![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
74 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Population Explosion |
The worlds exponential population growth of the past 200 years |
|
|
Demography |

The study of population statistics E.g. : births, deaths, income, education, disease, etc. |
|
|
Crude Birth Rate |
The total number of live births in a year for every 1,000 people alive in a society |
|
|
Crude Death Rate |
The total number of deaths in a year for every 1,000 people alive in a society |
|
|
Overpopulation |
When the number of people in an area exceed the capacity of the environment to support life at a decent standard of living |
|
|
Carrying Capacity |
The largest number of people that an environment can support |
|
|
Environmental Degradation |
The harming of the environment E.g. : air population, water, pollution, habitat destruction |
|
|
Ecumene |
An area where people can live E.g. : water, food, flat terrain |
|
|
Underpopulation |
When there are too few people in an area to sufficiently develop its resources and improve its peoples quality of life E.g. some places around the world like Africa |
|
|
Arithmetic Density |
The total number of people divided by the total number of land area |
|
|
Physiology Density |
The total number of people per unit of arable (farmable) land. More helpful than arithmetic density |
|
|
Five population clusters |
1. East Asia 2. South Asia 3. Southeast Asia 4. Western and central Europe 5. Northeastern U.S and Canada |
|
|
Thomas Malthus |
Coined the term "overpopulation" worried that world agricultural production was only growing at a linear rate while world population was growing at an exponential rate |
|
|
Linear Growth |
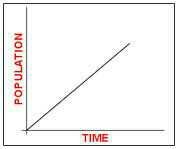
Growth at a constant rate |
|
|
Exponential Growth |
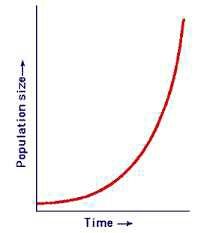
Growth at an increasingly rapid rate |
|
|
Neo-Malthusian |
Ideas which recommend various population control programs in order to ensure resources for current and future population E.g. : China's "one-child" policy |
|
|
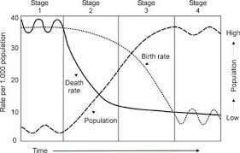
Demographic transition model |
Stage 1= low growth stage 2= high growth stage 3= moderate growth stage 4= low growth A country moves from high birth and death rates through time |
|
|
Infant mortality rate |
The number of babies per 1000 births, who die before their first birthday |
|
|
Total fertility rate |
The average number of babies that an average women delivers during her childbearing years |
|
|
Industrial revolution |
A period (1760-1860) during which predominantly agrarian rural societies in europe and America became industrial and urban |
|
|
Zero population Growth |
When crude birth rates equals crude death rate |
|
|
Population Pyramid |
A model used in population geography to show the age and sex distribution of a particular population |
|
|
Population projection |
An estimate of future population growth based on current data trends |
|
|
Dependency Ratio |
The number of people aged 0-14 and 65+ who cannot work and are dependent on the workforce for support |
|
|
Demographic Momentum |
When the population of a country will continue to grow for a number of years- even after the country reaches replacement-level fertility (2 children per woman) |
|
|
Demographic equation |
The population growth rate for the entire world (i.e. global births minus global deaths). Currently about 80-100 million per year |
|
|
Natality rate |
(Same as "crude birth rate") |
|
|
Birth control |
Factors that determine access. -money -education -religion -distance -Gender Gap (status, education) |
|
|
Enfrachisement |
The right to vote (a.k.a suffrage) |
|
|
Dowry |
Money or property that a wifes family gives to her new husband when they marry |
|
|
Dowry death |
Deaths of young women who are murdered or driven to suicide by husbands or in-laws in an effort to extort a bigger Dowry |
|
|
Birth incentive |
Incentives that may work -free child care -early kindergarten -maternity/Paternity leave |
|
|
Doubling time |
The number of years that it takes for a country to double it's population |
|
|
Sustainability |
The saving of resources for future generations so that their standards of living will be the same or higher than ours today |
