![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
52 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Geography |

-The science dealing with the areal differentiation of the earth's surface, as shown in the character, arrangement, and interrelations over the world of such elements as climate, elevation, soil, vegetation, population, land use, industries, or states, and of the unit areas formed by the complex of these individual elements. |
|
|
|
Eratosthenes |

-Greek mathematician and astronomer at Alexandria. |
|
|

Environmental Determinism |
-Known as climatic determinism or geographical determinism, is the belief that the physical environment predisposes human social development towards particular trajectories. -A relativity outdated theory which proposes that environments (like climate) determine cultures |
|
|
|
Possiblism |

the theory that the environment sets certain constraints or limitations, but culture is otherwise determined by social conditions.
|
|
|
|
Global Positioning System (GPS) |
a space-based satellite navigation system that provides location and time information in all weather conditions, anywhere on or near the Earth where there is an unobstructed line of sight to four or more GPS satellites. |
|
|
|
Satellite Imagery |

consists of images of Earth or other planets collected by satellites. Imaging satellites are operated by governments and businesses around the world |
|
|
|
Remote sensing |
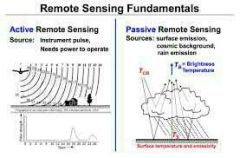
the scanning of the earth by satellite or high-flying aircraft in order to obtain information about it. |
|
|
|
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) |
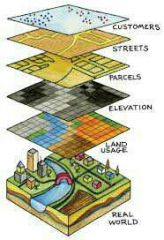
lets us visualize, question, analyze, and interpret data to understand relationships, patterns, and trends. |
|
|
|
Maps |
The basic tools geographers use to represent the earths surface in some way
|
|
|
|
Scale |
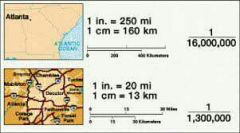
The relationship of the size of a map to the size of the area it represents on the planet |
|
|
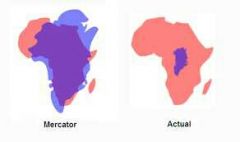
Distortion |
The inaccuracies that result when we try to represent our 3D earth on a 2D map |
|
|
|
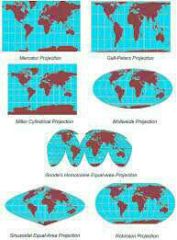
Projection |
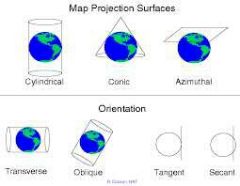
An attempt to portray the surface of the earth on to a flat surface |
|
|
|
Mercator Projection |
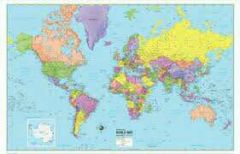
Famous map. Map projection created by Geradus Mercator Pro: easy straight line navigation Con: Major distortion |
|
|
|
Fuller Projection |
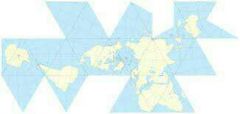
Map projection created by Buckminster Fuller Pro: Less distortion Con: More confusing |
|
|
|
Robinson Projection |
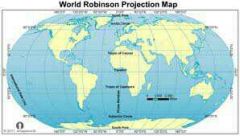
Map projection created by Arthur Robinson Pro: reduced distortion Con: Remaining distortion at poles |
|
|
Azimuthal Projection |
Pro: distance and direction are accurate Con: Shapes are distorted |
|
|
|
Thematic Maps |
Maps that depicts one or more variables (e.g population) in a specific area There are about 5 of them |
|
|
|
Topographic Map |
Thematic map uses isolines to represent constant elevation Used for hiking |
|
|
|
Dot map |
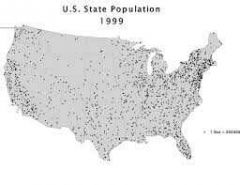
Thematic map that uses dots to show the presence of some feature and reveal a spatial pattern |
|
|
|
Proportional symbols Map |
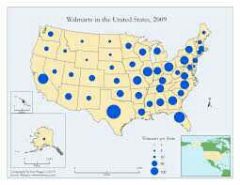
Thematic map in which the size of a chosen symbol indicates the relative magnitude of a statistical value |
Not as useful |
|
|
Choropleth Map |
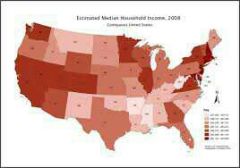
Thematic map that uses tones of colors to represent spatial data as an average value per unit area |
|
|
|
Cartogram |
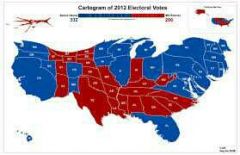
Thematic map that transforms space such that the political unit with the greatest greatest value for some type of data is represented by the largest relative area |
|
|
|
Human geography |
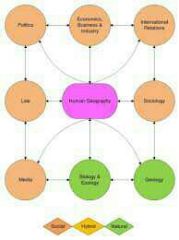
The study of human behavior and how it relates to the physical world (e.g. cultures, religions, migrations, urbanization, quality of life, etc) |
|
|
|
Physical geography |

