![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
58 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the three phenothiazine drugs? |
Chlorpromazine Fluphenazine Perphenazine |
|
|
What is the thioxanthene drug? |
Thiothixene |
|
|
What is the biphenylbutylpiperdine drug? |
Haloperidol |
|
|
Clozapine, risperidone, olanzapine, quetiapine, ziprasidone, aripiprazole, paliperidone, iloperidone, asenapine, lurasidone.
What drug type? |
Atypical |
|
|
Do dopamine agonists (like amphetamines, methylphenidate, and cocaine) make psychosis more or less severe? |
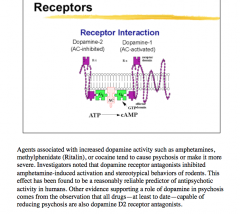
More severe |
|
|
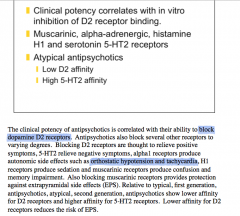
Blocking of D2 receptors correlates to what in regard to psychosis?
Blocking 5-HT2 relieves what?
What do alpha-1 receptor blocks produce?
H1 receptors?
Muscarinic receptors?
|
|
|
|
Comparing typical to atypical psychotics, which produce extrapyramidal side effects? |
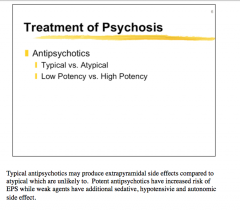
Typical Weak agents => sedative, hypotensive, and autonomic side effect |
|

Typical or atypical antipsychotic? |
Typical |
|

Typical of atypical antipsychotic? |
Atypical antipsychotics |
|
|
Are phenothiazines low or high potency antipsychotics? What does this mean in terms of adverse effects?
Which drug has a piperazine side chain? Potent or not? Adverse effect? |

|
|
|
Is haloperidol high or low potency? |
High potency |
|
|
Clonazine, olanzapine, quetiapine:
Typical or atypical High or low potency What additional receptor effects that may be useful in treating negative symptoms? |

|
|
|
Risperidone: Typical or atypical Antagonist for what two receptors? What does it function as at high dose?
What is the active metabolite of risperidone? Which atypical in this category has limited EPS effects? |

|
|
|
Aripiprazole:
Partial agonist of what two receptor? Agonist of which? Higher or lower incidence of side effects? |

|
|

Thought we didn't have to know these? |

|
|

What syndrome? |
Neuroleptic Syndrome |
|
|
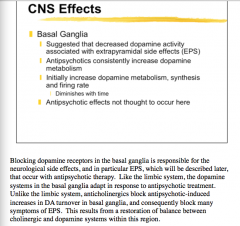
What system is the site of antipsychotic effects? What system adapts to long-term therapy? Do anticholinergics block therapeutic effect (DA turnover)? |

|
|
|
Decreased levels of what is associated with EPS? What is the effect of antipsychotics on dopamine metabolism?
Do anticholinergics block antipsychotic-induced increased in DA turnover in the basal ganglia and thus many symptoms of EPS? |
|
|

What are all of these? |
Extrapyramidal side effects
First four early on |
|

What are these symptoms of?
What is the treatment? |
Acute dystonia
Anticholinergic antiparkinsonian agents (benztropine) |
|

Symptoms of what? Treatment? |

|
|
|
Akinesia, mask facies, decreased arm movement, rigidity, tremor. What syndrome? Treatment?
What will happen if you use L-dopa or bromocriptine? |

|
|

Which syndrome? |
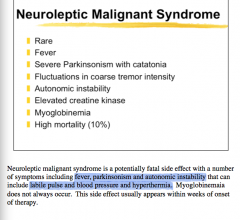
Neuroleptic malignant syndrome |
|
|
What is the treatment of neuroleptic malignant syndrome? |

|
|

|
Perioral tremor |
|

What is the side effect? How long does it take for it to appear? |

|
|
|
Is dopamine metabolism changed or unchanged in the cerebral cortex by long term antipsychotic treatment?
Which drug is more likely to lower seizure thresholds? |

|
|
|
Antipsychotics can ______ (increase or decrease) vasomotor reflexes, but reduced blood pressure is not life threatening. If nausea and vomiting is a result of stimulating dopamine receptors in the chemoreceptor trigger zone, than antipsychotics would be effective in ______ (increase, decrease) this response. Both occur at subtherapeutic doses. |

