![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
107 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The ____ is a part of respiratory system ONLY and contributes to upper respiratory pathway. (unlike the pharynx which is both).
|
larynx
|
|
|
the larynx is a Musculoligamentous structure with a ____ framework.
|
cartilaginous
|
|
|
The larynx Lies at the level of ____ thru ____ vertebral bodies
|
C3-C6
|
|
|
the larynx Connects ____ to the oropharynx with the trachea.
|
inferiorly
|
|
|
the larynx Opens into the pharynx _______.
|
posteriorly
|
|
|
What are three SINGLE cartilages of the larynx?
|
1. cricoid 2. thyroid 3. epiglottic
|
|
|
What are three PAIRED cartilages of the larynx?
|
1. arytenoid 2. corniculate 3. cuneiform
|
|
|
The larynx is highly mobile and can be moved by extrinsic muscles. During swallowing, the larynx is moved ___ and ____ by these muscles
|
superior and anterior
|
|
|
Superior part of which larungeal cartilage lies at the level of C4?
|
thryoid cartilage
|
|
|
Lamina of the thyoid cartilage unite anteriorly, forming a laryngeal prominence. Angle between the prominence is sharper (___ degrees) in men than in women (____ degrees).
|
90, 120
|
|
|
____ horns of the thyroid cartilage articulate with the cricoid cartilage (cricothyroid joints) – rotation and gliding causing changes of the length of vocal folds
|
Inferior
|
|
|
Thryoid cartilage - Superior border and superior horns attach to the hyoid bone by ____ membrane.
|
thyrohyoid
|
|
|
which laryngeal cartilage forms a full circle?
|
Cricoid cartilage
|
|
|
the ___ cartilage has a Thin arch anteriorly and broad lamina posteriorly.
|
Cricoid cartilage
|
|
|
The cricoid cartilage Attaches to the thyroid cartilage by median cricothyroid (can be palpated) and to the 1st tracheal ring by what?
|
cricotracheal ligaments
|
|
|
What part of the cricoid cartilage has 1. –Depressions for posterior crico-arytenoid muscles 2.–Ridge for attachment of the esophagus 3. –Facets for articulation with other laryngeal cartilages
|
lamina
|
|
|
which laryngeal cartilage Has a base that articulates with the lamina of the cricoid?
|
Arytenoid (Greek for “ladle shaped”)
|
|
|
which laryngeal cartilage Has a Muscular process for crico-arytenoid muscles?
|
Arytenoid (Greek for “ladle shaped”)
|
|
|
which laryngeal cartilage Has a Vocal process for vocal ligaments?
|
Arytenoid (Greek for “ladle shaped”)
|
|
|
which laryngeal cartilage Has an apex that articulates with the corniculate cartilages, and vestibular ligaments?
|
Arytenoid (Greek for “ladle shaped”)
|
|
|
what is the function of the Corniculate cartilages?
|
ligamentous attachment for extra leverage on Arytenoid
|
|
|
What laryngeal cartilage Is suspended in the fibroelastic membrane that attaches the arytenoid to the epiglottis?
|
Cuneiform (wedge shaped) cartilages
|
|
|
Vocal ligaments attach to vocal process of arytenoid and posterior surface of _____ cartilages.
|
thyroid
|
|
|
which joint provides Possible movement at – latero – medial sliding, antero-posterior tilting and rotation (movements provide approximating, tensing and relaxing of vocal cords ?
|
CRICOARYTENOID JOINT
|
|
|
what are found Between the junction of the lamina of the thyroid and vocal processes of both arytenoids?
|
VOCAL LIGAMENTS
|
|
|
What are the submucosal skeleton of the vocal folds?
|
Cricovocal membrane (conus elasticus) - Vocal ligaments
|
|
|
Cricovocal membrane (conus elasticus) has laterally extending what?
|
lateral cricothyroid ligaments. These attach to the vocal ligaments.
|
|
|
Conus elasticus and overlying mucosa close the tracheal inlet (subglottic area) except for the ___ ____
|
rima glottidis
|
|
|
which cartilage is Leaf-shaped?
