![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
List two subgroups in the traditional classification of primates.
|
- PROSIMIAN
- ANTRHOPOIDEA |
|
|
|
What type of classification would a primate with a grasping tail fall into?
|
NEW WORLD MONKEY
|
|
|
|
How do gorillas move around on the ground?
|
QUADRUPEDALLY
or “knuckle walking” |
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of a promiscuous mating system?
|
- Food is largely distributed
- Independent females |
|
|
|
Besides humans, what is the only primate species that lives in cold and snowy climates?
|
MACAQUES
|
|
|
|
Orangutans move about by brachiating and suspension. What are the physical traits of hindlimbs and forelimbs that are involved in this type of locomotion?
|
Longer arms and shorter legs.
|
|
|
|
What is the basic social unit seen in the majority of primates?
|
Mother with dependent offspring.
|
|
|
|
In chimpanzees, which individuals are the dominant members of the community?
|
There are no dominant members of the chimp community.
|
|
|
|
What is it called when a primate leaves its biological family?
What is it called when a primate stays with its biological family? |
DISPERSAL
NATAL |
|
|
|
BABOON BEHAVIOR:
Diet? Location? Habitat? |
Omnivorous
Found in Africa Live in grasslands |
|
|
|
TRUE OR FALSE:
1) Black and white colobus monkeys are leaf-eating monkeys. 2) Black and white colobus monkeys have cheek pouches. |
1 = TRUE
2 = FALSE |
|
|
|
Which subgroup of primates have wet noses?
|
Strepsirrhine
|
|
|
|
What type of non-human primate can have sex with females even when they’re not in estrus?
|
Chimpanzees
|
|
|
|
Prosimians can be both nocturnal and diurnal. Give an example of each.
|
NOCTURNAL = Microcebus (aka. Mouse lemur)
DIURNAL = Lemur catta (aka. Ring-tailed lemur) |
|
|
|
What does natural selection operate on?
What does sexual selection operate on? |
Natural selection → behavioral and physical traits
Sexual selection → reproductive organs |
|
|
|
List two traits that separate apes and monkeys.
|
1) TAIL (apes don’t have them and monkeys do)
2) BODY SIZE (apes are large and monkeys are smaller) |
|
|
|
List three aspects related to sexual dimorphism.
|
1) Polygynous mating system
2) Large body size 3) Terrestrial |
|
|
|
Which family members have the strongest social bonds among primates?
|
Mother and infant
|
|
|
|
Which primate species is classified as both a prosimian and an anthropoid?
|
TARSIER
|
|
|
|
Where do tarsiers live?
|
Southeast Asia
|
|
|
|
List four types of locomotion and give an example of a primate species for each type.
|
1) LEAPING (ex. Sifakas)
2) BRACHIATING (ex. Organgutans) 3) TERRESTRIAL (ex. Baboons) 4) KNUCKLE-WALKING (ex. Gorillas) |
|
|
|
Which primate species have tooth combs?
|
- Lemurs
- Galagos - Tarsiers |
|
|
|
What does intra-sexual selection involve?
|
Male-male combat
|
|
|
|
What classification do New World Monkeys fall into?
|
Platyrrhine
|
|
|
|
List a physical characteristic for spider monkeys, howler monkeys, and capuchin monkeys that makes them each distinctive in the primate world.
|
1) SPIDER → prehensile tail
2) HOWLER → loud call 3) CAPUCHIN → long tail |
|
|
|
Who are chimpanzees’ closest living relative?
|
BONOBOS
|
|
|
|
Which primates belong to the subgroup Anthropoidea?
|
- MONKEYS
- APES - HUMANS |
|
|
|
What is the scientific name for snow monkeys (aka. Macaques)?
|
Macaca fuscata
|
|
|
|
Which primate species display remarkable “cultural” behavior?
|
Macaques
|
|
|
|
TRUE OR FALSE:
1) Prosimians eat insects but most anthropoids don’t. 2) Prosimians are arboreal but most anthropoids aren’t. |
1 = FALSE
2 = FALSE |
|
|
|
Where do each of the following species live?