Antipsychotics can decrease vasomotor reflexes, but reduced blood pressure is not life threatening. If nausea and vomiting is a result of stimulating dopamine receptors in the chemoreceptor trigger zone, than antipsychotics would be effective in reducing this response. Both occur at subtherapeutic doses. |
|
|
Effect of antipsychotics on prolactin secretion? Should try to avoid this in which patients? |
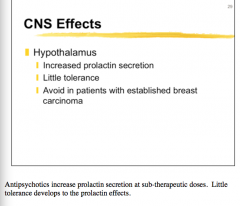
|
|
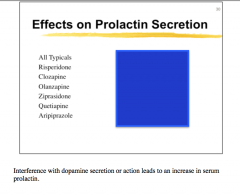
Effect of each on prolactin secretion? |

|
|

What are these all the clinical consequences of? |

|
|
|
Chlorpromazine: Effect on glucose tolerance, and insulin release. Which two atypicals most likely increase risk for type II diabetes? |

|
|
|
Low potency typical antipsychotics may cause what dangerous cardiovascular effect?
Which two drugs are more likely to cause orthostatic hypertension? Which two less likely? |
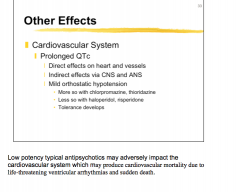
|
|

What type of side effects are these? Do antipsychotics have a high or low therapeutic index? |
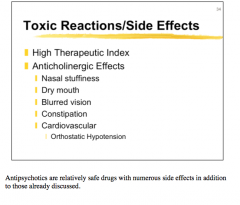
|
|
|
The use of what drug can cause jaundice in the 2nd-4th week? |

|
|
|
The use of clozapine is limited by the risk of what side effect? |

|
|
|
Skin reactions (urticaria or dermatitis) are more common with which two drugs? |
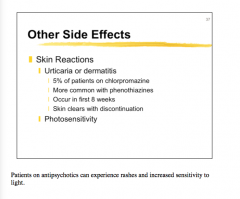
|
|
|
Which two drugs are most likely to cause weight gain?
Which to drugs least likely? |

|
|
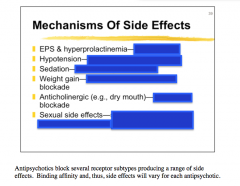
Identify the mechanism of each. |

|
|

Review |

|
|
|
When is peak plasma concentration achieved? What is the elimination half-life? How long does the biological effect usually last? Are plasma concentrations well correlated with therapeutic effect? |

No |
|
|
What is the main route of metabolism? Most metabolites are inactive, but what are the four exceptions? |
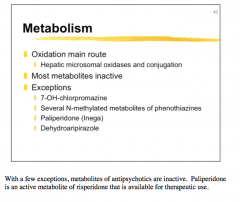
|
|
|
Are these drugs addicting? Do they cause physical dependence? |

|
|
|
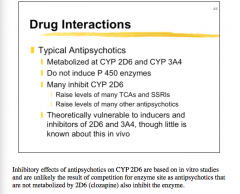
Typical antipsychotics: Metabolized by what two CYPs? Do they induce P450? Do they inhibit CYP 2D6?
|
|
|

What are these the target symptoms of? |

|
|
|
Identify the treatment of each:
Schizophrenia Bipolar disorder with psychotic features Schizoaffective disorder Major depressive disorder with psychotic features |

|
|
|
Treatment of each:
Psychosis due to substance abuse intoxication/withdrawal.
Psychosis due to general medical condition. |

|
|

|

|
|

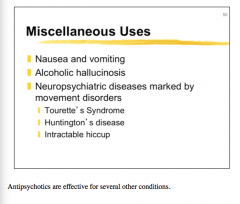
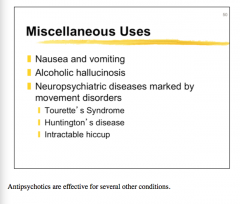
What type of drug would you consider with these patients? |

|
|
|
|
|
|
Haloperidol => week later agitated and having trouble sitting still. What do you do? |
Decrease the dose |
|
|
Which has greatest antimuscaric effect?
Haloperidol Fluphenazine Chlorpromazine Perphenazine |
Chlorpromazine |
|
|
Elderly patient with Alzheimer's consistently agitated. Which would you most likely use to treat patient?
Risperidone Ziprasidone Olanzapine Fluphenazine |
Cardiovascular concern with atypicals in elderly Use fluphenazine = only one that is not atypical |
|
|
19 year old woman, schizophrenia, worried about weight gain with antipsychotic treatment. Which might be a good option for her?
Clozapine Ziprasidone Quetiapine Olanzapine |
Ziprasidone |
|
|
What are atypical antipsychotics most effective in treating?
Positive symptoms Negative symptoms Cognitive deficits Both positive and negative symptoms |
Positive only |
|
|
Which is effective for preventing suicide and may be effective in patients who have not responded to other antipsychotics?
Haloperidol Clozapine Lurasidone Chlorpromazine |
Clozapine
If failed two antipsychotics, always use CLOZAPINE as your third choice. |
|
|
Schizophrenic with severe muscle cramps and torticollis a short time after treatment with haloperidol. What is the best course of action?
Add risperidone Discontinue haloperidol and observe Give oral diphenhydramine Inject benztropine Switch patient to fluphenazine |
Need to give anticholinergic Need to inject benztropine |
|
|
Trifluoperazine => young male with schizophrenia Complains of drug side effect Which would be unlikely to be on his list?
Constipation Disinterest in sex Dizziness upon sudden standing Drooling Difficulty in reading small print |
Drooling
|

