![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Ligament |
connective tissue that connects two bones |
|
|
tendon |
connective tissue that connects a muscle to a bone |
|
|
Classes of joints |
structural and functional |
|
|
Structural joints |
fibrous cartilaginous Synovial |
|
|
Fibrous Joints |
Bones are joined by dense fibrous CT No joint cavity No movement or slightly movable Three types (Suture, Gomphosis, Syndesmosis) (short collagen fibers, medium, long) |
|
|
Cartilaginous Joints (amphairthroses) |
Articular bones connected by cartilage Lack a joint cavity Not movable or slightly movable two types(synchondroses: hyaline cartilage, Symphyses: fibrocartilage) |
|
|
Synovial Joints (diarthroses) |
Articulating ends Covered with hyaline cartilage and surrounded by a joint cavity containing synovial fluid. Freely Movable Most common type of joint in the body |
|
|
Parts of Synovial Joints |
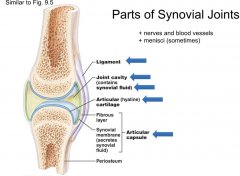
|
|
|
Bursa |
Flattened sac containing synovial fluid around a tendon |
|
|
Tendon Sheath |
elongated bursa that wraps around a tendon |
|
|
Menisci (meniscus) |
Pads of fibrocartilage that act as shock absorbers in a joint |
|
|
High Mechanical Advantage Levers |
Effort arm is longer than the resistance arm Lever moves a big load but the load moves a shorter distance than the effort arm does |
|
|
Low Mechanical Advantage levers |
resistance arm is longer than the effort arm the load moves farther than the effort arm |
|
|
Joint stability and range of motion are determined by... |
Shape of articular surfaces
Ligaments Muscle tendons |
|
|
Synovial Joint types |
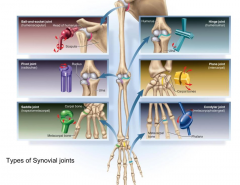
|
|
|
Common Joint Movements |
Flexion and Extension |
|
|
Flexion |
Bending that decreases the angle of the joint |
|
|
Extension |
Returning joint to anatomical position |
|
|
Abduction |
Away from the midline |
|
|
Adduction |
Toward the midline |
|
|
Temporomandibular Joint |
Joint between skull and mandible |
|
|
Glenohumeral Joint |
Shoulder Joint (muscle tendons fused to the joint capsule form the rotator cuff) (Glenoid Labrum: ring of fibrocartilage) |
|
|
Humeroulnar Joint & Humeroradial Joint |
The elbow |
|
|
Coxal Joint |
Hip Joint ( Acetabular labrum: cartilage lip that deepens the socket) |
|
|
Tibiofemoral Joint |
Knee (fibular and tibial collateral ligaments, Anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments) |
|
|
Lateral Blows to the Knee often damage... |
The three C's: Collateral ligaments, cruciate ligaments, and cartilages |
|
|
Talocrural Joint |
Ankle |
|
|
Tendonitis |
inflamed tendon |
|
|
Sprain |
torn ligament or tendon
|
|
|
Bursitis |
Inflammation of a bursa |
|
|
Osteoarthritis |
cartilage degenerates as we age |
|
|
Chronic Arthritis |
painful, stiff, inflamed joints Caused by general "wear and tear" of the hyaline cartilage |

