwined with Loop of Henle |
|
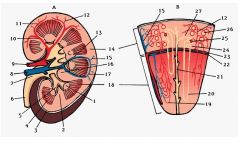
#10
|
Interlobar a.
Note: Between renal pyramids |
|
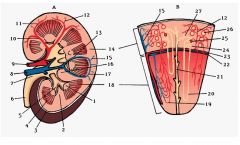
#11
|
Arcuate a.
Note: Base of renal pyramids |
|
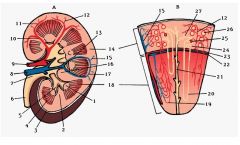
#12
|
Interlobular a.
Note: Branches from arcuate a. |
|
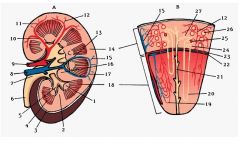
#2
|
Renal column
|
|
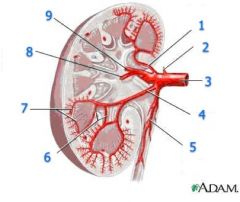
#1
|
Segmental a.
|
|
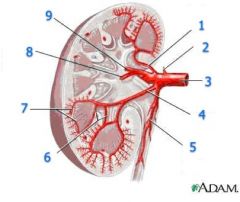
#4
|
Segmental a.
|
|
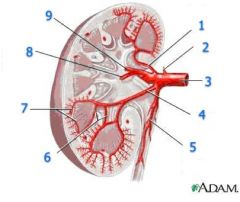
#6
|
Interlobar a.
|
|
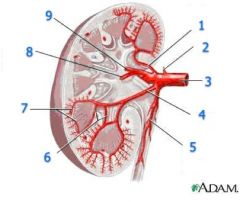
#2
|
Adrenal (suprarenal) a.
Note: Left/right |
|
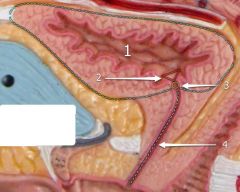
#1
[Female] |
Urinary bladder
|
|
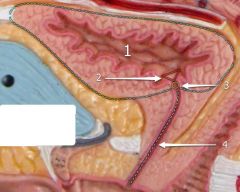
#2
|
Trigone
|
|
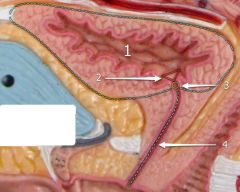
#3
|
Opening into urethra
|
|
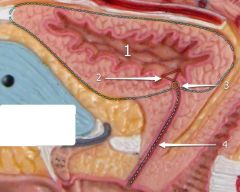
#4
|
Urethra
|
|
|
What did the hypotonic student drink?
|
750 mL of water
|
|
|
What did the hypertonic student drink?
|
150 mL of water with 5 g of salt
|
|
|
What did the isotonic student drink?
|
750 mL of water with 7 g of salt
|
|
|
Which student was dehydrated?
A. Hypotonic B. Isotonic C. Hypertonic |
Hypertonic
|
|
|
What are the two important hormones that control renal function?
|
ADH and aldosterone
|
|
|
What is another name for ADH?
|
Vasopressin
|
|
|
Which hormone keeps salt?
|
Aldosterone
Note: sALt = ALdosterone |
|
|
Which hormone keeps water?
|
ADH
|
|
|
Where does glomerular filtrate come from?
|
It comes from the 1728 liters of blood that pass through the kidney.
|
|
|
glomerulus
|
the only part of the nephron that filters
|
|
|
nephron
|
functional units of the kidney responsible for filtration, reabsorption, and secretion
|
|
|
What must be found in the urine to indicate that a person has diabetes mellitus?
|
Glucose
|
|
|
What is the specific gravity of water?
|
1.0
|
|
|
specific gravity
|
the weight of a unit volume of material (i.e. urine) compared to the same unit volume of water
|
|
|
What is average SG of each?
Student #1 Student #2 Student #3 |
Student #1: 1.005
Student #2: 1.015 Student #3: 1.019 |
|
|
What is average urine output of each?
Student #1 Student #2 Student #3 |
Student #1: 6.7 mL/min
Student #2: 1.2 mL/min Student #3: 5.0 mL/min (abnormal result) |
|
|
What is average pH of each?
Student #1 Student #2 Student #3 |
Student #1: 6.9
Student #2: 6.25 Student #3: 6.4 |

