![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
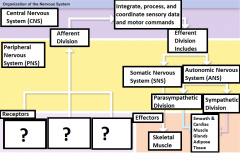
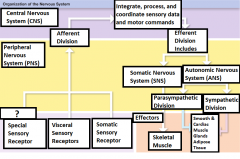
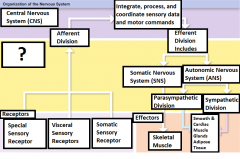
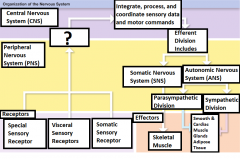
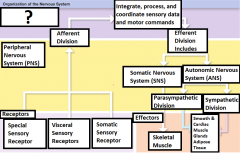
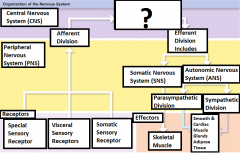
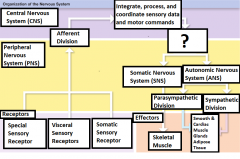
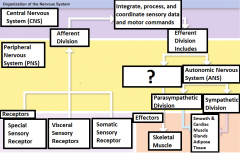
-Special sensory receptors -Visceral sensory receptors -Somatic sensory receptors |
What are the three receptors? |
|
|
Receptor |
Sensory information is carried from here through the PNS into the CNS |
|
|
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) |
Carries motor commands to the CNS |
|
|
Afferent Division |
Part of the PNS that brings sensory information to the CNS |
|
|
Central Nervous System (CNS) |
The brain and the spinal cord |
|
|
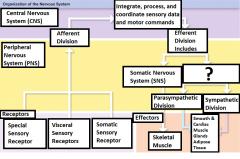
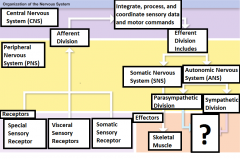
Integrate, process, and coordinate sensory data and motor commands |
The Functions of CNS |
|
|
Efferent division |
Carries motor commands from the CNS to muscles, glands, and adipose tissue |
|
|
Somatic Nervous System (SNS) |
The efferent division of the nervous system that controls voluntary and involuntary (reflexes) skeletal muscle contractions |
|
|
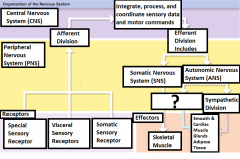
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) |
Controls the contractions of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, glandular secretions, and adipose tissue at the subconsious level |
|
|
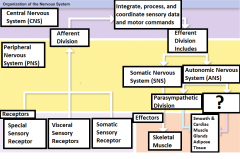
Parasympathetic Division |
Division of the ANS that has a relaxing effect |
|
|
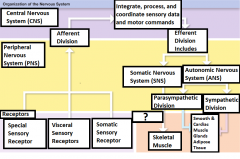
Sympathetic Division |
Division of the ANS that has a stimulating effect |
|
|
Effector |
The target cell or organ that responds to the efferent signal by doing something |
|
|
Smooth muscle, Cardiac Muscle, Glands, and adipose tissue |
Responds to signals sent from the 2 divisions of the ANS |
|
|
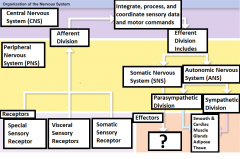
Skeletal Muscle |
The voluntary and involuntary contractions of this are controlled by the Somatic Nervous system |
|
|
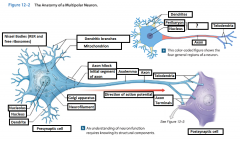
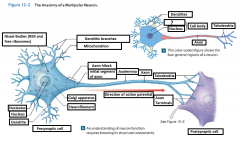
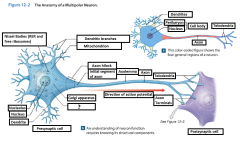
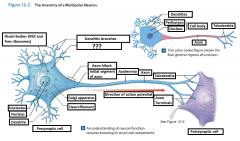
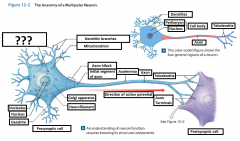
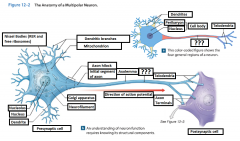
Cell Body |
The body of a neuron; also called soma |
|
|
Perikaryon |
The cytoplasm that surrounds the nucleus in the cell body of a neuron |
|
|
Neurofilaments |
Microfilaments in the cytoskeleton of the perikaryon (or the cytoplasm) of the neuron. |
|
|
Mitochondrion |
Generate ATP to meet the high energy demands of an active neuron |
|
|
Nissel Bodies (RER and free ribosomes) |
Also known as "grey matter" they are areas of the perikaryon that contain clusters of RER and free ribosomes. They are stained darkly and give gray color to areas containing neuron cell bodies. |
|
|
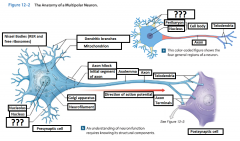
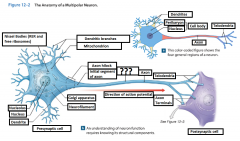
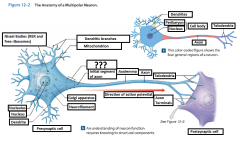
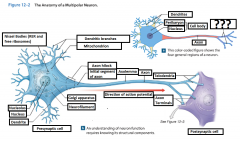
Axon |
is a long cytoplasmic process capable of propagating an electrical impulse known as an action potential |
|
|
Dendrites |
Slender, sensitive processes that extend out from the cell body |
|
|
Axolemma |
A specialized portion of the plasma membrane that surrounds the axoplasm. May be eposed to the interstitial fluid or may be covered by the cellular processes of neuroglia |
|
|
Axon Hillcock |
A thickened region of the neuron that joins the cell body to the Initial segment of the axon |
|
|
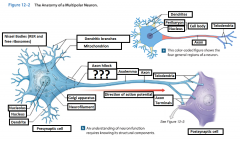
Telodendria |
Terminal axonal branches that end in axon terminals |
|
|
Initial Segament |
The base of the axon that is joined by the axon hillcock |
|
|
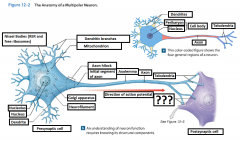
Axon Terminals |
Where the telodendria end, and plays a part in a synapse |
|
|
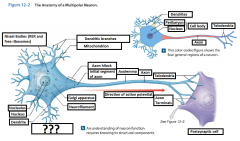
Presynaptic cell |
Sends a message and includes the axon terminal |
|
|
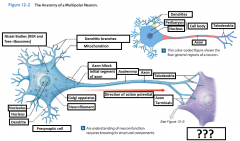
Postsynaptic cell |
Receives the message |