- Howler monkeys - Gorillas - Ring-tailed lemurs - Bonobos - Siamangs - Orangutans |
- Howler monkeys → Central America
- Gorillas → Africa - Ring-tailed lemurs → Madagascar - Bonobos → Borneo - Siamangs → India - Orangutans → Southeast Asia |
|
|
|
Name two physical traits that differentiate apes from humans.
|
1) Brain size
2) Feet (humans don’t have grasping ability) |
|
|
|
Describe the 5 physical traits that set primates apart from other mammals and explain the functional advantages of each.
|
1) OPPOSABLE THUMBS: tool use and ability to grasp and climb
2) LARGE BRAIN (relative to body size): smarter 3) BINOCULAR VISION: depth perception 4) NAILS (instead of claws): dexterity 5) ERECTED POSTURE: use of hands, extended vision, ability to run faster |
|
|
|
Draw the classification chart that shows the four major primate groups.
|
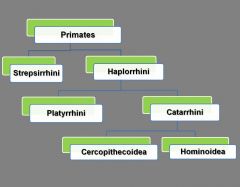
MAJOR GROUPS:
- Strepsirrhini - Platyrhini - Cercopithecoidea - Hominoidea |
|
|
|
How is infanticide a reproductive strategy?
|
It promotes genetic superiority; eliminate competition and ensure that your own genes survive.
|
|
|
|
What are the adaptive advantages of living in social groups?
|
- Defense of resources against rival troops
- Defense against predators = safety in numbers - Social control through dominance hierarchies - Group cohesion achieved through grooming - Protecting/raising young make mother-infant bonds become secure |
|
|
|
Why do primates engage in mutual grooming?
Who is involved? Is it altruism? |
- Mutual grooming = social cement
- Establishing and maintaining bonds and dominance hierarchies - Reconciliation after conflicts - Sign of affection All members of community involved. Can be form of altruism because time spent grooming might have been used for other activities (ex. search for food) |
|
|
|
Explain the patterns of altruistic behavior.
What factors are involved? Give an example from the book. |
ALTRUISTIC BEHAVIOR: benefits the fitness of the recipient at a cost to the fitness of the actor.
- Whether or not you help depends on: relatedness, recipient’s benefits (R), and actor’s costs (A). - Evolves through kin selection: more likely to help if closely related. - Aspects: grooming, sharing food, warning calls, backing up others, etc. - Example: female baboon tries to intervene when a male in her group is being attacked by a hyena. |
|
|
|
Compare reproductive strategies between males and females.
|
FEMALES
- Parental investment: increase offspring’s chances of survival - Promiscuous mating to ensure fertilization - Display secondary sexual characteristics to make themselves more attractive/alert males that they’re ovulating (ex. sexual swelling) MALES - Sperm Competition: amount of sperm that they produce - Male control polygyny: active defense of mates - Resource-defense polygyny: active defense or resources, which attracts females - Male-dominance polygyny: female mate choice |
|
|
|
A number of primate “cultures” are found in both chimpanzees and macaques. Give an example of cultural behavior for each.
|
MACAQUES: developed method for sorting wheat from sand by dropping mixture in water and allowing wheat to float and the sand to sink. Others eventually copied behavior.
CHIMPS: learned to fish termites out of their nests using sticks. Eventually, mothers started teaching it to offspring. |
|
|
|
What aspects are involved in dominance hierarchy?
|
- Mother’s social position
- Age - Intelligence - Motivation - Body mass - Aggression - Time spent in the group - Sex |
MAIM BATS!
|
|
|
Ecology and some skeletal biology are involved in the “Arboreal hypothesis.” Describe the adaptive mechanism of this hypothesis.
|
ARBOREAL HYPOTHESIS: living in trees was most important factor in primate evolution.
- Need depth perception and binocular vision to move through trees, look out for predators, etc. - Need grasping hands and feet with nails instead of claws - Generalized teeth for varying diet |
|
|
|
Describe the reproduction strategy, “scramble competition” that affects sexual dimorphism.
|
Polygyny in which males make no effort to defend individual exclusive mating territories, but instead attempt to outrace their competitors to receptive females.
|
|

