![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
161 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
The term bone can refer to |
A tissue, an organ or a type of cell |
|
|
|
Joints |
Bind bones Allow bones to grow Enable body parts to move |
|
|
|
Joints are also called |
Articulations |
|
|
|
Classifying joints as synarthrotic, amphiarthrotic, or diarthrotic represents |
The degree of movement possible at the joint |
|
|
|
Types of fibrous joints include |
Syndesmosis, suture, and gomphosis joints |
|
|
|
A suture is an example of a |
Fibrous joints |
|
|
|
A tooth root attached to a jawbone by a periodontal ligament is a |
Gomphosis |
|
|
|
The joint between adjacent vertebral bodies is a |
Symphosis that is amphiarthrotic |
|
|
|
Cartilagenous joints are connected by |
Hyaline cartilage or fibrocartilage |
|
|
|
A fibrous joint in which an interosseous ligament binds bones is a |
Syndesmosis |
|
|
|
A gomphosis is a _____ joint |
Fibrous |
|
|
|
A synchondrosis |
Allows bone growth |
|
|
|
Which of the following is not a type of fibrous joint |
Symphosis |
|
|
|
Trochanter (greater/lesser) Only found in proximal femur |
"Runners" Bumps on limbs to grab tendons |
|
|
|
Teres |
Round or cylindrical |
|
|
|
The longest bone of the body is the |
Femur |
|
|
|
Bag of synovia |
Bursae |
|
|
|
Coracoid |
Isn't sharp |
|
|
|
Acromion |
Spine of the scapula |
|
|
|
Croinoid |
Is sharp |
|
|
|
Ligament |
Attach bone to bone |
|
|
|
Tendon |
Attach muscle to bone |
|
|
|
Bones of a synovial joint are held together by |
A joint capsule |
|
|
|
Bones of a synovial joint are held together by |
A joint capsule |
|
|
|
Greg trips over a toy and experiences a sharp pain his physician diagnosis a torn meniscus Greg has injured his |
Knee joint |
|
|
|
Bones of a synovial joint are held together by |
A joint capsule |
|
|
|
Greg trips over a toy and experiences a sharp pain his physician diagnosis a torn meniscus Greg has injured his |
Knee joint |
|
|
|
Articular cartilage receives oxygen and nutrients from |
Surrounding synovial fluid |
|
|
|
A joint capsule is reinforced by |
Ligaments binding articular ends of bones together |
|
|
|
Fluid filled sacs containing synovial fluid are called |
Bursae |
|
|
|
Calcaneus |
Heel bone |
|
|
|
So Long Top Part Here Comes The Thumb |
Scaphoid Lunate Triquetrum Pisiform Hamate Capitate Trapezoid Trapezium |
|
|
|
Cuneiform |
Wedge like |
|
|
|
Toes |
Navicular |
|
|
|
Toes |
Navicular |
|
|
|
Hands |
Sciff |
|
|
|
Cuboid |
Hold up the fourth and fifth digit |
|
|
|
The number of bones in the human body is |
206 but it varies some people lack certain bones or others have extra |
|
|
|
Greenstick fracture |
Is incomplete and occurs on the convex surface of the bone |
|
|
|
Greenstick fracture |
Is incomplete and occurs on the convex surface of the bone |
|
|
|
Fissured fracture |
Incomplete longitudinal break |
|
|
|
Greenstick fracture |
Is incomplete and occurs on the convex surface of the bone |
|
|
|
Fissured fracture |
Incomplete longitudinal break |
|
|
|
Comminuted fracture |
Complete fracture and fragments the bone |
|
|
|
Transverse fracture |
Complete and occurs at a right angle to the axis of the bone |
|
|
|
Oblique fracture |
Complete fracture that Occurs at an angle other than a right angle |
|
|
|
Spiral fracture |
Occurs by excessive twisting of bone |
|
|
|
Osteoporosis |
When bones break easily because bone matrix is lost faster than it is replaced |
|
|
|
Osteopenia |
Is not as serious as osteoporosis |
|
|
|
Long bones |
Longitudinal axes and expanded ends |