|
epiglottis
|
|
|
which cartilage is Attached to the thyroid (thyro-epiglottic ligament) and hyoid (hyo-epiglottic ligament)?
|
epiglottis
|
|
|
the epiglottis Projects _______
|
posterosuperiorly
|
|
|
The pharyngeal aspect of the tongue related to the anterior surface of which laryngeal cartilage?
|
epiglottis
|
|
|
the ____ membrane is between arytenoid and epiglottis and its free inferior margin forms vestibular ligaments (skeleton of vestibular folds).
|
Quadrangular
|
|
|
Superior margin of the _____ membrane is ary-epiglottic ligament
|
Quadrangular
|
|
|
epiglottis is posterior to the tongue and ____ to laryngeal inlet and provides the defense during swallowing
|
anterior
|
|
|
what membrane Spans between the thyroid cartilage and the hyoid bone?
|
Thyrohyoid membrane
|
|
|
what membrane Has a lateral opening for superior laryngeal arteries, nerves, and lymphatics?
|
Thyrohyoid membrane
|
|
|
What membrane Attaches the ant. surface of the epiglottis to the hyoid bone?
|
Hyo-epiglottic ligament (singular)
|
|
|
what ligament Attaches the cricoid cartilage to the trachea?
|
Cricotrachael ligament
|
|
|
The ____ ligaments define the internal laryngeal architecture. They are composed of two parts: lower cricothyroid and upper quadrangular membrane
|
intrinsic
|
|
|
which ligament is Attached to the cricoid cartilage below and ends in a free upper margin within the thyroid cartilage?
|
Lower cricothyroid ligament
|
|
|
The free upper margin of the lower cricothyroid ligament attaches to what posteriorly and anteriorly?
|
Posteriorly, the vocal part of the arytenoid cartilage. Anteriorly, the inner surface of the thyroid cartilage
|
|
|
The free upper margin of which ligament thickens to form the vocal ligament?
|
Lower cricothyroid ligament
|
|
|
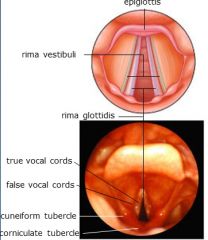
When surrounded by mucosa, the vocal ligaments are the (true or false) vocal cords?
|
TRUE
|
|
|
what membrane attaches the epiglottis to the lateral surface of the arytenoid cartilages and the corniculate cartilages, bilaterally?
|
Upper quadrangular membrane
|
|
|
the free lower margin is thickened to form the vestibular ligament which forms the (true or false) vocal cords when surrounded by mucosa, these also attach to the inner surface of the thyroid cartilage.
|
FALSE
|
|
|
because the vestibular ligament is lateral to the vocal ligament, when viewed from above, the false vocal cords are lateral to the TRUE OR FALSE vocal cords.
|
TRUE
|
|
|
Laryngeal Cavity Divisions (Vestibule, Middle Part, Infraglottic Space) is the upper chamber between the laryngeal inlet and vestibular folds?
|
Vestibule
|
|
|
Laryngeal Cavity Divisions (Vestibule, Middle Part, Infraglottic Space). Which one is between the vestibular and vocal folds?
|
Middle Part
|
|
|
Laryngeal ventricles & saccules - between vocal folds the mucosa bulges, thus creating saccules. What is numerous here?
|
numerous mucous glands secrete mucus to lubricate the focal cords
|
|
|
Laryngeal Cavity Divisions (Vestibule, Middle Part, Infraglottic Space). which one is between true vocal folds and trachea?
|
Infraglottic space
|
|
|
When viewed from above, there are two slit-like (rima) openings in the larynx. The apex of the triangle is ___ and the base is ____. (anterior or posterior)
|
anterior, posterior
|
|
|
Rima _____ is the triangular space between vestibular folds.
|
vestibuli
|
|
|
Rima ____ is the triangular space between vocal folds.
|
glottidis
|
|
|
Both the rima vestibuli and rima glottidis can be opened and closed by the movement of ___ and ____ cartilages and ____ constriction
|
arytenoid, thryoid, vestibular
|
|
|
what do the Cricothyroid Muscles do?
