![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Sympathetic
Origins, synapses, branching |
1. Sympathetic – thoracolumbar outflow. Preganglionic Intermediolateral columns spinal cord → synapse ganglion cells in 22 pairs paravertebral sympathetic ganglia. Each preganglionic synapses w/ 20-10K sympathetic ganglion via collateral fibers
|
|
|
Parasympathetic
Origins (including CN), synapses |
Parasympathetic – craniosacral outflow. Arrise CN3,7,9,10 & sacral part of spinal cord. Preganglionic synapse near effetor organ.
|
|
|
Enteric
Origin, Extrinsic control |
Enteric – intrinsic to the GI. Collection is in myenteric (betw. Muscle) & submucosal. Under some extrinsic symp/parasymp activity.
|
|
|
Sympathetic/Parasympathetic Effect (table)
pupil heart most arterioles salivary gland lacrimal gland GI smooth muscle Bronchial muscle Spleen Capsule |
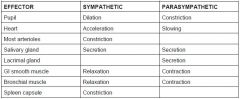
|
|
|
Single Innervation sympathetic have 2 functions
|
Sympathetic activation vessels = vasoconstriction. Turn it off and vessels vasodilate (forces from BP). Possibly then a certain tone is maintained.
|
|
|
3 types NT and sites of action
|
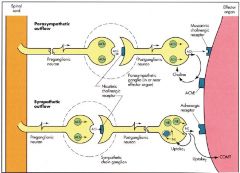
|
|
|
Mech. of inactivation for
Ach NE |
Ach inactivation = acetylcholinesterase (takes only milliseconds)
NE inactivation = 1.reuptake 2.MAO (mitochondria) 3.COMT 4.diffusion NE out of cleft |
|
|
2 types adrenergic receptors
|
NT = NE and hormone = Epi
Alpha – gen. excitatory except gut Beta – gen. inhibitory except heart |
|
|
Origin/Site of release Epinephrine
|
Chromaffin cells in Adrenal medulla (symp. pregangl innervation via greater splanchic n.) (stim = EPI release)
|
|
|
Sympath/Parasympath NT & receptors for changing heart rate
|
Sympathetic stim → NE released post-ganglionic → β adrenergic receptor stimu → ↑HR & F contraction = ↑↑CO
Parasympathetic stim. → Stim travels down vagal fiber → Ganglion in heart where Ach is release → Muscarinic receptors in AV/SA nodes stim = inhibition conduction → ↓HR |
|
|
Sympath/Parasympath effects on pupil size
|
Sympathetic stim → ↑ pupil size & ciliary muscle relaxed & lens flattens for distant vision
Parasympathetic stim → ↓pupil size & ciliary muscle contracts & lens becomes round for near vision |
|
|
Cholinergic crisis
|
Cholinergic Crisis – rx overdose, ingestion poisonous mushrooms, nerve gas.
SLUDGE Salivation, lacrimation, urination, defecation, gastrointestinal upset, emesis RECALL sweating is only sympathetic using Ach |
|
|
Cholinergic antagonist SE
|
SE can be predicted based on blocking Ach activity (antagonists bind receptor but no stimulus). Examples are dry mouth, dry skin, dilated pupils, tachycardia, decreased gut & bladder activity, sedation, excitation confusion.
|

