![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
187 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Tracheal collapse is often seen |
With inspiratory dyspnea |
|
|
Which of these species is most prone to asthma attacks? -caprine -canine -equine -feline |
Feline |
|
|
Bronchodilation and bronchoconstriction are controlled by |
The autonomic nervous system acting on smooth muscle |
|
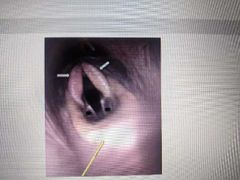
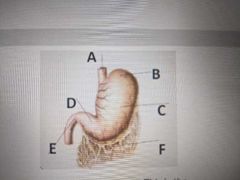
This cartilage indicated by the yellow line is called the |
Epiglottis |
|
|
The flow of oxygen from inspired air in the alveolar into the capillary is dependent on the |
PO2 in the alveoli being higher than the PO2 in the capillary |
|
|
When passing a nasogastric tube in the horse, the tube is directed ventromedially in the nasal cavity to avoid the |
Nasal turbinates |
|

Identify the lung lobe, including right or left |
Cranial lobe of the right lung |
|
|
The ________ is formed from the epiglottis, the arytenoid, cricoid and thyroid cartilages |
Larynx |
|
|
The vocal cords are composed of |
Fibrous connective tissue |
|
|
Phonation in an animal begins in the |
Larynx |
|
|
The epithelial tissue lining the trachea is ___________ columnar epithelium |
Pseudostratified |
|
|
In a relaxed state the diaphragm assumes a dome shape with |
The convex surface facing in a cranial direction |
|
|
The actual exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide occurs across |
Two layers of simple squamous epithelium |
|
|
The unconscious act of breathing is controlled by the respiratory center in the |
Brainstem |
|
|
Which thoracic structure would you find outside of the mediastinum? -lungs -lymph nodes -heart -trachea |
Lungs |
|
|
Blood entering lungs from the heart is dark red because of the |
The high carbon dioxide content |
|
|
The walls of the thoracic cavity and the mediastinum are lined with________ pleura |
Parietal |
|
|
If an animal breathes in 500 milliliters with each resting breath and takes 15 breaths per minute, how many liters has the animal inspired and expired in 1 minute? |
7.5 |
|
|
The acceptable range of pH in most animals is |
7.35-7.45 |
|
|
The respiratory passages cross the digestive tract in the________ |
Pharynx |
|
|
The upper respiratory tract includes all structures |
Outside the lungs |
|
|
If the CO2 level in blood rises above a present limit, how will the respiratory center adjust the breathing to compensate? |
Increase rate and depth of respiration |
|

Identify the lung lobe, including right or left |
Caudal lobe of the left lung |
|
|
The heart, the trachea, the esophagus, and major blood vessels in the thoracic cavity are all found within the |
Mediastinum |
|
|
Tracheal rings are composed of |
Hyaline cartilage |
|
|
The hilus is found |
On the medial surface of each lung |
|
|
The _____ ______ divides the right and left sides of the nasal cavity |
Nasal septum |
|

Identify the lung lobe |
The accessory lobe of the right lung |
|
|
The space between each tracheal ring is composed of |
Smooth muscle and fibrous tissue |
|
|
When the external intercostal muscles contract, they rotate the ribs |
Upward and forward |
|
|
The nasal meatus is created by the |
Turbinates |
|
|
The _______ respiratory tract includes the nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, and trachea |
Upper |
|
|
Low levels of oxygen can bring on |
Sighs |
|
|
According to your lab manual, in most domestic species, except the horse, the left lung has __________ lobes |
Two |
|
|
Each of the lung lobes is lined with visceral _______ |
Pleura |
|
|
In most domestic species, except the horse, the right lung has _______ lobes |
Four |
|
|
The opening into the larynx is called the |
Glottis |
|
|
The ciliated epithelium that lines the trachea has a layer of ________ on top of it to trap foreign debris |
Mucus |
|
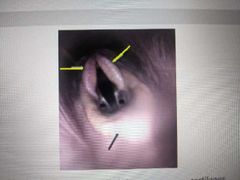
These cartilages indicated by the yellow line are called the _________ cartilages |
Arytenoid |
|
|
The tracheal rings are somewhat rigid so they prevent the trachea from collapsing during inhalation. These rings are made up of |
Hyaline cartilage |
|
|
Antitussives are best used to treat a |
Nonproductive cough |
|

