![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Hematocrit |
the volume percentage of red blood cells in blood. |
|
|
|
Heparin |
medication which is used as an anticoagulant |
|
|
|
Centrifuge |
Spinning blood so it separates. |
|
|
|
3 parts if whole blood after centrifuge (anticoagulant) |
•Plasma - no cells •Buffy Coat - WBC and Platelets •Pallet -RBC |
|
|
|
Males have more hematocrit |
Males ~ 47% Fenales ~ 42% Because males have testosterone. |
|
|
|
2 parts after centrifuge |
•Serum - ions, other protwins, etc.. •Pallet - RBC, WBC, Platelets, and clotting proteins. |
|
|
|
Serum - |
It's plasma minus proteins/factors |
|
|
|
HbA1C Test |
Determines (pictures of) long term blood sugar control. |
|
|
|
Glycosylated |
When sugars attaches to a proteins making glycoprotein |
|
|
|
Normal HbA1C level |
~6% aka 6% of the hemoglobin in blood has sugar attached. 9%is high |
|
|
|
Blood Typying with A, B, AB, and O |
A = A antigen - antiB antibody B = B antigen - antiA antibody AB = Both - No antibody O = None - both antibody |
|
|
|
Anti A antibody |
Y-shaped protein produced mainly by plasma cells that is used by the immune system to neutralize pathogens such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. |
|
|
|
RhoGAM |
Used to prevent an immune response of Rh positive blood in people with an Rh negative blood type. |
|
|
|
HDN (Hemolytic Disease of the New Born) |
•When a Rh- mom is pregnant with a newborn that is Rh+. •Occurs on second pregnancy. •If Rh+ enters mom, she creates antibodies. |
|
|
|
Erythropoiesis |
RBC production |
|
|
|
Possible Reasons for Hypoxia |
•Low hemoglobin •Low O2 in high altitude •Low RBC |
|
|
|
Hypoxia |
a condition in which the body or a region of the body is deprived of adequate oxygen supply at the tissue level. |
|
|
|
Erythropoietin |
a glycoprotein cytokine secreted by the kidney in response to cellular hypoxia. |
|
|
|
Erythropoietin process |
Erythropoietin-> Red Bone Marrow (Stem Cells)-> Erythroblasts-> Reticulocytes-> Erythrocytes |
|
|
|
Retic Count |
measures the number of new red blood cells in your body. |
|
|
|
Intrinsic Factor |
•A glycoprotein produced in stomache mucose of the stomach. It is necessary for the absorption of vitamin B12. •May be low in elderly. |
|
|
|
Pernicious Factor |
One of the most frequent causes of vitamin B12 deficiency; it is often an immune disease. This disease is characterized by chronic inflammation and atrophy (thinning or shrivelling) of the mucous membrane of the stomach and the diminished amount, or total lack, of parietal cells and intrinsic factor. |
|
|
|
pH of Blood Effects ISF |
•pH level is 7.35-7.45 •H+ goes to equilibrium •< 7.35 is considered more acidic=acidosis •> 7.45 is considered alkalosis |
|
|
|
Blood Buffers |
•Proteins in Blood/Plasma •Phosphate Ion System •Carbonate System |
|
|
|
Proteins in Blood (buffers) |
•Greatest •Unregulated Eg. Hemoglobin Eg. Plasma Proteins |
|
|
|
Phosphate Ion System (buffer) |
•Uses a weak acid and base |
|
|
|
Carbonate System |
•Relates CO2 with pH CO2+H2O<--->HCO3-+H+ |
|
|
|
CO2+H2O<-->H2CO3<-->HCO3-+H+ |
Occurs in RBC at lungs, tissues, in kidneys 4 pH, stomache Acid, Pancreas which makes bicarbonate, cerebral spinal fluid for regulation or breathing. |
|
|
|
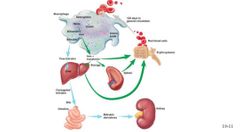
Hb Breakdown |
Hb->Heme->Bilirubin->liver->bile->small intestine->CDON->Feeces or from small intestine->blood->Kidney->urine |
|
|
|
Jaundice |
•increased bilirubin in blood (yellowish cdor) •Decreased function: hepatitis, fatty liver desease, and cirrhosis. |
|
|
|
Neonatal Jaundice |
•increase breakdown of fetal Hb and replaced with adult Hb •Increased bilirubin toxicity to brain •treatment: vit k shot which boosts liver function and uv exposure |
|
|
|
Hemostasis (3x steps) |
(Stops bleeding) •Vascular spasm •Platelet form (not a clot) •Coagulation |
|
|
|
Vascular Spasm |
•increase vasorestiction •more damage causes more effect |
|
|
|
Platelet Forms |
•Normally not sticky •Exposed Collagen + Chemicals from damage tissue activates Platelets which then they become sticky |
|
|
|
Coagulation |
Intrinsic Pathway: •Exposed Collagen •Platelet factors Extrinsic Parhway: •Damaged tissue release chemicals into blood Eg. Tissue factor (Both have a common pathway) |
|
|
|
Contraindication |
•Bleeding disorder •Surgery •Allergic to Asprin |
|
|
|
Thromboxane |
•Promotes Vascular Spasm •Activates Platelets |
|
|
|
Heart: 2 pumps |
•R Side-Pullmonary Circuit •High Flow and Low Pressure •100% CO | 25/8 |
|
|
|
Heart: 2 Pumpss |
Left Side=Systemic Circuit High Flow and high Pressure 100%CO | 120/80 |
|
|
|
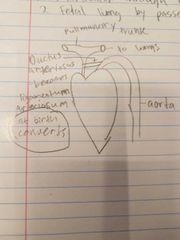
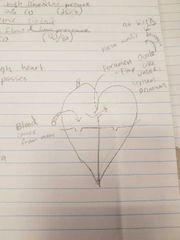
Fetal Circulation Through Heart |
|
|
|
|
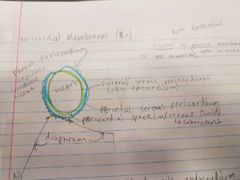
Pericardial Membranes |
•Fibrous Pericardium-inelastic connective tissue •Visceral Serous Pericardium aka epicardium •partial serous Pericardium |
|
|
|
All Blood Vessels are Lined with Endocardium |
True |
|
|
|
Electrical Construction System |
2x of heart tissue 1)Contractil Muscles 2) Autorythmic Conduction Cells-Pacemaker cells that produce AP |
|

