![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
62 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Depth of invasion of melanoma
vs. Depth of invasion of SCC |
Breslow thickness
Surface of the epithelium (discounting the keratin layer) SCC: adjacent basement membrane of the closest dermal papilla |
|
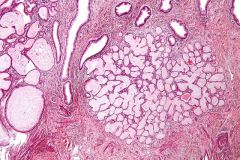
Cervix from prolapsed uterus
|
Endocervical tunnel clusters!
Benign mimic of adeno Bland Lobular architecture |
|
|
Give the classic locations for the following cysts:
Bartholin Skene Gartner |
Bartholin: 4 & 8:00 introitus, mucinous
Skene: paraurethral Gartner: lateral vag wall, simple columnar |
|
|
BerEp4 & B72.3
|
+ in adeno, - in mesothelioma
|
|
|
nuclear beta-catenin in a pancreatic neoplasm
|
abnormal Wnt signaling pathway
SOLID PSEUDOPAPILLARY NEOPLASM (endocrine and ductal neoplasms will have membranous staining) |
|
|
IHC to PCP detects what forms?
|
Cysts AND trophs
|
|
|
Skin nodule
+ PAX5, CD99, chromo/synapto + punctate perinuclear CK20 - CK7 |
Merkel cell carcinoma
|
|
|
another name for AMACR
|
p504s. + in prostatic neoplasms
|
|
|
+ CK, p63 lesional cells
+ CD3, CD1a, TdT, CD99 lymphs What if also CD5 & ckit+? |
thymoma
CD5 & ckit are markers for thymic carcinoma |
|
|
CK7-
CK20- CAM5.2+ PAX2+ TTF1- CDX2- CEA- variations? |
RCC
(PAX2 does not stain chromophobe) (chromophobe & papillary RCC are CK7+) |
|
|
Primary HCC stains how:
CK7, CK20, AE1/AE3, Cam5.2, pCEA, HepPar1 How is fibrolamellar variant different? |
CK7-
CK20- focal AE1/AE3 Cam5.2+ pCEA + canalicular HepPar1+ (fibrolamellar variant is CK7+) |
|
|
Phenotype of PEComas?
CK S100 SMA MelanA HMB45 tyrosinase ? |
CK -
S100 - SMA + MelanA + HMB45 + tyrosinase + (50%) |
|
|
What are the limitations of using AEC as a chromogen?
|
It is alcohol soluble and must have an aqueous medium for cover slipping
DAB is preferred, it is alcohol insoluble and forms a brown pigment, but may be a carcinogen |
|
|
Most sensitive IHC in MPNST?
|
Collagen IV
|
|
|
IHC nephrogenic adenoma
|
AMACR, PAX2
|
|
|
Patient population and tumor type of lung cancers with activating EGFR mutations
|
Female
Non-smoker Adenocarcinoma |
|
|
prognostic groups in neuroblastoma
|
Good px:
Hyperdiploidy, no structural chromosomal abnormalities, expression of Trka neurotrophin receptor Unfavorable: Diploid, -1p, -11q, +17q, MYCN amplification Kids < 1 better px unless MYCN amplification |
|
|
ASPL-TFE3 gene fusion see in what 2 tumors?
|
Alveolar soft part sarcoma
Xp11.2 renal cortical tumors t(x;17) |
|
|
Fli1 chromosome
|
11
|
|
|
Name 5 tumors with t(11;22)
|
Ewings/PNET
Desmoplastic small round cell tumor Clear cell sarcoma of soft parts Extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma Myxoid liposarcoma (rarely) |
|
|
Genes involved in alveolar RMS?
