![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
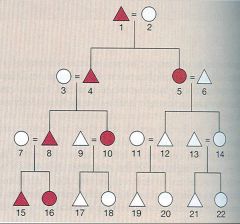
Ambilineal Descent
|
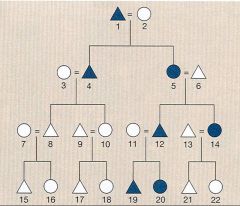
This is a rule of descent that affiliates an individual with kin related to him or her through men or women.
|
Rare & Confusing
|
|
|
Cousins Marriage
|

Triangle-male
Circle-female |
|
|
|
Frequency of different types of Residence Rules.
Which is most common? |
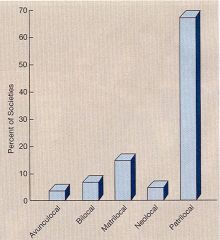
Patrilocal
|
|
|
|
Matrilineal Descent
|
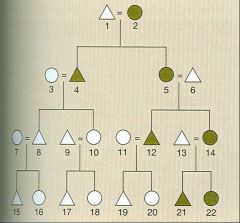
Affiliates an individual with kin of both sexes related to him or her through women only.
|
|
|
|
Model of SocioCultural Change
|
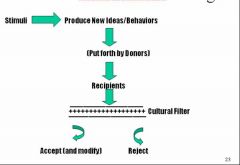
Example: Cumputers created from too much paperwork
|
|
|
|
Patrilineal Descent
|
Affiliates an individual with kin of both sexes related to him or her through men only
|
|
|
|
Socioculture System
|
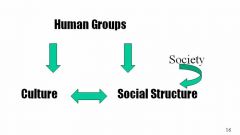
they affect each other
|
|
|
|
The Ecological Base
|
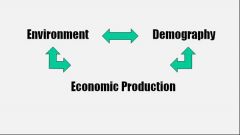
A change in one effects a change in all the others
|
|
|
|
The Evolution of the State
|
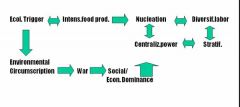
State Evolution
|
|
|
|
Some characteristics of states:
|
Hierarchical and centralized decision making
Urban centers Surplus Large/varied population Full-time craft specialists Military Economic stratification Organized state religion Taxation Written language |
|
|
|
But…This Comes at a Cost:
(States) |
Loss of egalitarian relations
Competition for resources Warfare Stratification within and between city-states |
|
|
|
First States:
|
Susa
Sumer |
|
|
|
First States: Susa
|
In Mesopotamia 5,500 ya
50 settlements divided into three groups: Large center called Susa Three or four “towns” Small villages Clay seals for trading |
|
|
|
Sumer
|
Sumer was in area of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers.
7,000-5,000 is formative period with population shifts due to irrigation By 5,500 ya there are cities By 5,000 ya all of Sumer is unified Sumerian empire. Capital is Warka |
|
|
|
Achievements of Sumerians
|
Great urban centers
Elaborate system for the administration of justice Sewer systems Specialized crafts (e.g., jewelry making, leather working, metallurgy, sculpture, etc.) Wheeled wagons, sailboats, horse-drawn chariots Much social stratification |
|
|
|
5,000 yo Sumerian Ziggurats
|
An example of monumental architecture
They were places of worship and centers for food distribution This structure in Warka had a temple up top |
|
|
|
At Sumer, the first writing was found
|
around 5,000 ya in the form of cuneiform.
|
|
|
|
States developed in other parts of the world a little later
|
Teotihuacan
a great state in Mesoamerica |
|
|
|
Rise of Teotihuacan
|
Formative period from 3,000 to 2,300 ya
Small villages above valley By 2,300 and 2,200 ya small elite centers in valley 2,150 ya a few thousand people in villages in the valley By 1,500 ya (A.D. 500) there are well over 100,000 |
|
|
|
The Mayan
|
Replica of an elite person’s burial from the Mayan site of Tikal
This person was buried in a special funeral vault lined with jaguar and ocelot skins as well as 16 lbs of jade ornaments such as the necklace, headdress, and ear spools shown here |
|
|
|
Consequences of State Formation
Is “civilization” better? |
Larger and denser populations
Coordinated information Control access to land Freedom from direct food production Art, music, and literature Organized religion |
|
|
|
Downfalls of Civilization
|
Monopoly of force
Inequality Poor health Warfare |
|
|
|
What Happened to These States?
|
Environmental Degradation Theory
Overextension Theory Theory of Internal Conflicts |
|