Identify the lung lobe |
The middle lobe of the right lung |
|
|
The boundaries of the glottis are formed by the |
Arytenoid cartilages and vocal cords |
|

Identify the lung lobe |
The cranial lobe of the left lung |
|
|
Sinuses are outpouchings of the |
Nasal passages |
|
|
The blood vessel that brings blood to the lungs from the heart is the |
Pulmonary artery |
|
|
The main expiratory muscles are the |
Internal intercostal muscles and the abdominal muscles |
|
|
The __________ respiratory tract includes the bronchi and the lungs |
Lower |
|
|
The ______ separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity |
Diaphragm |
|
|
The trachea splits into two bronchi at the |
Bifurcation |
|
|
The openings into the nasal cavity are the |
Nares |
|
|
The major muscles of exhalation are the abdominal muscles and the _____ ________ muscles |
Internal intercostal |
|

Identify the lung lobe |
Caudal lobe of the right lung |
|
|
The nasopharynx sits ______ to the oropharynx in a standing animal |
Dorsal |
|
|
The major muscles of inspiration are the diaphragm and the ________ ________ muscles |
External intercostal |
|
|
The three main condition functions of the nasal passages are |
Warming, humidifying, and filtering air |
|

Identify the lung lobe |
Cranial lobe of the left lung |
|
|
Another name for the buccal cavity is the |
Oral cavity |
|
|
Food in a semiliquid state that leaves the stomach and enters the duodenum is called |
Chyme |
|
|
Which one of these animals has the least ability to vomit? -dog -horse -pig -cat |
Horse |
|
|
Which motility movement in the small intestine mixes the partially digested food but doesn't move it toward the large intestine? |
Segmentation |
|
|
Ketosis, or metabolic acidosis, is a result of excessive conversion of ______ to ketones |
Fatty acids |
|
|
Peptides are made up of |
Amino acids |
|
|
Which species of animal uses the cecum as a fermentation chamber? |
Equine |
|
|
Peyer's patches are made up of |
Lymphoid tissue |
|
|
When the lower jaw moves laterally and rostrally the movement is called |
Translation |
|
|
An example of an omnivore is a |
Pig |
|
|
Pepsin is a proteolytic enzyme that begins the chemical digestion of |
Proteins |
|
|
The two bones that are connected with the TMJ are the |
Mandible and temporal bones |
|
|
The cheek teeth are the |
Premolars and molars |
|
|
Which one of the following substances gives urine it's characteristic color? |
Urobilin |
|
|
The intestines are suspended from the abdominal wall by the |
Mesentery |
|
|
The 'true' glandular stomach of a ruminant is the |
Abomasum |
|
|
What is the correct order of the parts of the small intestine, starting with the first part? |
Duodenum, jejunum, ileum |
|
|
Which two gases are produced during the fermentation process in the ruminant stomach? |
Carbon dioxide and methane |
|
|
The part of the tooth where nerves and blood vessels enter the tooth is the |
Apex |
|
|
Plicae are |
Mucosal folds in the small intestine |
|
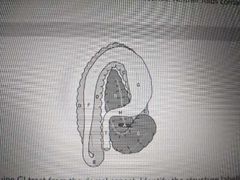
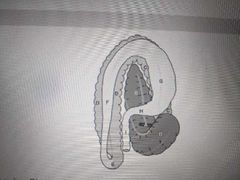
This is a view of the equine GI tract from the dorsal aspect. Identify H |
Transverse colon |
|
This is a view of the equine GI tract from the dorsal aspect. Identify E |
Pelvic flexure |
|
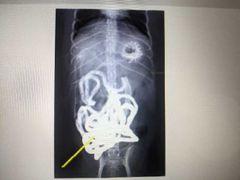
Which portion of the intestine is filled with barium in this radiograph? |
Jejunum |
|
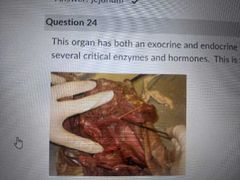
This organ has both exocrine and endocrine function and is often described as L shaped. It produces several critical enzymes and hormones |
Pancreas |
|
|
Bile acids are produced in the _______ and stored in the _______ |
Liver; gallbladder |
|