|
|
|
Short bones |
Are cube like with equal lengths and widths |
|
|
|
Short bones |
Are cube like with equal lengths and widths |
Sesamoid bones |
|
|
Flat bones |
Plate like structures with broad surfaces |
|
|
|
Short bones |
Are cube like with equal lengths and widths |
Sesamoid bones |
|
|
Flat bones |
Plate like structures with broad surfaces |
|
|
|
These kinds of bones can contain air filled sinuses which are lined with mucous membranes |
Irregular Flat |
|
|
|
The structure that covers the outer surface of bones and serves as an attachment site for tendons and ligaments |
Periosteum |
|
|
|
The growing zone of a bone is known as |
Epiphyseal plate |
|
|
|
These bones are classified as irregular |
Vertebrae and sphenoid |
|
|
|
These are all one shapes except |
Regular bone |
|
|
|
This hormone stimulates an increased number of osteoclasts which increases blood calcium levels |
Parathyroid |
|
|
|
This hormone stimulates an increased number of osteoclasts which increases blood calcium levels |
Parathyroid |
|
|
|
Vitamin c deficiency causes this disorder which is characterized by ulcerations, hemorrhage, and poor wound healing |
Scurvy |
|
|
|
This hormone which is secreted by the anterior pituitary, increases bone growth by stimulating interstitial cartilage growth and appositional bone growth |
Growth hormone |
|
|
|
This hormone which is secreted by the anterior pituitary, increases bone growth by stimulating interstitial cartilage growth and appositional bone growth |
Growth hormone |
|
|
|
This kind of tissue has many small spaces, is found mainly in the epiphysis and is arranged into trabeculae |
Cancellous (spongy) bone |
|
|
|
These kinds of fractures are complete fractures in which the bone breaks into multiple pieces |
Communited |
|
|
|
If a fracture occurs in the diaphysis of a long bone the structure that forms between the ends of the bone as well as the medullary cavity is called this |
Internal callus |
|
|
|
This process of bone repair requires the longest amount of time |
Bone remodeling |
|
|
|
( true/false) the definition of bone remodeling is the construction of bone around blood vessels forming an osteon |
False |
|
|
|
Bone remodeling is involved in |
Bone growth Changes in bone shape Calcium regulation in the body Bone repair |
|
|
|
When a fracture is healing these cells move into the fracture site and tear down the damaged bone |
Osteoclasts |
|
|
|
Growth in bone width occurs in this order |
1 osteoblasts lay down bone to form ridges with grooves in between 2 grooves are changed into tunnels 3 concentric lamellae are made 4 an osteon is produced |
|
|
|
In this zone of the epiphyseal plate new cartilage is produced as the Chondrocytes divide and form stacks of cells |
Proliferation |
|
|
|
This can be said of intramembraneous ossification |
1 it forms the frontal and parietal bones 2 fontaneles are found between skull bones 3 osteoblasts lay down matrix around collagen fibers |
|
|
|
Bones produced by intramembraneous or endochondral ossification are indistinguishable because both initially produce woven bone which is then remodeled (true/false) |
True |
|
|
|
Endochondral ossification begins at this time |
During fetal development |
|
|
|
(True/false) nutrients travel to osteocytes in this order |
1 blood vessels in the medullary cavity 2 central canal 3 canaliculi 4 perforating canals 5 cytoplasm of osteocytes (False) |
|
|
|
Osteochondral progenitor cells give rise to |
Osteoblasts Chondroblasts |
|
|
|
The flexible strength of bone is attributed to |
