![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
52 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Derive xⁿ |
nxⁿ⁻¹ |
|
|
Derive aˣ |
ln(a)aˣ |
|
|
Derive f(g(x)) |
[f'(g(x))] g'(x) |
|
|
Derive logₐ(x) |
1 x•ln(a) |
|
|
Derive sinx |
cosx |
|
|
Derive cosx |
-sinx |
|
|
Derive tanx |
sec²x |
|
|
Derive secx |
secx•tanx |
|
|
Derive cscx |
-cscx•cotx |
|
|
Derive cotx |
-csc²x |
|
|
Derive tan⁻¹x |
1 (1+x²) |
|
|
Derive sin⁻¹x |
1 √(1-x²) |
|
|
Derive cos⁻¹x |
-1 √(1-x²) |
|
|
Trig sin²θ - 1 = |
cos²θ |
|
|
Trig tan²θ - sec²θ = |
-1 |
|
|
Trig 1 + cot²θ = |
csc²θ |
|
|
Trig sin²θ + cos²θ = |
1 |
|
|
Trig tan²θ + 1 = |
sec²θ |
|
|
Trig csc²θ - cot²θ = |
1 |
|
|
What three Pythagorean trig identities sum to one? |
sin²θ + cos²θ sec²θ - tan²θ csc²θ - cot²θ |
|
|
Trig sin2θ = |
2sinθcosθ |
|
|
Trig cos2θ = |
cos²θ - sin²θ |
|
|
Trig tan2θ = |
2tanθ 1 - tan²θ |
|
|
Trig (Not Pythagorean) sin²θ = |
(1/2) (1 - cos2θ) |
|
|
Trig (Not Pythagorean) tan²θ = |
1 - cos2θ 1 + cos2θ |
|
|
Log rules ln(xy) = |
ln(x) + ln(y) |
|
|
Log rules ln(x/y) = |
ln(x) - ln(y) |
|
|
Log rules ln(xʳ) = |
r•ln(x) |
|
|
Name three types of functions that are continuous everywhere they are defined. |
Polynomials Root functions Trig and inverse trig Exponentials Logs Rational Functions |
|
|
Describe the intermediate value theorem. |
If f(x) is continuous on [a, b] and n is any intermediate value on the y-axis between f(a) and f(b) inclusively, then there is some x value, c, in [a, b] which satisfies f(c) = n. |
|
|
What is the limit form of the derivative of f(x)? |
lim = f(a + h) - f(a) ʰ ⃗ ⁰ h |
|
|
How can you tell is a function f(x) is differentiable on (a, b)? |
Differentiable on (a,b) if f'(c) exists for every c element (a, b) |
|
|
General Newton Method formula: |
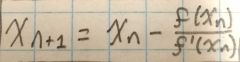
|
|
|
When do you use Newton's method? |
To "home in on" or approximate solutions for x |
|
|
Trig (Not Pythagorean) cos²θ = |
(1/2) (1 + cos2θ) |
|
|
Define a critical number (x = c) for function f(x) |
Any x value, c, within the domain of f for which f'(c) is undefined at x = c or f'(c) = 0 |
|
|
Define Fermat's theorem |
Local max and mins occur at critical numbers. At a local max/min (x = c) then f'(c) = 0 or is undefined |
|
|
Define the Mean Value Theorem |
For f(x) continuous and differentiable on [a, b], then there is some c ∈ [a, b] with f'(c) equal to the rate of change between (a, f(a)) and (b, f(b)). |
|
|
∫xⁿ = |
[(xⁿ⁺¹)/(n+1)] + C |
|
|
∫1 = |
x + C |
|
|
∫cosx = |
sinx + C |
|
|
∫sinx |
-cosx + C |
|
|
∫sec²x |
tanx + C |
|
|
∫secx•tanx |
secx + C |
|
|
∫eˣ |
eˣ + C |
|
|
∫bˣ |
(ln b)⁻¹ • bˣ + C |
|
|
∫ 1 1 + x² |
arctanx + C |
|
|
∫ 1 √(1 - x²) |
arcsinx + C |
|
|
∫ 1 √(1 + x²) |
arccosx + C |
|
|
∫sinhx |
coshx + C |
|
|
∫coshx |
sinhx + C |
|
|
∫1/x |
ln|x| + C |