|
During speech, these pull the thyroid cartilage anterior and down, thereby tensing the vocal cords.
|
|
|
What are the only intrinsic laryngeal muscles innervated by the superior laryngeal branches of the vagus nerves (CN X)
|
Cricothyroid Muscles
|
|
|
Besides the Cricothyroid muscles, all other intrinsic laryngeal muscles are innervated by which nerve/branch?
|
the recurrent laryngeal branch.
|
|
|
Damage to which nerve would result in flaccid vocal cords and a monotonous, low pitch to the voice?
|
the superior laryngeal nerve, (since the rest of the intrinsic laryngeal muscles, NOT cricothyroid , are innervated by the recurrent laryngeal).
|
|
|
what are The only muscles that open the glottis?
|
Posterior Crico-Arytenoid Muscles
|
|
|
Posterior Crico-Arytenoid Muscles - innervation?
|
They are innervated by the recurrent laryngeal branch of the vagus nerve
|
|
|
Posterior Crico-Arytenoid Muscles - origin and insertion?
|
Originate in the depression on the posterior lamina of the cricoid cartilage. Insert on the muscular processes of the arytenoid cartilages
|
|
|
Posterior Crico-Arytenoid Muscles - action?
|
They laterally rotate and abduct the arytenoid cartilages, thereby widening the rima glottidis
|
|
|
Lateral Crico-Arytenoid Muscles - innervation?
|
They are innervated by the recurrent laryngeal branch of the vagus nerve
|
|
|
Lateral Crico-Arytenoid Muscles - origin and insertion?
|
Originates from the arches of the cricoid cartilage. Insert - Attach to the muscular processes of the arytenoid cartilages
|
|
|
Lateral Crico-Arytenoid Muscles - action?
|
They abduct and internally rotate the arytenoid cartilages, thereby narrowing the rima glottidis
|
|
|
what is the unpaired laryngeal muscle that is attached to the posterior surface of the aretynoid cartilages?
|
Transverse arytenoid muscle
|
|
|
Transverse arytenoid muscle - action?
|
Adducts the arytenoid cartilages, closes rima glottidis
|
|
|
Transverse arytenoid muscle - innervation?
|
Innervated by the recurrent laryngeal branch of the vagus nerve
|
|
|
what laryngeal muscle Runs between the muscular process of one arytenoid cartilage to the apex of the other? (criss-cross)
|
Oblique arytenoid muscles
|
|
|
Oblique arytenoid muscles - action?
|
Are helpful in narrowing the laryngeal inlet
|
|
|
Oblique arytenoid muscles - innervation?
|
Innervated by the recurrent laryngeal branch of the vagus nerve
|
|
|
what muscle Runs lateral to and parallel with each vocal ligament (Attached to the thyroid and arytenoid cartilages adjacent to the vocal ligaments)?
|
Vocalis Muscles
|
|
|
Vocalis Muscles - action?
|
Adjust tension in the vocal folds
|
|
|
Vocalis Muscles - innervation?
|
Innervated by the recurrent laryngeal branch of the vagus nerve
|
|
|
which laryngeal muscle Originates on the inner surface of the thyroid cartilage and Attaches to the anterolateral surface of the arytenoid cartilages?
|
Thyro-Arytenoid Muscles
|
|
|
Thyro-Arytenoid Muscles - innervation
|
Innervated by the recurrent laryngeal branch of the vagus nerve
|
|
|
Thyro-Arytenoid Muscles - action?
|
Vestibular sphincter. shortens and relaxes vestibular and vocal ligaments. Also can rotate aretynoid cartilage medially to approx vocal folds and close rima glottidis.
|
|
|
Which laryngeal muscles are broad and lateral to the quadrangular membrane, so they can act as a sphincter of the vestibule?
|
Thyro-Arytenoid Muscles
|
|
|
if I take a deep breath, (forced inspiration), what cartilage rotates laterally, and by the action of what muscle?
|
Arytenoid cartilages are rotated laterally by the posterior crico-arytenoid muscles, As a result, the vocal folds are abducted and the rima glottidis widens
|
|
|
in Quiet respiration, the rima's are open, as well as the laryngeal inlet and vestibule. The aretynoid cartilages are in what position?
