![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
86 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Agency |
The extent to which someone controls their own life |
|
|
Exponential/Growth Decay |
a function that increases |
|
|
Increments |
the difference between two the coordinates of 2 points that are close to each other (a small difference) |
|
|
Delta |
Small difference |
|
|
Slope |
rise/run |
|
|
Parallel Lines |
two linear lines that have the same slope and never intersect |
|
|
Perpendicular Lines |
two linear that have the opposite reciprical slope and intersect once at 90 degree angle |
|
|
Point Slope Equation for a line |
y-y2=m(x-x2) |
|
|
General Linear Equations |
Ax+Bx=C |
|
|
Function |
the values of one variable often depend on the values for another |
|
|
Dependent Variable |
the output (y value) ; depends on something
|
|
|
Independent Variable |
the input (X Value) ; does stand on its own |
|
|
Natural Domain |
The domain is assumed to be the largest set of x values for which the formula gives the real y value |
|
|
Boundary Points |
The end points of an interval |
|
|
Interior Points |
the remaining points inside an intervalOpen Interval |
|
|
Open Interval |
contains no boundary points ; often has open endpoints |
|
|
Closed Interval |
contains all of its boundary points; often has closed endpoints
|
|
|
Even Function |
f(-x)=(x) symmetric about the y-axis |
|
|
Odd functions |
f(-x)= -f(x) symmetric about the origin |
|
|
Compound Formula |
y=P*a^x |
|
|
Asymptote |
is a horizontal or verticle that a line approaches but never cross or touch
|
|
|
Exponential Growth |
Base is greater than 1 |
|
|
Exponential Decay |
When the graph is declining
|
|
|
One to One Function |
When you do the horizontal line test and they don't have the same output |
|
|
Inverse Function |
a function that inverses another function f^-1 |
|
|
Identity Function |
f(x)=x |
|
|
Area of a Circle |
A=πr^2
|
|
|
Circumference of a circle |
2πr |
|
|
Area of a circle |
side^2 |
|
|
Area of a rectangle |
side1 * side 2 |
|
|
Area of a Triangle |
( height * base ) / 2 |
|
|
Pythagorean Thereom |
a^2 + b^2= c^2 |
|
|
logarithm function |
y=a^x (the inverse is |
|
|
base |
bottom of logarithm |
|
|
argument |
inside of a logarithm |
|
|
natural log (ln) |
base of e |
|
|
euler's constant |
irrational number 2.71 |
|
|
General formula tranformtions |
y = A * f[2pi/B (x-c)] + D |
|
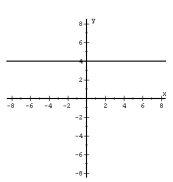
|
f (x) = a |
|
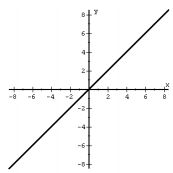
|
f(x) = x |
|
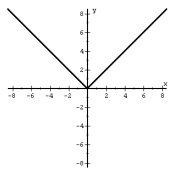
|
f(x) = |x| Absolute Value |
|
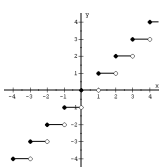
|
f(x) = int ( x ) = [ x ] |
|
|
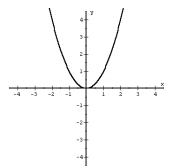
f (x) = x^2 Quadratic |
|
|
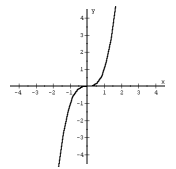
f(x) = x^3 Cubic |
|
|
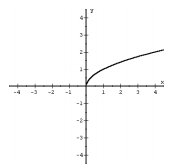
f(x) = sqrt(x) Square Root |
|
|
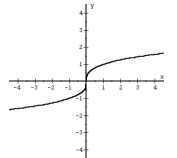
f(x) = 3sqrt(x) Cubic Root |
|
|
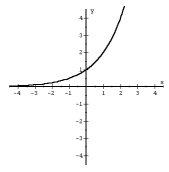
f(x) = a^x |
|
|
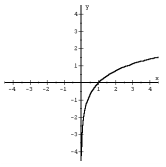
log base of a x Logarithm |
|
|
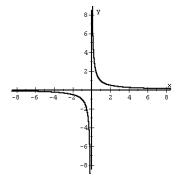
