![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
In this position, the body is erect, feet slightly apart, palms facing forward, thumbs point away from body
|
Anatomical Position
|
|
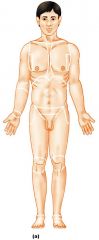
Name this position
|
Anatomical Position
|
|
|
Toward the head
|
Superior
|
|
|
Away from the head
|
Inferior
|
|
|
Toward the front of the body
|
Anterior
|
|
|
Toward the back of the body
|
Posterior
|
|
|
Toward the midline
|
Medial
|
|
|
Away from the midline
|
Lateral
(the arms are lateral to the chest) |
|
|
Between the medial and lateral structure
|
Intermediate
(the collarbone is intermediate between the breastbone and shoulder) |
|
|
Closer to the origin of the body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk
|
Proximal
(the elbow is proximal to the wrist) |
|
|
Farther from the origin of the body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk
|
Distal
(the knee is distal to the thigh) |
|
|
Toward the body surface
|
Superficial
(the skin is superficial to the skeletal muscles) |
|
|
Away from the body surface; more internal
|
Deep
(the lungs are deep to the skin) |
|
|
This planes divides the body into Right and Left parts
|
Sagittal
|
|
|
The sagittal plane that lies on the midline
|
Midsagittal or medial
|
|
|
This plane divides the body into anterior and posterior parts
|
Frontal or coronal
|
|
|
This plane divides the body into superior and inferior parts
|
Transverse or Horizontal (cross section)
|
|
|
This body plane is cut diagonally
|
Oblique section
|
|
|
Over 90% of all anatomical strucures match textbook descriptions, with 2 exceptions
|
1. Nerves or blood vessles may be out of place
2. Small muscles may be missing |
|
|
What does the dorsal cavity do? And what does it consist of?
|
It protects the nervous system and divided by 2 subdivisions:
1. Cranial cavity 2. Vertebral cavity |
|
|
Where is the Cranial cavity?
|
Within the skull and encases the brain.
|
|
|
Where is the Vertebral cavity?
|
runs within the vertebral column; encases the spinal cord.
|
|
|
What does the Ventral cavity hold?
|
Internal organs (viscera) and divided by 2 subdivisions:
1. Thoracic 2. Abdominopelvic |
|
|
The Thoracic cavity is divided how?
|
1. two pleural cavities
2. Mediastinum 3. Pericardial |
|
|
What does the pleural cavites house?
|
The lungs
|
|
|
What does the Medialstinum house?
|
The pericardial cavity and surrounds the remaining thoracic organs.
|
|
|
What does the pericardial cavity house?
|
The heart
|
|
|
What does the adominopelvic cavity house?
|
1. The Abdominal cavity
2. The Pelvic cavity |
|
|
What separates the adominopelvic cavity from the superior thoracic cavity?
|
The dome-shaped diaphram
|
|
|
What does the abdominal cavity house?
|
Stomach, intestines, spleen, liver and other organs
|
|
|
What does the pelvic cavity house?
|
Bladder, reproductive organs and rectum
|
|
|
What does the Parietal serosa do?
|
Lines internal body walls
|
|
|
What does the Visceral serosa do?
|
Covers the internal organs
|
|
|
What does the Serous fluid do?
|
Separates the serosae
|
|
|
What is Pleurisy?
|
aka Pleuritis: the inflamation of the lining of the pleural cavity (surrounding the lungs)
|
|
|
What is Peritonitis?
|
Inflamation of the perotoneum (the serous membrane that surrounds the part of the abdominal cavity)
|
|
|
Define X-ray.
|
A shadowy negative of internal structures.
|
|
|
What does CT stand for?
|
Computed Tomography (formally CAT)
|
|
|
What is a CAT?
|
Computerized Axial Tomography (aka CT)
|
|
|
What is a PET?
|
Positron Emission Tomography(excels in observing the metobolic process)
|
|
|
What is sonography or ultrasound imaging?
|
pulses of sound waves cause echos when reflected on body tissue, computer in turn translates to outline of subject.
|
|
|
What is MRI?
|
Magnetic Resonance Imaging, better at producing images of soft tissue (over x-ray and CT scans). Distinguishes body tissue based on water content.
|

