![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
12 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what is a radiculopathy?
|
Sensory or motor dysfunction caused by injury to a nerve root or spinal nerve
|
|
|
a dorsal root radiculopathy will cause sensory or motor disturbances?
|
sensory
|
|
|
a ventral root radiculopathy will cause sensory or motor disturbances?
|
motor
|
|
|
radiculopathies are usually caused by what?
|
vertebral disc herniations
|
|
|
What is the autonomous zone of the C6 spinal nerve dermatome?
|
the pad of the thumb
|
|
|
In a radiculopathy, are the muscles paralyzed or weak?
|
weak. a radiculopathy only affects one spinal nerve, causing a loss of sensory in a specific dermatome (which do overlap but have autonomous zones of no overlap), but, because of the great overlap of the myotomes, often other nerves would be able to allow muscles to work poorly and not be fully paralyzed.
|
|
|
what is a peripheral nerve injury called?
|
a neuropathy. at this far down in the nerves, you have a mixture of the spinal nerves, leading to multiple nerve loss and possible paralysis.
|
|
|
In a diabetic, numbness and tingling in both feet is a sign of what?
|
"glove and stocking" patterns indicate a diabetic neuropathy.
|
|
|
What kinds of motor deficits are found with neupathies?
|
neuopathies cause muscle paralysis, atrophy, and fasiculations in muscle - as multiple spinal nerves are affected, and overlap wont allow just weakness.
|
|
What is this picture showing?
|
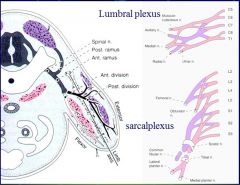
This is a helpful diagram showing development of muscles into two axis.
The preaxial mass pink gives rise to flexors, adductors and medial rotators. Hug chest like native american indian hello. The postaxial mass purple gives rise to extensors, abductors, and lateral rotators. Jesus christ The trunks give off anterior and posterior divisions. The anterior divisions innervate muscles derived from the preaxial mass. The posterior divisions innervates muscles derived from the postaxial mass. Keep this in mind when trying to pair muscles with nerves and visa versa. It becomes very important when trying to understand motor deficits involving many muscles - but really only a single movement. |
|
|
A 20-year-old man was attacked while walking down 14th Street in Bradenton. The attacker’s thin knife blade penetrated the man’s right coracobrachialis muscle. Bystanders chased the attacker away before he could inflict further damage and the man was rushed to the emergency department at Manatee Memorial. On arrival, bleeding from the small puncture wound was stopped and the man was examined. He had complete inability to flex his right elbow or supinate his hand. In addition, he had a complete loss of sensation over the lateral aspect of his forearm. He had no other sensory or motor deficits.
Where is the injury? What is the most likely cause of this injury? How would you record this injury in the patient’s record? |
Where is the injury? Musculocutaneous nerve
What is the most likely cause of this injury? transection of the nerve as it passes through the coracobrachialis m. How would you record this injury in the patient’s record? Traumatic musculocutaneous neuropathy |
|
|
While working out, a 40-year-old man feels a sharp pain in the left side of his neck and sudden weakness in his left upper limb. His wife takes him to the emergency department and an examination reveals loss of sensation over the lateral aspect of his left shoulder and weakness on abduction of his left upper limb and flexion at his elbow. He cannot retract his left scapula. Adduction against resistance of his left upper limb is unaffected. There are no other sensory deficits. Sensation in his left hand and digits is intact. He has no other deficits.
Where is the injury? What is the most likely cause of this injury? How would you record this injury in the patient’s record? |
Where is the injury? C5 spinal nerve
What is the most likely cause of this injury? C4/C5 disk herniation How would you record this injury in the patient’s record? C5 radiculopathy |

