![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
62 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
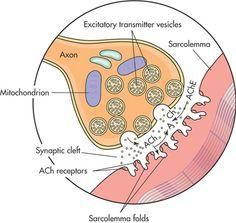
Acetylcholine is removed from the synaptic cleft by
|
acetylcholinesterase
|
|
Troponin is associated with which muscle protein?
|
Actin
|
|

Calcium is released by which myofiber structure
|
sarcoplasmic reticulum
|
|
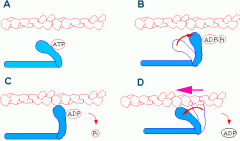
ATP is associated with which muscle protein
|
myosin
|
|
Secretory vesicles within the axon terminus release acetylcholine into what area?
|
the synaptic cleft
|
|
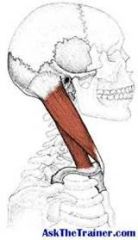
The sternocleidomastoid muscle is named for its
|
origin/insertion
|
|
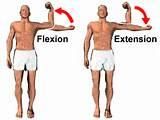
When extending the forearm, the triceps brachii is the....
|
agonist
|
|
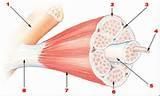
Gross to fascicle to myofiber to
|
myofibril
|
|
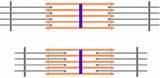
Which of the following is NOT associated with the I band of a sarcomere?-Actin-Myosin-is bisected by the Z line-is the light band of the sarcomere
|
myosin
|
|
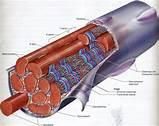
Myofibers can exhibit graded responses to stimuli.
|
False
|
|
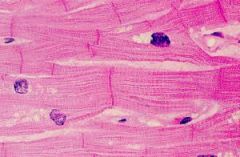
Involuntary,highly aerobic, striated muscle is probably what kind of muscle?
|
cardiac
|
|
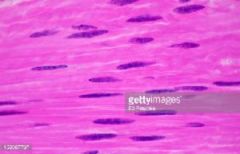
What muscle type utilizes wavelike contractions and can function when stretched?
|
smooth
|
|

"Syn"translates into....
|
together
|
|
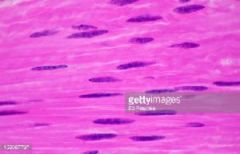
sarcomeres are found within all but which of the following muscle types?
|
smooth
|
|
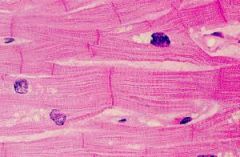
Intercalated disks are associated with which muscle type?
|
cardiac
|
|
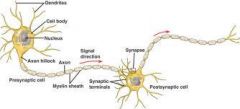
In which direction does an efferent neuron send its signals?
|
away from the cell body orCNS
|
|
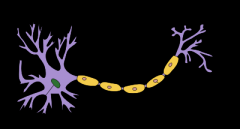
Which of the following increases the rate of neuron signal transmission?
|
myelin
|
|
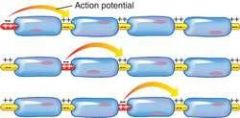
"Saltatory" translates into.....
|
leap or jump
|
|
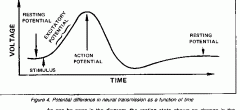
A resting potential is maintained by.....
|
the Na+/K+ pump
|
|
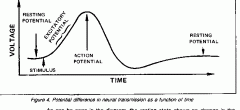
depolarization involves the movement of.....
|
Na+ into the cell
|
|
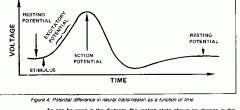
The minimum stimulus required for a response is termed.........
|
threshold
|
|
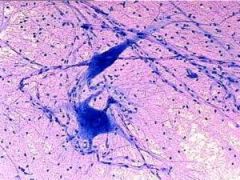
Non-conducting cells that support nervous tissue are called.......
|
glial cells
|
|
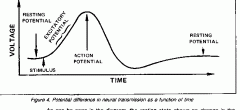
Which of the following is NOT associated with an action potential?
|
ATP
|
|
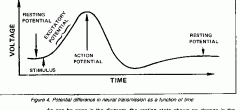
What can be found between Schwann cells?
|
the axon
|
|
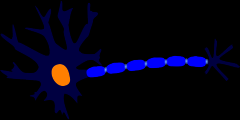
How many axons can be seen on a multipolar neuron?