|
abducted.
|
|
|
in phonation, The arytenoid cartilages and vocal folds are _____ (abducted OR adducted) and air is forced through the narrow opening
|
adducted
|
|
|
the adduction of the aretynoid cartilages and vocal folds produces a vibration and sound that can be modified by what?
|
upper parts of the airway and oral cavity
|
|
|
in phonation, Tension of the vocal cords is adjusted by which two different muscles?
|
the vocalis and cricothyroid muscles
|
|
|
Effort Closure - Occurs when air is retained in the thoracic cavity to stabilize the trunk, or to increase intra-abdominal pressure. The rima glottidis and vestibuli are both ______ closed as is the lower parts of the vestibule
|
completely
|
|
|
in swallowing, The rima glottidis and vestibuli are closed and the laryngeal inlet is _____
|
narrowed
|
|
|
in swallowing The larynx moves in which direction?
|
up and forward
|
|
|
in swallowing, The epiglottis swings in which direction?
|
downward toward the arytenoid cartilages. This action causes the esophagus to open.
|
|
|
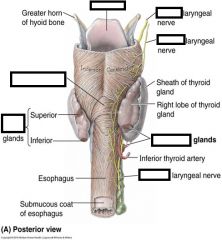
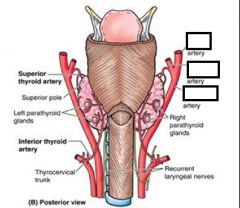
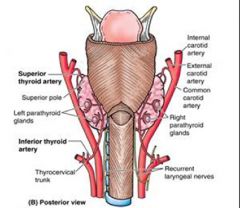
which artery Branches off the superior thyroid artery near the upper border of the thyroid cartilage? (It accompanies the superior laryngeal nerve through the thyrohyoid membrane to reach the larynx)
|
Superior laryngeal artery
|
|
|
Which artery Branches off the inferior thyroid artery Accompanies the recurrent laryngeal nerve as it ascends in the groove between the esophagus and trachea? (It enters the larynx deep to the inferior constrictor muscle of the pharynx)
|
Inferior laryngeal artery
|
|
|
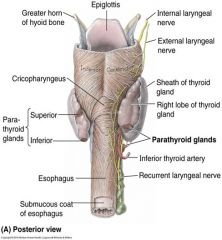
the superior laryngeal nerves originate from the inferior vagal ganlgia and descend ____ to the internal carotid artery.
|
medial
|
|
|
the superior laryngeal nerves originate from the inferior vagal ganlgia and descend medially to which artery?
|
internal carotid artery
|
|
|
Near which bone, do the superior laryngeal nerves divide into internal and external branches?
|
hyoid bone
|
|
|
Which nerve penetrates the thryoid membrane after branching from the superior laryngeal nerve?
|
internal laryngeal nerve
|
|
|
Internal laryngeal nerve Passes anteroinferiorly, from its division from the superior laryngeal nerve, then penetrates what?
|
the thyroid membrane
|
|
|
the _____ laryngeal nerve, is mainly sensory and supplies the laryngeal cavity down to the vocal folds
|
internal. (branch of the superior laryngeal nerve)
|
|
|
which nerve after dividing from the superior laryngeal nerve, descends along the lateral wall of the pharynx?
|
external laryngeal (a branch of the superior laryngeal nerve)
|
|
|
which nerve enters the larynx by piercing the inferior constrictor muscle?
|
external laryngeal (a branch of the superior laryngeal nerve)
|
|
|
what nerve innervates the cricothyroid muscle?
|
external laryngeal (a branch of the superior laryngeal nerve)
|
|
|
Sensory to the laryngeal cavity below the vocal folds is by which nerve?
|
Recurrent laryngeal nerves
|
|
|
motor to all intrinsic laryngeal muscles, except the cricothyroid, is by which nerve?
|
Recurrent laryngeal nerves
|
|
|
what regulates secretion of the thyroid gland?
|
pituitary gland
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
|
|