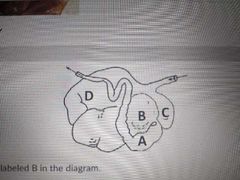
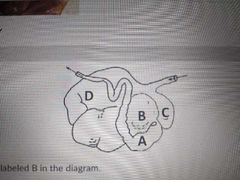
B |
Ascending colon |
|
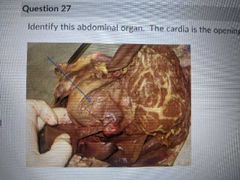
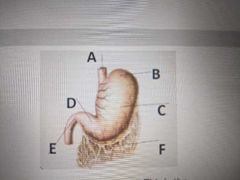
The cardiac is the opening into this organ |
Stomach |
|
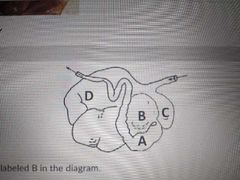
B |
Omasum |
|
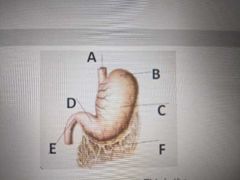
C _____ of the stomach |
Body |
|
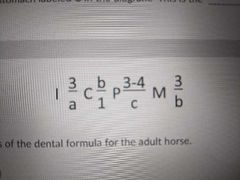
Identify a, b, c, d |
a 3 b 1 c 3 d 3 |
|
|
Insulin is a hormone secreted by the |
Endocrine pancreas |
|
|
How many canine teeth does a ewe have! |
0 |
|
|
The function of the myenteric plexus is |
To control movement of food through the GI tract |
|
|
The terminal part of the stomach that opens into the duodenum is the |
Pylorus |
|
|
Where is albumin produced? |
Liver |
|
|
Which of the following species does not have a gall bladder? -canine -feline -bovine -equine |
Equine |
|
|
In herbivores the process of converting plant material into usable nutrients is accomplished through |
Fermentation |
|
|
Which chamber of the ruminant stomach has mucosa that resembles a honeycomb? |
Reticulum |
|
|
Gastrin and cholecystokinin are |
Hormones |
|
|
The esophageal groove connects the |
Esophagus to the omasum |
|
|
An example of a hindgut fermenter is a |
Horse |
|
|
What effect does sympathetic nerve stimulation have on digestion? |
Inhibits digestion |
|
|
The surfaces of the teeth that come together when an animal closes it's mouth are the ______ surfaces |
Occlusal |
|
|
The largest fermentation chamber of the ruminant stomach is the |
Reticulorumen |
|
|
The vestibule is |
The space between the outer surface of the teeth and the surrounding lips and cheeks |
|
|
In the triadan system for documenting teeth, the left mandibular arch contains teeth in the _______ series |
300 |
|
|
Which salivary gland, located ventral to the ear, produces nearly half of the total volume of saliva produced? |
Parotid |
|
|
Which one of the following animals has a dental pad? |
Cow |
|
|
What type of tooth grows continually throughout the life of an animal? |
Aradicular hypsodont teeth |
|
|
Where will gluconeogenesis most likely take place in a ruminant? |
Liver |
|