|
1 |
|
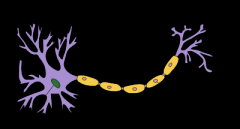
The central nervous system (CNS) consists of all but the following….
|
Sensory receptors |
|

The “fight or flight” component of the nervous system is associated with all but which of the following? |
Sensory system |
|
Skeletal muscle is stimulated by which motor division of the nervous system?
|
Somatic |
|
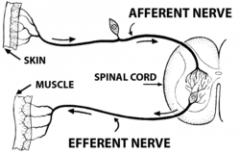
Afferent signals travel along which pathway?
|
Sensory |
|
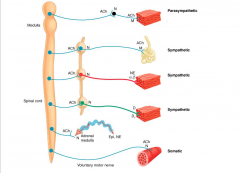
Smooth muscle is stimulated by which motor division of the nervous system?
|
Both sympathetic and parasympathetic |
|
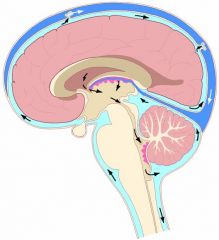
Ventricles…
|
Contain cerebrospinal fluid |
|
The motor component of the cerebral cortex is associated with all but which of the following? -mood and memory -parietal and temporal lobes of the cerebrum -skeletal muscle movement |
Skeletal muscle movement |
|
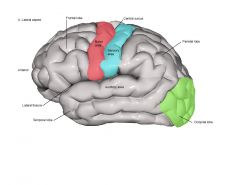
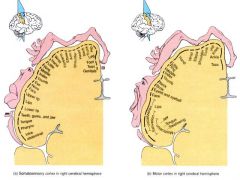
Spatial discrimination (the ability to identify the specific region of the body being stimulate) is associated with which of the following?
|
The sensory component of the cerebral cortex |
|
When you write with your right hand, which cerebral hemisphere initiates the action? |
Left
|
|
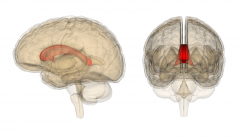
The corpus callosum connects which portions of the brain?
|
Left and right cerebral hemispheres |
|
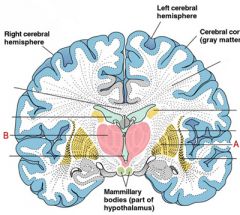
Which of the following serves as a “relay center’ for the cerebral cortex?
|
Thalamus |
|
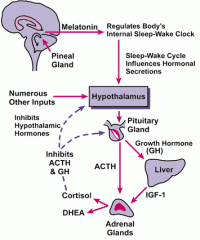
Melatonin is associated with all but which of the following?
-epithalamus -pineal gland -sleep cycle -hypothalamus |
Hypothalamus
|
|
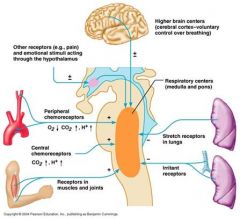
Which of the following does not assist in coordinating heart rate and breathing rate?
-midbrain -Pons -Medulla oblongata |
Midbrain
|
|
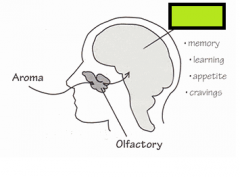
“Emotional” memory, frequently associated with the sense of smell, arises from which region of the brain? |
Limbic system
|
|
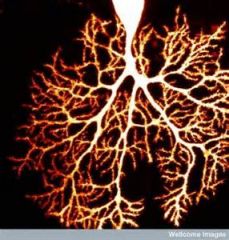
Coordination of movement is controlled by which brain region?
|
Cerebellum
|
|
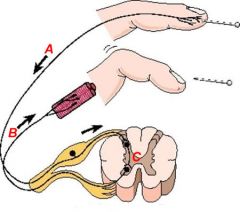
A basic reflex consists of all but which of the following? -Receptor -Association Neuron -Effector -Brain |
Brain
|
|

The “resting and digesting”portion of the PNS is termed…
|
Parasympathetic
|
|

If the sympathetic autonomic nervous system increases heart rate, what does it do to the digestive system?
|
Decreases the rate of digestion
|
|
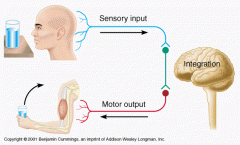
Which of the following exhibits the greatest diversity in neural response?
