![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the main thing that plant cells have but animal cells don't? |
(A) Cell Wall |
|
|
Peroxisomes... |
(perform metabolic reactions, and ) break down substances. |
|
|
Active transport involves.... |
Making energy by going against the gradient. |
|
|
Passive transport involves... |
using energy going through the gradient. |
|
|
Ectotherm's temperatures do/do not depend on their environment |
DO |
|
|
Endotherm's temperatures do/do not depend on their environment |
DO NOT |
|
|
What is a frameshift mutation? |
A mutation that occurs as a result of an addition/deletion of a nucleotide base |
|
|
Which of these ISN'T composed of glucose? a) Starch b) Cellulose c) Glucagon d) Chitin |
Glucagon is a hormone. |
|
|
What is Batesian mimicry? |
Batesian mimicry involves a palatable, unprotected species (the mimic) that closely resembles an unpalatable or protected species (the model). (One example is this fly which looks like a bee. Birds know not to attack a bee as they will be stung.) |
|
|
What is Mullerian mimicry? |
(In Mullerian mimicry, the model is not defined and several unpalatable ) species share warning colors or patterns to evade predation. ( Both models and mimics are toxic. Several species from several different orders may comprise a mimicry complex. The advantage is that the predators need only encounter one form to shun the entire complex.) |
|
|
Aposematic Coloration? |
WARNING coloration |
|
|
Do fungi OR ferns need fertilization? |
Ferns need fertilization, fungi do not. |
|
|
As a zygote, is a fungus diplod, or haploid? |
(It is the only cell in the fungus that is ) DIPLOID |
|
|
What is the product of meiosis? |
4 haploid daugther cells, each with 10 chromosomes, (with each chromosome having only 1 DNA molecule.) |
|
|
If a cell has 20 chromosomes, then, after meiosis there will be __ number of chromosomes in each of the __ cells? |
10 chrom, 4 cells. |
|
|
What's a Detritivore? |
(Detritivore, also known as detritophages, detritus feeders, detritus eaters, or saprophages, are) heterotrophs that obtain nutrients by consuming (detritus (decomposing plant and animal parts as well as faeces) |
|
|
What organelle is involved in the development of spindle fibers in cell division? |
The Centriole |
|
|
What is an example of an organism from Kingdom Monera? |
Monera is a kingdom that contains unicellular organisms (with a prokaryotic cell organization, such as bacteria.) |
|
|
What purpose does RNA polymerase serve in DNA replication? |
NONE! |
|
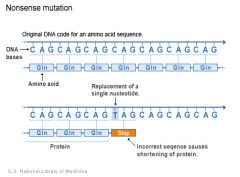
What is happening here? |
(Nonsense mutation (illustration) A nonsense mutation is also a change in one DNA base pair. (Instead of substituting one amino acid for another, however, the altered DNA sequence prematurely signals the cell to stop building a protein. This type of mutation results in a shortened protein that may function improperly or not at all.) |
|
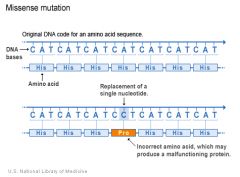
What is happening here? |
(Missense mutation (illustration) This type of mutation is a change in one DNA base pair that results in the substitution of one amino acid for another in the protein made by a gene. |
|
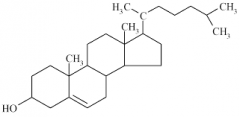
|
Cholesterol, which makes steroid hormones. |
|
|
What is Purine? |
a colorless crystalline compound (with basic properties, forming uric acid on oxidation. (Adenine and Guanine are purines) |
|
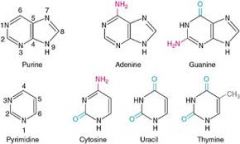
All of these structures are involved with what? |
DNA |
|
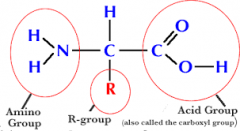
What is this? |
A protein(... DUH) |
|
|
Which of these diseases is genetic? Huntingtons, Turner's, Hemophilia. What do all of them do? |
HUNTINGTONS: An inherited condition in which nerve cells in the brain break down over time Turner Syndrome: A chromosomal disorder that affects only females Hemophilia: A disorder in which blood doesn't clot normally |
|
|
What is Fibrosis? |
Fibrosis is the formation of excess fibrous connective tissue in an organ |
|
|
What do you know about the Blastula? |
(The blastula (from Greek βλαστός (blastos), meaning "sprout") is a hollow sphere of cells, (referred to as blastomeres, surrounding an inner fluid-filled cavity called the blastocoele formed during an early stage of embryonic development in animals.) |
|
|
Give an example of adaptive radiation. |
The finches of the Galapagos Islands provide a classic example of adaptive radiation(—the evolutionary process through which a single lineage gives rise to species occupying diverse environmental niches.) |
|
|
What is pressure potential? |
In a plant cell, pressure exerted by the rigid cell wall that limits further water uptake. |
|
|
Miller and Urey performed an experiment that "proved" this theory of origin. |
The lightning spark theory |
|
|
The theory of panspermia has to do with life originating on earth by.... |
An object from elsewhere in space colliding, or coming into contact with earth. |
|
|
Do invertebrates have specific or non-specific immune systems? |
Nonspecific |
|
|
What is the chromosomal basis of inheritance? |
Genes have a specific loci (specific location of a gene) |
|
|
List the two (main) important extracellular signaling molecules. |
Neurotransmitters and hormones (like insulin) |
|
|
Explain a signal transduction cascade. |
Activation of the receptor transmits the signal (but not the signaling molecule) to the first in a series of enzymes inside the cell, which in turn activates others, until the ultimate enzyme (or enzymes) is reached that causes the final response. |
|
|
What is substrate level phosphorylation |
Substrate-level phosphorylation is directly phosphorylating ADP with a phosphate and energy provided from a coupled reaction. SLP will only occur if there is a reaction that releases sufficient energy to allow the direct phosphorylation of ADP. |
|
|
What is Oxidative phosphorylation |
Oxidative phosphorylation is when ATP is generated from the oxidation of NADH and FADH2 and the subsequent transfer of electrons and pumping of protons. That process generates an electrochemical gradient, which is required to power the ATP synthase. |