Collagen fibers |
|
|
|
Chondrocytes receive nutrients in this manner |
Diffusion through matrix |
|
|
|
In hyalin cartilage the cells that produce new matrix are called |
Chondroblasts |
|
|
|
These joints have no joint cavity and exhibit little or no movement |
Fibrous |
|
|
|
These joints have no joint cavity and exhibit little or no movement |
Fibrous |
|
|
|
These specialized joints consists of pegs that fit into sockets and are held together by regular collagenous connective tissue |
Gomphoses |
|
|
|
The joint found between intervertebral discs is |
Symphysis |
|
|
|
This extensions of a synovial membrane extends as a pocket to provide a cushion between structures that would rub against each other |
Bursa |
|
|
|
These are all hinge joints found between these bones except |
Femur and tibia Phalanges Humerus and ulna radius Not Atlas and axis |
|
|
|
(True/false) flexion at the knee moves the leg in an anterior direction |
False |
|
|
|
This movement consists of moving a structure in a gliding motion in an anterior direction |
Protraction |
|
|
|
Abduction of the fingers will do this |
Spread them apart |
|
|
|
This movement of the forearm will allow you to hold a bowl of soup in your hands |
Supination |
|
|
|
These movements will move the right upper limb from the anatomical position to touch the right side of the head with the fingertips |
Shoulder flexion/ elbow flexion Shoulder abduction/elbow flexion |
|
|
|
The shoulder joint is a ball and socket joint between the head of the humorous and glen kid activity (fossa) of the scapula |
True |
|
|
|
Glenoid cavity |
Is a fossa of the scalula |
|
|
|
These movements are possible at the temporomandibular joints except |
Depression Protraction Excursion Not rotation |
|
|
|
Temporomandibular joint |
Is a modified hinge |
|
|
|
The following describe the elbow joint |
Hinge Can produce rotation Olecranon bursa covers olecranon process Surrounded by joint capsule |
|
|
|
The following describe the elbow joint |
Hinge Can produce rotation Olecranon bursa covers olecranon process Surrounded by joint capsule |
|
|
|
This structure helps to stabilize the shoulder joint |
Rotator cuff muscles |
|
|
|
The following describe the elbow joint |
Hinge Can produce rotation Olecranon bursa covers olecranon process Surrounded by joint capsule |
|
|
|
This structure helps to stabilize the shoulder joint |
Rotator cuff muscles |
|
|
|
This statement about a shoulder dislocation is true |
-Most common dislocated joint -Usually occurs inferior to the axilla -axillary nerve can be damaged |
|
|
|
The hip joint is an ellipsoid (condyloid) joint, which is a modified ball and socket joint |
False |
|
|
|
Ball and socket joint |
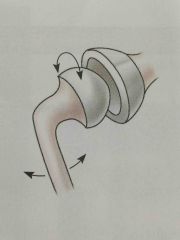
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Condylar joint |
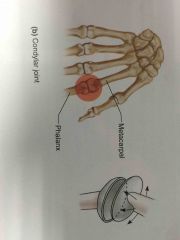
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Plane joint |
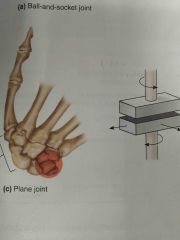
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Hinge joint |
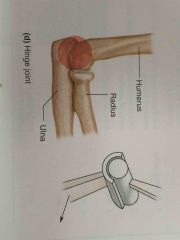
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Pivot joint |
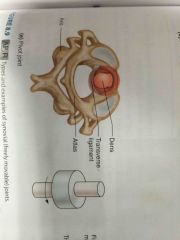
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Saddle joint |
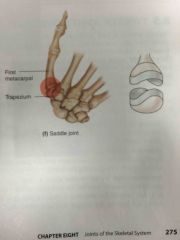
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Abduction and adduction |
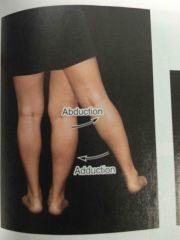
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Dorsiflexion and plantarflexion |
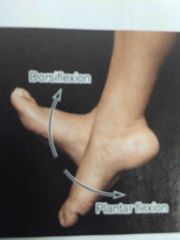