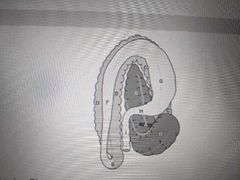
C |
Transverse colon |
|
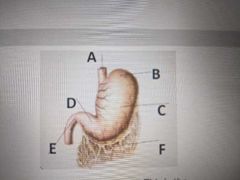
B _____ of the stomach |
Fundus |
|
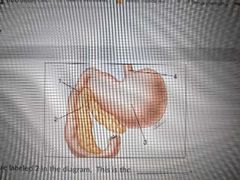
2 |
Pancreas |
|
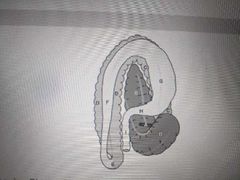
This is a view of the equine GI tract from the dorsal aspect. I |
Small colon |
|
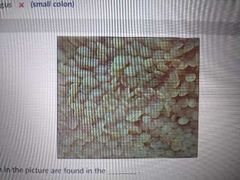
The papilla seen in the picture are found in the |
Rumen |
|
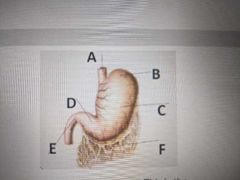
E |
Pylorus |
|
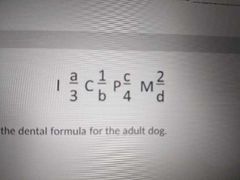
a b c d |
a 3 b 1 c 4 d 3 |
|
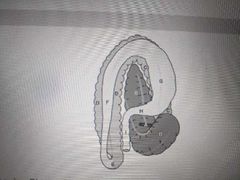
This is a view of the equine GI tract from the dorsal aspect. The turn between F and G is called the |
Diaphragmatic flexure |
|
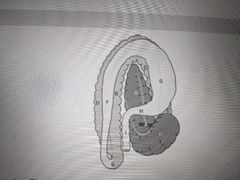
F |
Greater omentum |
|
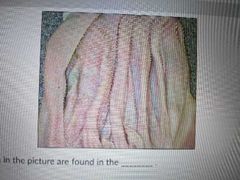
The folds of tissue seen in the picture are found in the |
Omasum |
|
|
Which part of the tooth extends above the gum line? |
Crown |
|
|
The brush border of the small intestines is made up of |
Microvilli |
|
|
In ruminants amino acids are absorbed from the intestinal mucosa and transported to the ________ by the bloodstream |
Liver |
|
|
The part of the stomach that allows the stomach to expand to store food after a large meal is the |
Fundus |
|
|
The position of the esophagus in relation to the trachea as it travels down the neck is |
To the left of trachea |
|
|
The surface of the tooth that faces the animals lips is the ______ surface |
Labial |
|
|
The serosa is the |
Outer layer of the wall of the GI tract |
|
|
The body of the tongue is made up of mostly |
Muscle tissue |
|
|
In which part of the large intestine does the most water absorption take place? |
Colon |
|
|
Where does the pancreatic duct enter the GI tract? |
Duodenum |
|
|
Muscle contractions in the stomach and intestines of a monogastric animal are regulated by |
Specialized smooth muscle cells |
|
|
Swallowing happens in three stages. Which stage(s) is/are voluntary and which stage(s) are involuntary? |
Stage one is voluntary, stages two and three are involuntary |
|
|
Another name for "chewing the cud" is |
Rumination |
|
|
The cardiac sphincter is located |
At the caudal end of the esophagus |
|
|
Acute ruminal tympany is also known as |
Bloat |
|
|
The pattern of muscle contraction that moves through the GI tract is called |
Peristalsis |
|
|
Another name for chewing is |
Mastication |
|
|
Acetate, propionate, and butyrate are examples of |
Volatile fatty acids |
|
|
The liver is located just caudal to the |
Diaphragm |
|
|
The mixing chamber of the stomach is the |
Corpus |
|

The honeycomb surface seen in the picture is found in the _______ |
Reticulum |
|
This is a view of the equine GI tract from the dorsal aspect. C |
Right ventral colon |
|
D |
Antrum |
|
C |
Reticulum |
|
This is a view of the equine GI tract from the dorsal aspect. The turn between C and D is called the |
Sternal flexure |
|