-Sensory -Motor |
Motor
|
|
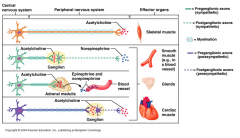
Skeletal muscle is stimulated by both parasympathetic and sympathetic autonomic stimuli.
|
False |
|
|
Skeletal muscle contraction requires nerve stimulation, calcium, and ATP. Diagram a muscle contraction (you may draw arrows from one step to the next;do NOT include relaxation here) and clearly identify the areas where nerve stimulation, calcium, and ATP are used. How many additional ATP molecules would you need in order to relax your muscle? |
1. motoraxon terminates at neuromuscular junction; vesicles within axon terminus release acetylcholine into synaptic cleft..... 2.actionpotential generated throughout interior of myofiber via t tubules....3.sarcoplasmic reticulum releases calcium in responseto action potential along t tubules.......4.calciumbinds to troponin, exposing myosin binding sites.....5.actin and myosin bind; ATP is released by myosin;head "swivels" (contraction occurs)........6.actionpotential ends.....7. newATP attaches to myosin; head returns to original position and "breaks" from actin......8.troponinresumes original position within troponin complex; myosin binding sites are "re-hidden"; calcium is taken up by sarcoplasmic reticulum......................2 ATPs are required in order to relax your muscles.
|
|
|
A skeletal muscle is named according to a particular characteristic or combination of characteristics associated with it. Explain the probable basis for the name of each of the following muscles: trapezius, sternocleidomastoid,pectoralis major, orbicularis oculi, adductor longus.
|
Pectoralis Major-----Convergent muscle has a broad origin, and its fascicles converge toward a single tendon of insertion. Such a muscle is triangular or fan shaped.-------Sternocleidomastiod-----named according to their points of origin and insertion. The origin is always named first.------Adductor longus-----named for the movement they produce, action words such as flexo, extensor, or adductor appear in the muscle's name.-------Trapezius----Some muscles are named for their distinctive shapes.-----Orbicularis Oculi---Circular when the fascicles are arranged in concentric rings. Muscles with this arrangement surround external body openings, which they close by contracting. |
|
|
Organize the following elements into a final muscle:myofibers, myofilaments (actin and myosin), gross muscle, myofibrils, fascicles. Draw and label a sarcomere with the following: A band, I band, and Z line. What are the boundaries of your sarcomere? Where is myosin located? Actin? Which region(s) "shortens" during a contraction?
|
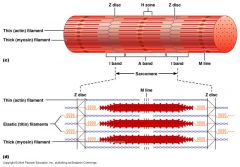
Myofilaments---Myofibril---Myofiber----Fascicle----Gross Muscle.....Z disc are the boundaries......In the THICK A band....in both the THIN I and A band.....Z line to Z line shorten. |
|
|
Distinguish between isotonic and isometric contractions with examples of activities that would demonstrate these types of contractions. Now…provide two activity examples that would demonstrate graded response via recruitment of muscle fibers
|
Isotonic contraction, "same strength"; involves motion. Picking up a book.-----Isometric, "same length"; no motion is invloved. Pushing up against a wall.--------Graded response via recruitment of muscle fibers picking up a book and picking up a golf bag. Isotonic contractions occur when the muscles shortens (concentric contraction) or lengthens (eccentric contraction) as the load is move.----Isometric contractions occur when muscle tension produces neither shortening nor lengthening. |
|
|
Distinguish between muscle types (as per your table).
|
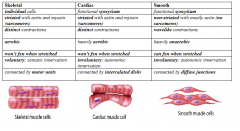
|
|
|
Draw a representative multipolar neuron. Label the following: soma, nucleus, dendrite, axon, Schwann cell, Nodes of Ranvier. Where is myelin located? Which is the receiving end? The conducting end?
|
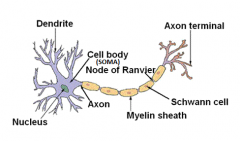
In between the layers of the Schwann cell.....Dendrites are the receiving end....along the axon is the conducting end. |
|
|
Describe how an active transport mechanism sets up a resting potential on a cell membrane. What happens during the depolarization and repolarization events of an action potential?
|
during active transport The Na+/K+ pump, Na+ out, K+ in. Stimulus appear and...if threshold is met....deploration occurs resulting in Na+ in and during repolarization K+ out. |
|
|
Define the following terms: meninges, ventricle,cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). How are these terms related? What is meant by a blood-brain barrier with regard to CSF?