|
|
J-curve |
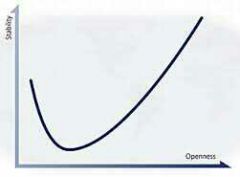
Places countries on a scale based on their openness and stability |
|
|
Disease Diffusion |
The spread of disease. The world is making HUGE progress on the issue |
|
|
Causes of Population decline |
1.natural hazards and disasters 2. War or political turmoil 3. Economic issues |
|
|
Causes of population increase |
1.Medical advances 2. Quantity and quality of food 3. Ethnic and religious issues 4.economic issues 5.gender issues |
|
|
Migration |
The movement of people |
|
|
Immigrant |
People who move in to a country or region |
|
|
Emigrants |
People who move out of a country or region |
|
|
Net migration |
The number of immigrants minus the number of emigrants |
|
|
Pull factor |
A positive perception about a location that motivates a person to move there |
|
|
Push factor |
A negative perception about a location that motivates a person to move away from there |
|
|
Four push/pull Factors |
1. Economic 2.political 3. Environmental 4. social |
|
|
Human Capital theory of Migration |
Educated workers from poor countries move to rich countries for higher paying jobs. Rich countries gain talented labor. Poor countries gain remittances |
|
|
Refugees |
People who are forced to migrate from their home country for fear of persecution or death |
|
|
Asylum seekers |
Immigrants who are seeking asylum (protection safety) in a new country after escaping their home country for fear of their lives |
|
|
Internally displaced people |
People who have been forced to move within their own countries but do not cross international borders as they flee |
|
|
Voluntary migration |
Permanent migration undertaken by choice E.g. STEM graduates moving to rich countries for better pay |
|
|
Place utility |
The process of increasing the attractiveness of a place in order to attract migrants |
|
|
Intercontinental Migration |
The movement of people across an ocean or continent |
|
|
Distance decay |
The "friction of distance" causes the interaction between two places to decrease as the distance between increases |
|
|
Migration Transition Model |
According to Wilber Zelinsky, migration transition occurs together with demographic transition |
|
|
Acculturation |
The process of adopting the culture of another group |
|
|
Life course Model |
Migration often occurs at certain turning points in peoples lives E.g. College, first job, marriage, having children, retirement, etc. |
|
|
Chain migration |
The social process by which immigrants from one place to a particular city or neighborhood |
|
|
Interregional Migration |
Internal migration from one region to another region within a country |
|
|
Intraregional migration |
Internal migration within a region within a country |
|
|
Rural to urban migration |
A population shift from rural (farming) areas to urban (city) areas |
|
|
Cyclic movement |
Nomadic seasonal human/animal migration that is repeated every year |
|
|
Transhumancs |
the action or practice of moving livestock from one grazing ground to another in a seasonal cycle, typically to lowlands in winter and highlands in summer. |
|
|
Intervening obstacles |
Any forces or factors that may limit humans migration |
|
|
Physical environment |
Physical factors that may limit human migration Ex: natural disasters |
|
|
Distance and cost |
Distance and cost factors that may limit human geography |
|
|
Language |
Language and other cultural factors may limit human migration |
|
|
Quota |
Limits that governments put in the number of immigrants they allows into their countries |
|
|
Coyote |
A person who snuggles illegal immigrants |
|
|
Amnesty |
Am official pardon (forgiveness) for breaking the law |
|
|
Remittances |
Transfers of money by a foreign worker to a person in his/her home country |
|
|
Intervening opportunities |
The opposite of an Intervening obstacle |
|
|
Forced migration |
Permanent movement compelled by force. When someone is forced to move from one to another Ex: slavery, native Americans forced off their land and onto reservations |
|
|
Transmigration |
The removal of people from one place and their relocation somewhere else within a country |
|
|
Census |
A detailed counting of the population |