f(x) = 1/x Reciprical |
|
|
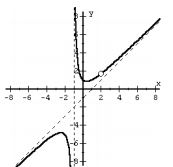
f(x) =[( x^2+1) ( x-2 )] / [( x +1 ) ( x - 2 )] |
|
|
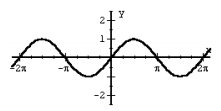
f (x) = sin x |
|
|
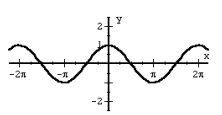
f (x) = cos x |
|
|
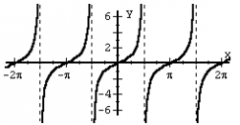
f (x) = tan x |
|
|
Limit |
When I plug-in x-values that get closer and closer to "a" the y-values get closer & closer to a certain number. |
|
|
Lim x-> 0 (sin(x))/x = |
1 |
|
|
Conjugate |
(a-b) --> (a+b) |
|
|
One sided limit thereom |
The limit of a exists if the right and the left side are equal |
|
|
Limit |
The y value that a function approaches as x approaches a |
|
|
Continuity |
The idea of being connected |
|
|
Discontinuity |
Places where a function is "broken" or does not continue |
|
|
Removable Discontinuity |
Where there is not a point in an interval but its at another y-value |
|
|
End Behavior Model |
f(x)/g(x)=1 |
|
|
Secant Line |
a line connecting two points on a function |
|
|
Tangent |
A line that touches a curve without crossing it at that point |
|
|
Average Change |
Find the y-values of both points in interval and find the slope |
|
|
Continuous of a closed interval |
if a function is continuous, you automatically know that every y-value in between gets hit by the function |
|
|
Jump Discontinuity |
Where the limit of the left side does not equal the limit of the right side in a function |
|
|
Oscillating Behavior |
Mostly always sine & cosine (functions is moving up & down) |
|
|
Infinite Discontinuity |
When the limit of the left side or right side of a function is going to infinity |
|
|
Vertical asymptote |
when lim x->a+/- f(x) = +/- infinity |
|
|
Horizontal asymptote |
when lim x-> -/+ infinity f(x) |
|
|
4 different types of End Behaviors |
Infinity, -infinity, constant, and oscillating |
|
|
Limit Premise |
know that both f(x) and g(x) exist to make the limit two separate limits |
|
|
Derivative |
The derivative of f(x) is a function whose output at x is the slope of f at x |
|
|
Primes |
f'(x)= prime of x , f'= f prime, y'= y prime |
|
|
Alternative definition of a Derivative |
Lim x-> a F(x)-f(a) / x-a |
|
|
As the original's function increases, what happens to the y-values of the derivative function? |
The y-values are above the x-axis. |
|
|
If the original function has a vertex, what is happening in the derivative function? |
There is a zero (x-intercept) |
|
|
If the original function is decreasing (y-values getting lower), what happens to the derivative function? |
The y-values are below the x-axis. |
|
|
Units for a Derivative |
The units for y PER the units for x |
|
|
Midpoints between two x-values are calculated by |
X1+X2/2 |
|
|
Difference Quotient |
The limit as h approaches 0 of f(x+h)-f(x) / h |
|
|
Cusp |
The slope approaches infinity on one side and -infinity on the other |
|
|
Corner |
The slope of f(x) on different sides of x=a are different |
|
|
Vertical Tangent |
The slope f(x) approaches infinity or -infinity the same from both sides |
|
|
Discontiniuity |
The derivative fails to exist on one side or both sides |