|
t(2;13)
PAX3-FOXOA1 (FKHR) high risk subgroup 55% t(1:13) PAX7-FOXOA1 (FKHR) Favorable group 22% can be amplified as double minutes |
|
|
name the cardiomyopathy:
1. dilation of all 4 chambers 2. Hypertrophic septum 3. Thin RV replaced by fat 4. bilateral dilation of atria |
1. dilated CM
- large, flabby heart, viral/EtOH/pp/drug 2. hypertrophic CM - sudden death; haphazard array of myocytes; loose ground substance 3. Arrhythmogenic RV dysplasia - young adults sudden death; familial 4. Restrictive CM - #1 ww: endomyocardial fibrosis (kids, tropics) - US: amyloid, hemochromatosis |
|
|
2 syndromes with cardiac myxomas
|
Carney syndrome
TS |
|
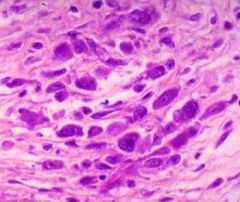
cardiac section
|
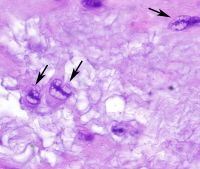
aschoff nodule
Anitschkow cell: caterpillar nucleus! |
|
|
Libman sacks endocarditis
|
BOTH sides of valve
fibrinoid necrosis with lots of POLYS SLE |
|
|
Cardiac myxomas usually occur in the ______ unless associated with a familial syndrome in which case they more commonly occur in the ________
|
LA
RA |
|
|
DDx eos in the heart
|
Toxo
CMV drug |
|
|
Diseases that recur after cardiac transplant
|
sarcoid
chagas giant cell myocarditis amyloid Fabry |
|
|
Best stain for cardiac myxoma vs sarcoma?
|
calretinin (+ in myxoma)
|
|
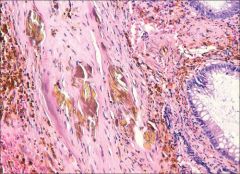
ignore the glands. what is the name for these bodies, and where are they seen?
|
Gamna Gandy bodies
formed by calcific elastic fiber degeneration with hemosiderosis Seen in atrial myxomas, and spleen, associated with cardiac congestion and sickle cell anemia. |
|
|
What cardiac tumor is associated with extramedullary hematopoiesis?
|
myxoma, 10%
|
|
|
most sensitive marker for angiosarc
|
CD31
|
|
|
small vessel vasculitides
|
HSP
Wegeners Churg Strauss MPA Cutaneous leukocytoclastic vasculitis |
|
|
name the classic association in these medium-vessel vasculitides
Giant cell arteritis Polyarteritis nodosa Thromboangiitis obliterans Takayasu |
Giant cell arteritis - polymyalgia rheumatica
Polyarteritis nodosa - HBV Thromboangiitis obliterans - smoking Takayasu - aortic root dilation |
|
|
Which vasculitis is treated with intravenous gamma globulin?
|
Kawasaki disease is an inflammatory disease of the large, medium, and small arteries and affects children younger than 4 years of age. The major risk is the development of coronary artery aneurysm formation with subsequent rupture or thrombosis and possible sudden death. Intravenous gamma globulin is the treatment of choice for preventing coronary artery aneurysm formation and is used in conjunction with aspirin.
|
|
|
Most common primary cardiac sarcoma?
cardiac sarcoma most likely to involve valve? |
Angiosarcoma; RA; TP53 mut
rhabdomyosarcoma; KRAS mutation |
|
|
#1 cause of pulmonary-renal syndrome?
|
ANCA disease (55%)
(anti-GBM disease 5% |
|
|
What type of steatosis is seen in Reyes syndrome, and what is the causative agent?
|
Microvesicular. Also classically seen in HAART therapy
Aspirin |
|
|
What drug classically shows hepatocellular necrosis with inflammation? Antidote?
|
Acetaminophen
N-acetylcysteine |
|
|
Ring granuloma
|
Q fever (rickettsial illness with coxiella)
|
|
|
Name the gene:
HCC Cholangiocarcinoma Liver cell adenoma Alagille |
HCC: p53
Cholangioca: Kras, c-myc LCA: HNF-1a Alagille: Jagged-1 |
|
|
Victoria blue or rhodamine stain of liver
|
Excess copper in liver cells:
Wilson's disease Chronic biliary diseases such as PSC, late state PBC Also HBV |
|
|
What are Mallory bodies composed of?
|
constitutively ubiquitinated cytokeratins 8&18 & other byproducts of cellular stress
can be seen in ASH, NASH, Wilson's.... |
|
|
What liver cell makes fibrosis
|
stellate cell, aka Ito cell, lipocyte
Major vitamin A storage; located in space of disse. Transform to activated myofibroblast cells that make collagen, and then they stain for SMA |
|
|
Megamitochondria are seen in?
