![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Vaporisers Latent heat of vaporisation what is the vaporiser chamber made of? How does the bimetallic strip work? What are the other ways of heat compensation? |
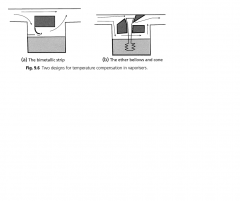
The energy that must be added to a substance to transform a quantity of that substance into a gas. Non-linearly related to the temperature of the liquid. The vaporising chamber made of dense metal with high specific heat capacity and high thermal conductivity to act as a heat to allow heat to move rapidly between the atmosphere and the vaporising chamber. Bimetallic strips: consisting of two metal strips with different coefficients of thermal expansion. Acting as a cap over the bypass chamber or vaporising chamber, As temperature decreases, the strip bends, allowing more fresh gas flow to enter the vaporizing chamber. Aneroid bellows: these are connected by a rod to a cone in the orifice of the bypass chamber. A reduction in temperature causes the bellows to contract, resulting in the cone partially obstructing the bypass channel, increasing flow through the vaporizing chamber. |
|
|
Henry's law Bunsen and Oswald Solubility coefficient Boyle law partition coefficient Saturated Vapor pressure |
Henry - for a fixed temp the solubility of a gas in a liquid, is proportional to its partial pressure in equilibrium with the liquid Bunsen - volume of gas dissolved per litre of liquid at relevant temp, the partial pressure of gas is corrected to std temp and pressure OStwald- volume of gas dissolved per litre of liquid at relevant temp uncorrected. Boyle - PV=k Partition coefficent - ratio of amount of substance in two different phases, when the two phases are equal volume and in equilibrium SVP, At any given temperature, a point of dynamic equilibrium will come to exist where the number of molecules leaving the liquid phase equals the number re-entering it—at this point, the vapour is saturated and the pressure it exerts is known as the saturated vapour pressure (SVP). |
|
|
what is the maximum fractional output concentration in the vaporising chamber? If vaporiser dial is set to 1%, how does output relate to ambient pressure and SVP and dial setting? |
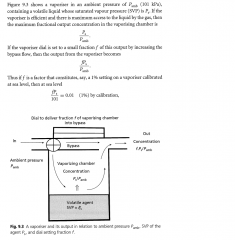
|
|
|
Gastric Acid secretion Mechanism of action of antacid Difference of onset of action of H1 and PPI. |
- |
|
|
Work of breathing Change in Volume pressure curve in asthma |
- |
|
|
Mechanism of action of LA |
- |
|
|
Pharmacogenetics related to sux and codeine |
- |
|
|
CBF, autoregulation, change in pressure autoregulation in brain injury, what happens then? Mechanism of myogenic autoregulation. |
- |
|
|
Coagulation cascade, fibrinolytic mechanism, natural anticoagulation mechanism in body, MOA of tranexamic acid, tPA |
- |
|
|
Angina |
- |
|
|
What is the difference between the sevoflurane and desflurane vaporisor?
|
|
|
|
GTN
|
Pharm
|
|
|
SNP
|
Pharm
|
|
|
Draw a volatile
|
sevoflurane
|
|
|
Sevoflurane
|
-
|
|
|
Desflurane
|
-
|
|
|
TOF
|
-
|
|
|
SUX vs ROC
|
-
|
|
|
Strain gauge
|
-
|
|
|
Draw Wheatstone bridge
|
-
|
|
|
Colligative properties
|
Freezing Boiling point vapour pressure osmotic |
|
|
osmoreceptors mechanism of action
|
-
|
|
|
pressure receptor mechanism of action
|
-
|
|
|
Outline the pharmacology of antimicrobial drugs and their interactions with other drugs used during the perioperative period
|
-
|
|
|
Explain the principles of antibiotic prophylaxis
|
-
|
|
|
Outline the pharmacology of antiseptics and disinfectants, their clinical use and associated risks
|
-
|