|
Meninges: protective coverings of the central nervous system; from the most external to the most internal, the dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater.------Ventricle: Paired, inferiority located heart chambers that function as the major blood pumps; cavities in the brain.----Cerebrospinal Fluid is plasmalike fluid that fills the cavities of the CNS and surrounds the CNS externally; protects the brain and spinal cord.----They are all characteristics of the brain---Blood brain barrier protects the brain from harmful substances. |
|
|
Outline the organization of the nervous system (CNS and PNS) and give a brief description of each component.
|
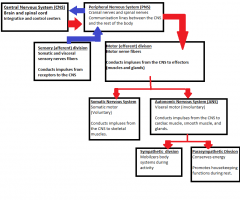
|
|
|
Describe the functional aspects of motor, sensory, and association areas of the cerebral cortex and where each can be located within the cerebrum.
|
Motor is voluntary and located in the frontal lobe. Aids in skeletal muscle movement; repetitious/learned skills, mechanics of speech, and eye muscles----Sensory is involuntary and located in the Parietal, Temporal, and Occipital Lobes. Aids in spatial discrimination, association, vision, audition, gustation, olfaction.-----Association is mixed; aids in cognition, intellect, language cognition, mood, memory, personality, perception. |
|
|
What is meant by contralateral control with regard to the cerebral cortex? Explain how asymmetry appears in the cortex. What connects the left and right hemispheres so that both hemispheres "communicate"with each other?
|
Contralateral (relates to the opposite side) each hemisphere is concerned with the sensory and motor functions of the opposite side of the body-----(Lateralization, not equal in function)----asymmetry means there is a division of labor where each hemisphere has abilities not completely shared by its partner. 90% of people are "left dominant"------ Corpus Callosum connects left and right hermispheres. |
|
|
Why is the thalamus (translates to "bark") frequently described as a "relay center" for the cerebral cortex? To which brain region is the pituitary attached? The pineal gland? Which gland is associated with sleep cycles?
|
- --Thalamus is the relay station for impulses traveling to and from the spinal cord, brain stem, cerebellum and cerebrum. Function in directing sensory input to the appropriate place in the cerebral cortex.---pituitary gland is attached to the hypothalamus.----Pineal Gland is attached to the Epithalamus.------The pineal gland is associated with the sleep cycle.
|
|
|
Explain the survival advantages seen by having the following brain components: corporaquadrigemina, pons, medulla oblongata, limbic system.
|
corporaquadrigemina, visual and auditory reflexes------pons, maintains breathing and rhythm, sets a rhythm for breathing, regulating respiration -----medulla oblongata, sets a rhythm for our heart, regulate respiratory rhythm, heart rate, and blood pressure. ------limbic system, memory associated with smell (spoiled milk), and maintains the alert state of the cerebral cortex (Reticular system) "awareness" . |
|
|
Diagram a reflex arc. Distinguish between basic and learned reflexes.
|
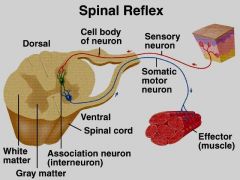
learned reflexes are from repetition or practice, they are automatic. ----basic reflexes you are aware, your brain thinks, Ex. you drop a pot of boiling water you move your body out of the way because you know you will get burned. |
|
|
Differentiate between somatic and autonomic nervous divisions with regard to muscle type stimulated. Which are you most likely to be using after a Thanksgiving dinner (be specific)? When running to catch a bus (be specific)?
|
Somatic stimulates skeletal muscle.....Automatic nervous system innervates(stimulates) Cardiac and smooth muscle....after a thanksgiving dinner you will be using the parasympathetic (rest and digest) where you body keeps energy as low as possible blood pressure and heart rate regulated at low normal levels, stomach digest food. In order to catch a bus you will be using the Sympathetic (fight or flight) digestion stops, visceral blood vessels constricts, shunting blood to active skeletal muscles and vigorously working heart, dilated bronchioles in the lungs, increasing air flow, stimulates liver to release more glucose into the blood to accommodate the increase energy needs of body cells. |
|
|
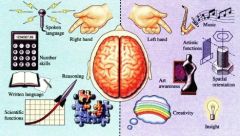
Left hemisphere is dominant |
Specialized for language and mathematical skills
|
|
|
Right Hemisphere is dominant |
Visual spatial skills and creative endeavors. |

