![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Osgood Schlatter Disease |
The disruption of the epiphesal plate at the tibial tuberosity. Chronic and reoccurring pain during adolescence, especially in young athletes. |
|
|
Anterior compartment of the thigh |
Quadriceps and sartorius Innervated by the femoral nerve Supplied by the femoral artery |
|
|
Sartorius |
Proximal Attachment- Anterior superior illiac spine Distal attachment- superior medial tibia Action- Lateral rotation and flexion at knee and hip joints. |
|
|
Quadricepts and proximal attachments |
Proximal Attachments Rectus femoris-anterior inferior illiac spine, illium Vastus lateralis-greater trocanter femur Vastus medialis-intertrocanter line Vastus intermedius- Anterior, lateral femur. |
|
|
Quadriceps- Distal attachment and action |
Distal attachment- Quadriceps tendon to patellar ligament to tibial tuberosity Action- extend the leg at the knee (rectus femoris helps flex at hip) |
|
|
Femoral nerve |
L2,L3,L4 Anterior thigh, pectinius, illacus |
|
|
Psoas Major |
Proximal Attachment- T12-L5 vertebrae Distal attachment- converges into iliopsoas, lesser trocanter Innervation- Anterior Ramni of L2,L3,L4 Action-Flex and laterally rotate the thing, bilaterally flexes the trunk. |
|
|
Illiacus |
Proximal Attachment- illiac fossa, crest Distal attachment- converges into illiopsoas, lesser trocanter Innervation femoral nerve Action-flex and laterally rotates the thigh, Bilateral trunk flex. |
|
|
Cutaneous distribution of the femoral nerve |
Anterior cutaneous branches of femoral nerve Innervate skin of the thigh. Saphenous nerve Innervates skin of the medial aspect of the leg and foot |
|
|
Muscles of the medial compartment of the thigh |
Adductor magnus Adductor longus Adductor brevis Pectineus Gracilias Obturator externis |
|
|
Things of note about adductor magnus |
It has an adducter part and a hamstring part. It is a very large muscle and it contains perforations for the passage of the perforating branches of the femoral artery |
|
|
Adductor Magnus-adductor component |
Proximal attachment- ischopubic ramnus Distal attachment- posterior proximal femur, medial linea aspera Innervation-Obturator nerve Action- Adduct the thigh (helps medially rotate) |
|
|
Adductor Magnus- Hamstring component |
Proximal attachment- ischeal tuberosity Distal attachment- adducter tubercle of femur Innervation- tibial division of sciatic nerve |
|
|
Riders bones |
Ossification of adductor tendons from chronic use and irritation, inflammation, and ultimately ossification. |
|
|
Path of the Obturator Nerve |
The obturator nerve (L2,3,4) descends along the posterior abdominal wall medial to the psoas muscle. It enters the medial thigh (with the obturator artery) via the obturator canal, divides into an anterior & posterior branch before innervating most of the adductor muscles and obturator externus muscle. |
|
|
Cutaneous innervation by the obturator nerve |
Innervates a small patch of skin on the inner thigh |
|
|
Adductor longus and brevis |
Proximal attachment- pubis Distal attachment- linea aspera Innervation- obturator nerve Action- adducts thigh |
|
|
Pectineus |
Proximal attachment- Pectineal line of pubis Distal attachment- femur, inferior to lesser trocanter Innervation- Femoral nerve Action- Adducts and flexes the thigh |
|
|
Gracilis |
Proximal attachment- pubis Distal attachment- superior medial surface of tibia Innervation -obturator nerve Action- adducts thigh(helps flex leg medially rotate the knee) ** Can be surgically transplanted with nerves and vessels to replace damaged structures in forearm and hand |
|
|
Obturator externis |
Proximal attachment- external surface of obturator membrane Distal attachment- trocanteric fossa Innervation- Obturator nerve Action- external rotation of femur |
|
|
Pes Anserinus |
sartorius, gracilis & semitendinosus tendons as they attach inferior to the medial side of the knee joint on the tibia. All 3 of these muscles flex the knee
|
|
|
Nerves of the anterior thigh |
The saphenous nerve runs through the adductor canal but not through the adductor hiatus. The femoral nerve also sends a muscular branch through the adductor canal to the vastus medialis It also does not traverse the adductor hiatus! |
|
|
Blood Supply to the anterior and medial thigh |
The deep femoral artery gives off lateral and medial circumflex femoral arteries as well as three of four perforating arteries that pass through the adductor magnus to supply the anterior thigh. lateral circumflex femoral supplies the anterior thigh along with muscular branches directly off the deep femoral artery. |
|
|
The femoral sheath |
The femoral sheath is a funnel shaped tube of fascia deep to the inguinal ligament The femoral Nerve is NOT in the sheath. The femoral sheath is subdivided into three compartments. (lateral) femoral artery, femoral vein, lymph canal (medial) |
|
|
The femoral triangle |
Superior border-inguinal ligamnet medial border- adductor longus lateral border- sartorius roof- fascia lata, skin floor- muscle contents- NAVL (femoral verve artery, vein, lymph) |
|
|
Clinical relevance- femoral triangle and artery |
Femoral pulse can be palpated inferior to midpoint of inguinl ligamnet with patient supine. If femoral artery is to be ligated circumflex arterie supply May compress artery against femur head to stop bleeding in a trauma. |
|
|
Adductor canal |
Lateral border- vastus medialis Medial border- sartorius Posterior border- adductor longus and magnus contents- femoral artery and vein, saphenous nerve, nerve to vastus medialis |
|
|
Femoral hernia |
Occurs inferior to the inguinal ligament- a loop of small intestine can protrude into the femoral canal |
|
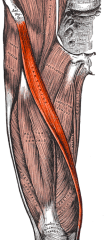
|
Sartorius |
|
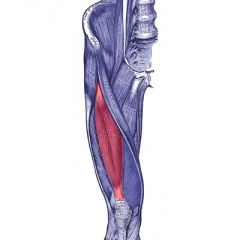
|
Rectus femoris |
|
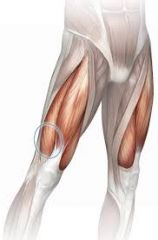
|
Vastus lateralis |
|
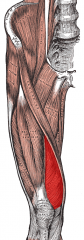
|
Vastus medialis |
|
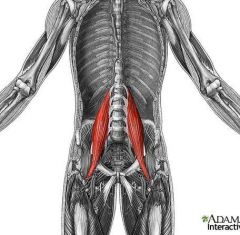
|
Psoas major |
|
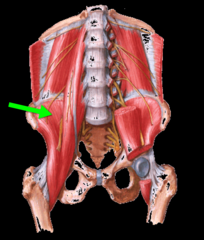
|
Illiacus |
|
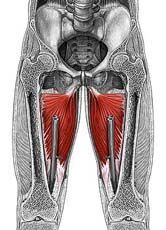
|
Adductor magnus |
|
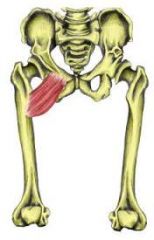
|
Pectinius |
|
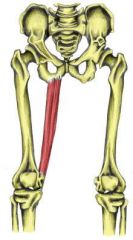
|
Gracilis |