|
alcoholic liver disease
|
|
|
what condition has string of beads on radiology and has 10% risk of cholangiocarcinoma?
|
PSC
|
|
|
name 2 syndromes that can have pancreatoblastoma
|
Beckwith Weidemann
FAP |
|
|
Ranson criteria at presentation
48h |
Age, WBC, glucose, LDH, AST
hct, BUN, Ca, base deficit, edema, O2 sat |
|
|
what forms of PCP can be seen on slides?
virulence? |
Cysts - classically
Can see trophs on Diff-Quik with oil immersion Trops attach to type 1 pneumocytes |
|
|
What cell type covers most of the surface area of the lung?
What cell type can replicate in lung injury? What cell type makes surfactant and therefore has lamellar bodies on EM? |
Type 1 pneumocytes cover 97% surface area of the lung, though they are less in number overall
Type 2 pneumocytes are rounded and larger, and can replicate into Type 1 pneumocytes. They make up 60% alveolar cells. Type 2 secretes surfactant, and has lamellar bodies on EM. MUC1 stains Type 2. |
|
|
Associations with avascular necrosis
|
long term steroid use
deep sea diving hemoglobinopathies EtOH Gaucher |
|
|
cytokeratins expressed in synovial sarcoma?
adamantinoma? |
CK8 & 18
CK14 & 19 |
|
|
What GYN tumor is associated with enchondromatosis?
|
Juvenile granulosa cell
|
|
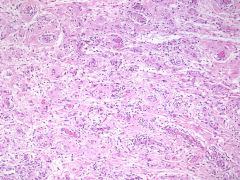
Vulvar lesion
Painless + vimentin, desmin, ER, PR, CD34 |
Angiomyofibroblastoma
Tumor cells are concentrated around vessels Mast cells common |
|
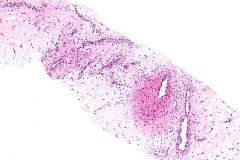
10cm vulvar lesion
+SMA, ER, PR, CD34. desmin |
Aggressive angiomyxoma
Stellate cells, loose matrix, prominent vasculature |
|
|
what cytokine is responsible for causing pulmonary fibrosis?
|
TGF-B
|
|
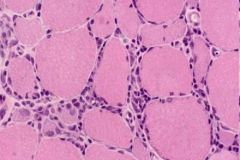
muscle biopsy
|
Polymyositis
ENDOMYSIAL inflammation with CD8+ Tcells |
|
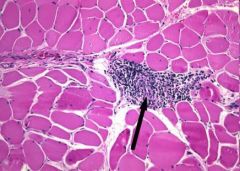
muscle biopsy
what to worry about? |
Dermatomyositis
PERIMYSIAL inflammation with CD4+ Tcells also has perfascicular atrophy 40% associated with paraneoplastic syndrome! |
|
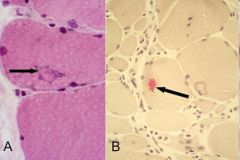
muscle biopsy
|
inclusion body myositis
~ polymyositis in many ways |
|
|
Major difference between myositis and muscular dystrophies?
|
In muscular dystrophy, inflammation is associated with NECROTIC FIBERS
|
|
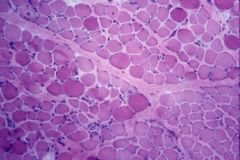
Muscle biopsy
|
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
Endo & perimysial fibrosis Atrophy & hypertrophy = size var Necrotic fibers “Hyaline fibers”: large, dark, glassy Increased internal nuc |
|
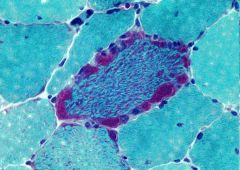
Muscle biopsy
|
Ragged red fibers of mitochondrial myopathy
MERRF (myoclonus epilepsy with RR fibers) MELAS (mitochondrial encephalomyopathy with lactic acidosis & stroke) Kearns-Sayre syndrome |