E |
Cecum |
|
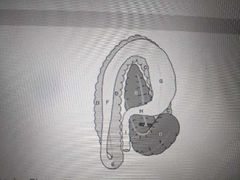
D |
Left ventral colon |
|
|
The gallbladder is found between the ______ lobe and the _______ lobe of the liver |
Quadrate; medial |
|
A |
Abomasum |
|
|
The molecule with which an enzyme reacts is the |
Substrate |
|
|
Postparturient ketosis usually appears |
During lactation |
|
|
The major cellular fuel for the body is |
ATP |
|
|
Starches are what? What food do they come from? |
Polysaccharides that come from grains, root vegetables, and legumes |
|
|
In animals that require taurine as an essential nutrient, a deficiency can lead to |
Retinal degeneration |
|
|
Most enzymes end with the suffix |
-ase |
|
|
Plant and grain protein digestion in ruminants occurs primarily in the |
Rumen |
|
|
Which of the following minerals is the most abundant in the body? |
Calcium |
|
|
Of the six categories of nutrients, which three produce energy when they are consumed? |
Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins |
|
|
In total, what is the maximum number of ATP molecules that can be formed from each molecule of glucose that enters a cell? |
38 |
|
|
During catabolic metabolism protein is broken down by hydrolysis into |
Amino acids |
|
|
Taurine is an essential nutrient for which species of animal? |
Feline |
|
|
During dehydration synthesis a ______ molecule is produced |
Water |
|
|
Cellulose is what? What food is it found in? |
Polysaccharide found in most vegetables |
|
|
How many amino acids are there? |
22 |
|
|
The third stage of catabolic metabolism occurs in the |
Mitochondria |
|
|
The fat-soluble vitamins are |
A, D, E, K |
|
|
Which system in the body is the most unaffected by starvation? |
Skeletal |
|
|
A loss of a minimum of _______ of its water would be fatal to an animal |
15% |
|
|
Examples of macrominerals are -iodine, iron, sodium -nickel, phosphorus, selenium -calcium, magnesium, potassium -sulfur, copper, chlorine |
Calcium, magnesium, potassium |
|
|
Examples of microminerals are -cobalt, calcium, chromium -manganese, magnesium, mylobdenum -copper, iodine, iron -magnesium, zinc, fluorine, sulfur |
Copper, iodine, iron |
|
|
When an animal starts breaking down body fat to compensate for a caloric deficiency in its diet, _____ are released into the bloodstream |
Ketones |
|
|
Where in the cell would you find cristae? |
Mitochondria |
|
|
On average, most mammals are about ____% water |
70% |
|
|
The second stage of catabolic metabolism occurs in the |
Cytosol |
|
|
More than _______ amino acids linked together is considered a protein |
50 |
|
|
During catabolic metabolism fats are broken down by hydrolysis into fatty acids and |
Glycerol |
|
|
During catabolic metabolism carbohydrates are broken down by hydrolysis into |
Monosaccharides |
|
|
What happens to the enzyme after an enzymatic reaction is complete? |
Nothing happens |
|
|
Insulin is classified as a ______ protein |
Regulatory |
|
|
The nitrogen balance in a body is maintained by excretion of nitrogen primarily by the |
Kidneys |
|
|
The primary function of dietary vitamins is to |
Activate enzymes |
|
|
Hemoglobin is classified as a ______ protein |
Transport |
|
|
The first stage of catabolic metabolism occurs in the |
Stomach |
|
|
Triglycerides are named for their |
Three fatty acids attached to a glycerol molecule |
|
|
The most important dietary steroid is |
Cholesterol |
|
|
Each enzyme has the capability of initiating a maximum of how many types of enzymatic reactions |
1 |
|
|
A catalyst ______ the activation energy of a reaction and ____________ the reaction |
Lowers; speeds up |
|
|
Examples of trace elements are -cobalt, fluorine, sulfur -chlorine, selenium, fluorine -calcium, potassium, sodium -iodine, iron, zinc |
Cobalt, fluorine, sulfur |
|
|
In general, cofactors and coenzymes assist with |
Enzymatic reactions |
|
|
The second stage of catabolic metabolism occurs in the |
Cytosol |