The study of the natural processes of the physical world (e.g. climate, plate tectonics, etc) |
|
|
|
Place |

A location that can be described in terms of "what it is like" (e.g. hot, crowded, modern, hip, etc.) |
|
|
|
Region |
A concept that links places together E.g. : Germany, The Midwest, Southeast Asia, The Bible Belt, etc. |
|
|
|
Distance Decay |

Interaction between two people/ places decreases as the distance between them increases E.g : local restaurant - local people |
|
|
|
Location |
The position that something occupies on earths surface |
|
|
|
Site |

A location and its physical characteristics E.g. : landforms, climate, vegetation, water, soil, minerals, wildlife, etc. |
|
|
|
Situation |
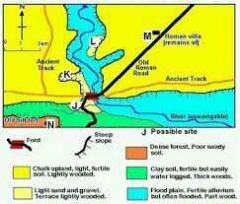
A location and its relation to its surroundings and other places E.g. : accessibility, connections, proximity to raw materials, etc. |
|
|
|
Mental Map |

A mental picture of a place or region |
|
|
|
Latitudes |
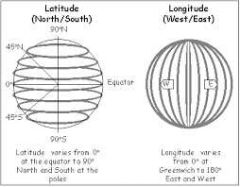
(Aka "parallels") parallel lines that run east-west on the surface of the earth |
|
|
|
Equator |
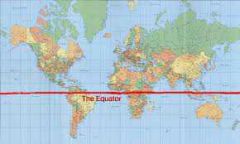
The latitude line that runs in the middle of the earth ( 0 degrees latitude) |
|
|
|
Longitudes |
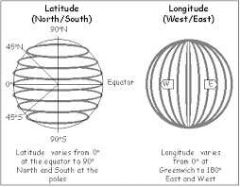
(Aka " meridians) lines that run north and south |
|
|
|
Prime Meridian |
0 degrees longitude. Runs through Greenwich, England |
|
|
|
International Date Line |
180 degrees longitude. Add a day by going west. Subtract a day by going east |
|
|
|
Human-environmental Interaction |
A theme of geography that analyzes how people modify the environment to fit their needs |
|
|
|
Movement |
A theme of geography that analyzes how a place is linked to the outside world |
|
|
|
Diffusion |
The movement of knowledge, ideas, customs, and materials E.g. : food, language, fashion, technology |
|
|
|
Hearth |
The place where the diffusion's knowledge, idea, custom, or material started E.g. : religion, fashion trend, music trend, sushi |
|
|
|
Relocation diffusion |
The spread of knowledge, ideas, customs, or ideas through the migration of people
E.g. : spaghetti and pizza in America |
|
|
|
Expansion Diffusion |
The pattern originates in a central place and then expands outward in all directions to other locations. Three kinds: 1. Hierarchical, 2.contagious 3. Stimulus |
|
|
|
Hierarchical Diffusion |
The pattern originates with an influential person or place and spreads to general population E.g. : hammer pants |
|
|
|
Contagious Diffusion |
The pattern begins at a hearth and then moves outward to nearby locations E.g. : diseases, viral videos |
|
|
|
Stimulus Diffusion |
The pattern where an underlying principle diffuses and then stimulates the creation of new products or ideas E.g. : yoga |
|
|
|
Distribution |
The arrangement of things im space. Three aspects 1) density 2) density 3)pattern E.g. : buildings, people, desks |
|
|
|
Density |
How many things there are in a certain area E.g. : people |
|
|
|
Population Density |
How many people there are in a certain area E.g. : Monaco vs. Australia |
|
|
|
Arithmetic Density |
Calculate density by considering the number of people per unit of total area E.g. : all of Wyoming |
|
|
|
Physiological Density |
Calculates density by considering the number of people per unit of area suitable for farming E.g. : not all of Wyoming |
|
|
|
Concentration |
The geographic location of a specific cluster. "Clustered" if close together. "Dispersed" if far apart |
|
|
|
Pattern |
The arrangement of objects on the earths surface relative to each other |
|