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Flexion and extension |
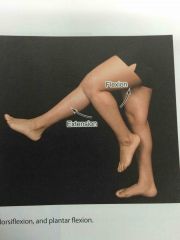
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Circumduction |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Medial and lateral rotation |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Supination and pronation |
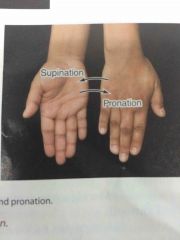
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Inversion and eversion |
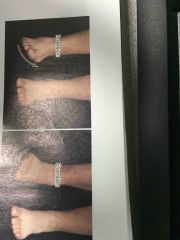
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Protraction and retraction |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Elevation and depression |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Synovial joints are |
Ball and socket or spheroidal joints -condylar joint or ellipsoidal joint -plane or gliding joint -hinge joint -pivot or trochoid joint -saddle or sellar joint |
|
|
|
Three type of joints are |
Fibrous Cartilagenous Synovial |
|
|
|
In some elderly when a suture becomes ossified, two bones grow together to become a single bone this is called |
Synostosis |
|
|
|
The ulnar collateral ligament and radial collateral ligament are found in this joint |
Elbow |
|
|
|
This condition is a severe form of arthritis that is an autoimmune attack against the joint tissue |
Rheumatoid arthritis |
|
|
|
These are all results of the aging of joints except |
Ligaments and tendons stretch
-Production decline of synovial fluid -production decline of new matrix -tissue repair slows |
|
|
|
Supination and pronation |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Inversion and eversion |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Protraction and retraction |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Elevation and depression |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
The hip joint is formed by these bone features |
Femoral head and acetabulum |
|
|
|
This movement is produced at the knee joint |
Flexion and extension |
|
|
|
A sprained ankle is most often a result of |
Torn calcaneofibular ligament |
|
|
|
This ligament can be torn when the knee receives a blow to the anterior surface or if it is hyperextended |
ACL (anterior cruciate ligament) |
|
|
|
The thumb joint is a |
Saddle joint |
|
|
|
Fascia |
Muscle covering |
|
|
|
Fascia |
Muscle covering |
|
|
|
Aponeuroses |
Fibrous sheets |
Cover the skull and the abdomen |
|
|
Epimysium |
Surrounds skeletal muscle |
|
|
|
Epimysium |
Surrounds skeletal muscle |
|
|
|
Perimysium |
Separates the muscle tissue into small sections |
|
|
|
Epimysium |
Surrounds skeletal muscle |
|
|
|
Perimysium |
Separates the muscle tissue into small sections |
|
|
|
Endomysium |
Houses a muscle fiber |
|
|
|
Transverse process |
Extend laterally |
|
|
|
Transverse process |
Extend laterally |
|
|
|
Spinous process |
Extend posteriorly |
|
|
|
Epimysium |
Upon |
|
|
|
Epimysium |
Upon |
|
|
|
Perimysium |
Around |
|
|
|
Epimysium |
Upon |
|
|
|
Perimysium |
Around |
|
|
|
Endomysium |
Within |
|
|
|
Sarcomere |
Striations that form a repeating band |
|
|
|
Acetylcholine |
Neurotransmitter involved in moving muscle |
|
|
|
Action potential |
Conducts electrical potential |
|
|
|
Axon |
Bowl full of neurotransmitter |
|
|
|
Sodium |
Electrifies a membrane |
|
|
|
Creatine phosphate |
Stores energy that quickly converts ADP to ATP |
|
|
|
Latent period |
Brief period of time between stimulation and beginning of contraction May last less than 2 milliseconds |
|
|
|
Creatine kinase |
Changes Creatine to phosphocreatine and back |
|
|
|
Tubercle |
Is on the humorous |
|

