![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the anterior abdominal wall? |
The area between the rib cage and the pelvis |
|
|
How are the quadrants drawn for the anterior abdomen? |
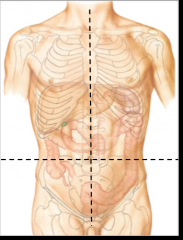
vertical line is drawn at the midline of the body through the middle of the sternum and belly button and the horizontal line is drawn through the belly button |
|
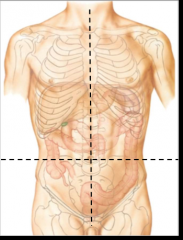
name these quadrants |
-Right upper -Right lower -Left upper -Left lower |
|
|
How would you split the abdomen into regions? |
-Draw two verticle lines at the middle of the clavicles -One horizontal line will be drawn at the bottom of the rib cage (superiorly at the subcostal plane) -Another horizontal line will be draw at the top of the iliac crest (inferiorly at the intertubercular plane) -This will create 9 regions |
|
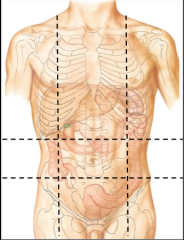
name these regions |
R. hypochondriac R. Lumbar R. Iliac Epigastric Umbilical Hypogastric L. Hypochondriac L. Lumbar L. Iliac |
|
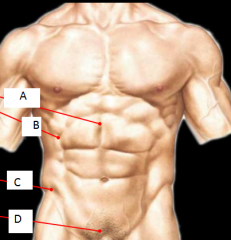
Name these superficial palpations |
A- Linea alba B- Linea semilunarus C- Anterior superior iliac spine D- Pubic tubercle |
|
|
What are the muscles that you will be able to palpate on the anterior abdominal wall? |
-rectus abdominus -External oblique |
|
|
What are the bony landmarks that we will be able to palpate on the anterior abdomen? |
-costal arch -Sternum (xyphoid) -Anterior superior iliac spine -Pubic tubercle |
|
|
What are the three bones of the pelvis? |
-Ilium -Ischium -Pubis |
|
|
When do the three bones of the pelvis fuse? |
puberty |
|
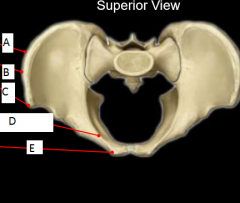
|
A- Iliac crest B- Iliac tubercle C- Anterior superior iliac spine D- Pectin pubis (pectineal line) E- Pubic tubercle |
|
|
Describe the borders of the anterior abdominal cavity |
From: Costal arch coming from ribs 6-10 and the xyphoid process To: Iliac crest and inguinal ligament (stretching from anterior superior iliac spine to pubic tubercle) |
|
|
What are the functions of the abdominal wall? |
-Protection and stabilization of the abdominal contents -Trunk rotation and flexion (helps maintain posture) -Maintain and control intra-abdominal pressure for parturition (child birth) and defecation -Respiration: opposes diaphragm during exhalation |
|
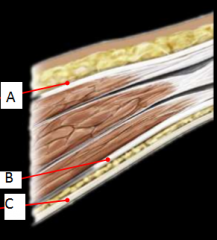
What are the layer of the anterior abdominal wall? |
-Skin A- Subcutaneous fascia (campers and scarpa's fascia) -Muscle layers covered in aponerotic tendinous fascia B- Transversalis Fascia C- Peritoneum (serous layer; mesentery) |
|
|
Describe camper's fascia |
Adipose (fatty) layer coursing with cutaneous nerves and blood vessels |
|
|
Describe Scarpa's Fascia |
Membranous fascial layer deep to the camper's fascia. Becomes Dartos fascia in scrotum and Colles' fascia in perineum |
|
|
What are the 4 muscular layers of the abdomen? |
-External oblique -Internal oblique -Rectus abdominis -Transversus abdominis |
|
|
External oblique: -Origin -Insertion -Action -Innervation |
-Origin: external surface of ribs 5-12 -Insertion: Linea alba, pubic tubercle, and anterior half of iliac crest -Action: compress and support abdominal viscera; flex and rotate the trunk -Innervation: Thoraco-abdominal nerves (anterior rami of T7-T11) and subcostal nerve (T12) |
|
|
Internal oblique: -Origin -Insertion -Action -Innervation |
-Origin: Thoracolumbar fascia, anterior 2/3 of iliac crest, and connective tissue deep to inguinal ligament -Insertion: Inferior borders of rubs 1-12, linea alba and pubis via conjoin tendon -Action: Compress and support abdominal viscera; flex and rotate trunk -Innervation: Thoraco-abdominal nerves (anterior rami of T7-T11) and first lumbar nerve (L1) |
|
|
Transversus abdominus: Origin: Insertion: Action: Innervation: |
-Origin: Internal surfaces f tibs 7-12 costal cartilages, thoracolumbar fascia, iliac crest, and connective tissue deep to inguinal ligament -Insertion: Linea alba wit aponerosis of internal oblique, pubic crest and pectin pubis via conjoin tendon -Action: Compress and support abdominal viscera -Innervation: Toraco-abdominal nerves (anterior rami of T7-T11) and first lumbar nerve (L1) |
|
|
Rectus abdominis: Insertion: Action: Innervation: |
-Origin: Pubic symphysis and pubic crest -Insertion: Xiphoidprocess and costal cartilages 5-7 -Action: Flexes trunk(lumbar vertebrae) and compresses abdominal viscera (can act as an antagonist to the diaphragm. Stabilizes andcontrols pelvic tilt (antilordosis) -Innervation:Thoraco-abdominal nerves (anterior rami of inferior six thoracic nerves)| |

